How to get biogas from manure: an overview of the basic principles and design of a production plant
Farmers annually face the problem of disposal of manure. Considerable funds that are required to organize its export and burial go nowhere. But there is a way that not only saves you money, but also makes you serve this natural product for your own good.
Zealous owners have long been using ecotechnology in practice, which allows them to obtain biogas from manure and use the result as fuel.
Therefore, our material will focus on the technology of biogas production, we will also talk about how to build a bioenergy installation.
The content of the article:
Pros of using biotechnology
Technology biofuel production from various natural sources is not new. Research in this area began in the late 18th century and successfully developed in the 19th century. In the Soviet Union, the first bioenergy plant was created in the forties of the last century.
Biotechnologies have long been used in many countries, but today they are acquiring special significance. Due to the deterioration of the environmental situation on the planet and the high cost of energy, many are turning their eyes towards alternative sources of energy and heat.
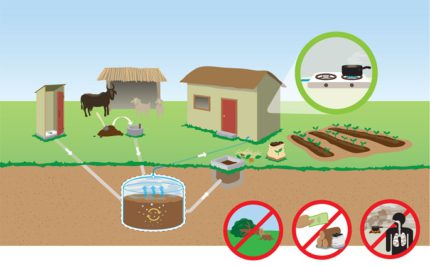
Of course, manure is a very valuable fertilizer, and if the farm has two cows, then there are no problems with its use. Another thing when it comes to farms with large and medium livestock, where tons of fetid and rotting biological material are formed per year.
In order for manure to turn into high-quality fertilizer, you need areas with a certain temperature regime, and this is an extra expense. Therefore, many farmers store it where necessary, and then take it to the fields.
If storage conditions are not observed, up to 40% of nitrogen and the main part of phosphorus disappear from manure, which significantly worsens its quality indicators. In addition, methane gas is released into the atmosphere, which has a negative impact on the ecological situation of the planet.
Modern biotechnology allows not only to neutralize the harmful effects of methane on the environmental situation, but also to make it serve for the benefit of man, while extracting considerable economic benefits. As a result manure processing biogas is formedfrom which you can then get thousands of kW of energy, and the waste products are a very valuable anaerobic fertilizer.
The mechanism of gas formation from organic raw materials
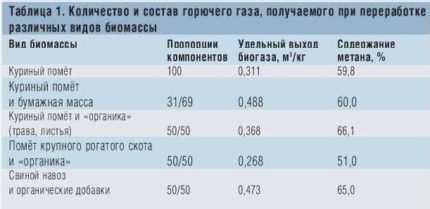
Biogas is a volatile substance without color or any odor, which contains up to 70% of methane. By its quality indicators, it is approaching the traditional type of fuel - natural gas. It has a good calorific value, 1m3 biogas emits as much heat as is obtained by burning one and a half kilograms of coal.
We owe the formation of biogas to anaerobic bacteria, which are actively working on the decomposition of organic raw materials, which are used for the dung of farm animals, bird droppings, waste from any plants.
To activate the process, it is necessary to create favorable conditions for the life of bacteria. They should be similar to those in which microorganisms develop in a natural reservoir - in the stomach of animals, where there is heat and no oxygen.
Actually, these are the two main conditions that contribute to the miraculous transformation of rotting manure into environmentally friendly fuel and valuable fertilizers.
To obtain biogas, a sealed reactor without air access is needed, where the process of manure fermentation and its decomposition into components will take place:
- methane (up to 70%);
- carbon dioxide (approximately 30%);
- other gaseous substances (1-2%).
The gases formed rise up the tank, from where they are then pumped out, and the residual product settles down - a high-quality organic fertilizer that retained all the valuable substances found in manure - nitrogen and phosphorus, and lost a significant part of pathogenic microorganisms as a result of processing.

The second important condition for the effective decomposition of manure and the formation of biogas is compliance with the temperature regime. The bacteria involved in the process are activated at a temperature of +30 degrees.
Moreover, in the manure contains two types of bacteria:
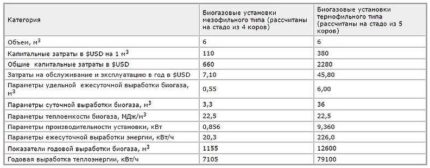
- mesophilic. Their vital activity occurs at a temperature of +30 - +40 degrees;
- thermophilic. For their reproduction, it is necessary to observe the temperature regime of +50 (+60) degrees.
The processing time of raw materials in plants of the first type depends on the composition of the mixture and ranges from 12 to 30 days. At the same time, 1 liter of reactor useful area gives 2 liters of biofuel. When using plants of the second type, the production time of the final product is reduced to three days, and the amount of biogas increases to 4.5 liters.
Despite the fact that the efficiency of thermophilic plants is ten times higher, they are used much less often, since maintaining high temperatures in the reactor is associated with high costs.
The maintenance and maintenance of mesophilic type plants is cheaper, so most farms use them to produce biogas.

Calculations of biogas efficiency
To evaluate all the benefits of using alternative biofuels, simple calculations will help. One cow weighing 500 kg produces about 35-40 kg of manure per day. This amount is enough to get about 1.5 m3 biogas, from which in turn it is possible to generate 3 kW / h of electricity.
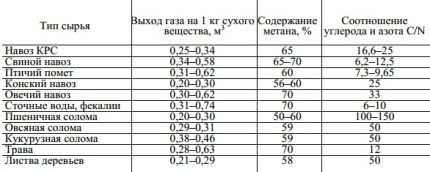
To obtain biofuels, you can use either one type of organic raw material or a mixture of several components having a moisture content of 85-90%. It is important that they do not contain extraneous chemical impurities that adversely affect the processing process.
The simplest recipe for the mixture was invented back in 2000 by one Russian peasant from the Lipetsk region, who built his own hands the simplest plant for biogas production. He mixed 1,500 kg of cow manure with 3,500 kg of waste from various plants, added water (about 65% of the weight of all ingredients) and heated the mixture to 35 degrees.
Two weeks later, free fuel is ready. This small installation produced 40 m3 gas per day, which was enough to heat the house and household buildings for six months.
Options for biofuel plants
After carrying out the calculations, it is necessary to determine how to make the plant in order to obtain biogas in accordance with the needs of its economy. If the number of livestock is small, then the simplest option is suitable, which is easy to make from improvised means with your own hands.
It is advisable for large farms that have a constant source of a large amount of raw materials to build an industrial automated biogas system. In this case, it is hardly possible to do without involving specialists who will develop the project and mount the installation on a professional level.
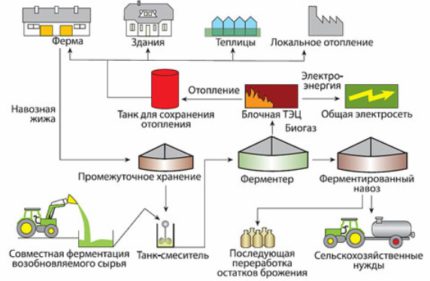
Today, there are dozens of companies that can offer many options: from ready-made solutions to the development of an individual project.To reduce the cost of construction, you can cooperate with neighboring farms (if available nearby) and build one unit for all biogas production.
It should be noted that for the construction of even a small installation, it is necessary to draw up the relevant documents, make a flow chart, plan for the placement of equipment and ventilation (if the equipment is installed in the room), undergo approval procedures with the SES, fire and gas inspection.
A mini-plant for the production of gas to meet the needs of a small private economy can be done with one's own hand, focusing on the design and specifics of the device installations, manufactured on an industrial scale.

Independent craftsmen who decide to start building their own installation must stock up on a water tank, water or sewer plastic pipes, corner bends, gaskets and a cylinder for storing the gas received in the installation.
Features of the biogas system
A full-fledged biogas plant is a complex system consisting of:
- Bioreactor, where the process of decomposition of manure;
- Automated organic waste feed system;
- Devices for mixing biomass;
- Equipment to maintain optimal temperature conditions;
- Gas tank - gas storage tanks;
- Solid waste receiver.
All of the above items are installed in industrial plants operating in automatic mode. Domestic reactors, as a rule, have a more simplified design.
The principle of operation of the installation
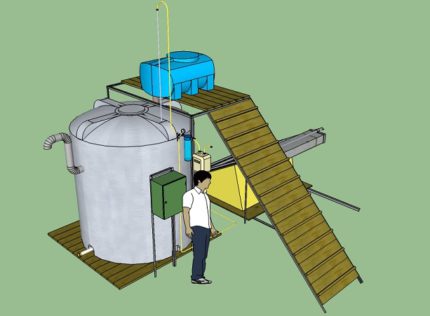
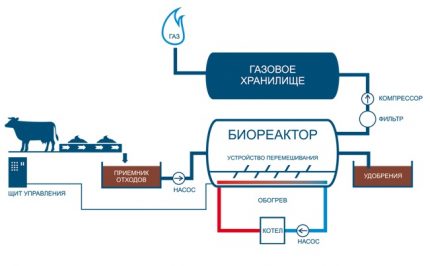
The main element of the system is a bioreactor.There are several options for its execution, the main thing is to ensure the tightness of the structure and eliminate the ingress of oxygen. It can be made in the form of a metal container of various shapes (usually cylindrical) located on the surface. Often, for these purposes, 50 cc empty fuel tanks are used.
You can buy ready-made containers of collapsible design. Their advantage is the ability to quickly disassemble, and, if necessary, transport to another place. It is advisable to use industrial surface installations in large farms where there is a constant influx of a large amount of organic raw materials.
For smaller farmsteads, the option of underground tank placement is more suitable. The underground bunker is built of brick or concrete. You can dig ready-made containers, for example, barrels of metal, stainless steel or PVC, into the ground. It is also possible to surface them on the street or in a specially designated room with good ventilation.

No matter where and how the reactor is located, it is equipped with a hopper for loading manure. Before loading the raw material, it must undergo preliminary preparation: it is crushed into fractions of not more than 0.7 mm and diluted with water. Ideally, the moisture content of the substrate should be about 90%.
Industrial-type automated plants are equipped with a feed system, including a receiver, in which the mixture is brought to the necessary moisture, a pipeline for water supply and a pumping unit for pumping the mass into the bioreactor.
In home installations, separate containers are used to prepare the substrate, where the waste is crushed and mixed with water. Then the mass is loaded into the receiving compartment. In the reactors located underground, the hopper for receiving the substrate is brought out, the prepared mixture by gravity flows through the pipeline into the chamber for fermentation.
If the reactor is located on the ground or indoors, the inlet pipe with the receiving device may be located in the lower side of the tank. It is also possible to bring the pipe to the upper part, and put a bell on its neck. In this case, the biomass will have to be pumped.
In the bioreactor, it is also necessary to provide an outlet, which is made almost at the bottom of the tank on the opposite side of the inlet hopper. In underground placement, the outlet pipe is installed obliquely upward and leads to a waste receptacle, shaped like a box of rectangular shape. Its upper edge should be below the level of the inlet.
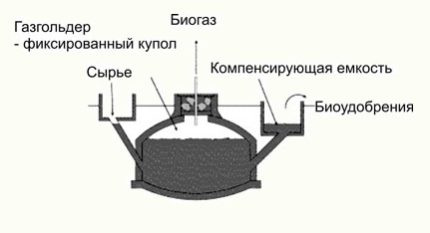
The process proceeds as follows: the inlet hopper receives a new batch of substrate, which flows into the reactor, at the same time the same amount of spent mass rises through the pipe to the waste receiver, from where it is later scooped up and used as high-quality biofertilizer.
Biogas storage is carried out in a gas tank. Most often, it is located directly on the roof of the reactor and has the shape of a dome or cone. It is made of roofing iron, and then, to prevent corrosive processes, it is painted with several layers of oil paint.
In industrial plants, designed to receive a large amount of gas, the gas tank is often made in the form of a separate tank connected to the reactor by a pipeline.
The gas obtained as a result of fermentation is not suitable for use, since it contains a large amount of water vapor, and in this form it will not burn. To clean it of fractions of water, gas is passed through a water seal.To do this, a pipe is removed from the gas tank, through which biogas enters the tank with water, and from there it is supplied to consumers through a plastic or metal pipe.
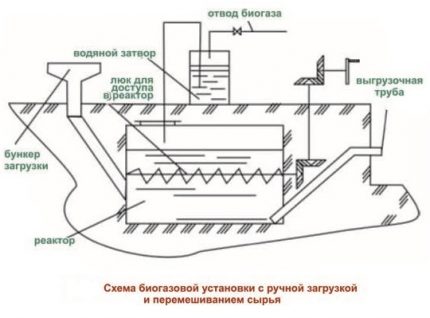
In some cases, special gas bags made of polyvinyl chloride are used to store gas. The bags are placed next to the unit and gradually filled with gas. As filling, the elastic material inflates, and the volume of the bags increases, allowing you to temporarily save a larger amount of the final product.
Conditions for the effective operation of the bioreactor
For the efficient operation of the installation and intensive biogas separation, uniform fermentation of the organic substrate is necessary. The mixture should be in constant motion. Otherwise, a crust forms on it, the decomposition process slows down, resulting in less gas than originally calculated.
To ensure active mixing of biomass, submersible or inclined type agitators equipped with an electric drive are installed in the upper or lateral part of a typical reactor. In artisanal installations, mixing is performed mechanically using a device resembling a household mixer. It can be controlled manually or equipped with an electric drive.
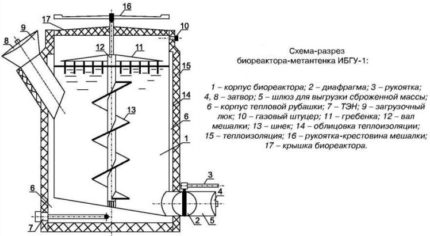
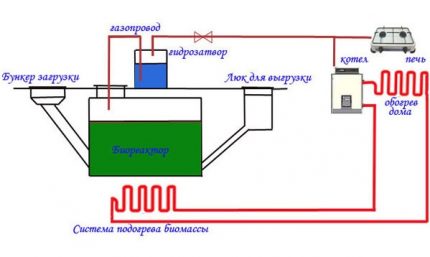
One of the most important conditions for biogas production is to maintain the required temperature in the reactor. Heating can be done in several ways. In stationary installations, automated heating systems are used that turn on when the temperature drops below a predetermined level and turn off when the required temperature is set.
For heating, you can use gas boilers, carry out direct heating with electric heaters or integrate a heating element in the base of the tank.
To reduce heat loss, it is recommended to build a small frame around the reactor with a layer of glass wool or cover the installation with thermal insulation. It has good thermal insulation properties. polystyrene foam and its other varieties.
Determination of the required volume
The volume of the reactor is determined based on the daily amount of manure produced on the farm. It is also necessary to consider the type of raw material, temperature and fermentation time. In order for the installation to work fully, the tank is filled to 85-90% of the volume, at least 10% must remain free for gas to escape.
The process of decomposition of organics in a mesophilic installation at an average temperature of 35 degrees lasts from 12 days, after which the fermented residues are removed, and the reactor is filled with a new portion of the substrate. Since the waste is diluted with water up to 90% before being sent to the reactor, the amount of liquid must also be taken into account when determining the daily load.
Based on the above indicators, the reactor volume will be equal to the daily amount of the prepared substrate (manure with water) multiplied by 12 (the time required for the decomposition of biomass) and increased by 10% (free tank volume).
Underground construction
Now let's talk about the simplest installation that allows you to get biogas at home at the lowest cost. Consider the construction of an underground system.To make it, you need to dig a hole, its base and walls are poured with reinforced expanded clay concrete.
On the opposite sides of the chamber, the inlet and outlet openings are inserted, where inclined pipes are mounted to supply the substrate and pump out the spent mass.
The outlet pipe with a diameter of about 7 cm should be almost at the very bottom of the hopper, its other end is mounted in a compensating container of a rectangular shape, into which the waste will be pumped. The pipeline for supplying the substrate is located approximately 50 cm from the bottom and has a diameter of 25-35 cm. The upper part of the pipe enters the compartment for receiving raw materials.

The upper part of the hopper is a gas holder with a dome or conical shape. It is made of metal sheets or roofing iron. It is also possible to complete the construction with masonry, which is then covered with steel mesh and plastered. On top of the gas tank you need to make a sealed hatch, remove the gas pipe passing through the water seal and install a valve to relieve gas pressure.
To mix the substrate, it is possible to equip the installation with a drainage system operating on the principle of sparging. To do this, vertically fasten plastic pipes inside the structure so that their upper edge is higher than the substrate layer. Make a lot of holes in them. Gas under pressure will fall down, and rising up, gas bubbles will mix the biomass in the tank.
If you do not want to build a concrete bunker, you can buy a ready-made PVC container. To maintain heat, it must be surrounded around a layer of thermal insulation - polystyrene foam. The bottom of the pit is poured with reinforced concrete with a layer of 10 cm. Tanks made of polyvinyl chloride may be used if the reactor volume does not exceed 3 m3.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
How to make the simplest installation from an ordinary barrel, you will learn if you watch the video:
How is the construction of an underground reactor, you can see in the video:
How the manure is loaded into the underground installation is shown in the following video:
A plant for producing biogas from manure will significantly save on the payment of heat and electricity, and put to good work organic material, which is abundant in every farm. Before starting construction, it is necessary to carefully calculate and prepare everything.
The simplest reactor can be made in a few days with your own hands, using improvised tools. If the farm is large, it is best to buy a ready-made installation or consult a specialist.
If you have any questions when familiarizing yourself with the information presented, or have suggestions that you want to share with site visitors, please leave comments in the box below.

 How to make biofuel with your own hands from manure at home
How to make biofuel with your own hands from manure at home  Biogas plant for a private house: recommendations for arranging homemade
Biogas plant for a private house: recommendations for arranging homemade  How to choose fuel for a biofireplace: a comparative overview of the types of fuel + analysis of popular brands
How to choose fuel for a biofireplace: a comparative overview of the types of fuel + analysis of popular brands  Biofuel for the fireplace: types of biofuel, its properties + how to choose and how to do it yourself
Biofuel for the fireplace: types of biofuel, its properties + how to choose and how to do it yourself  Types of Biofuel: Comparison of Solid, Liquid, and Gaseous Fuels
Types of Biofuel: Comparison of Solid, Liquid, and Gaseous Fuels  How to make a hydrogen generator for your home with your own hands: practical tips for manufacturing and installing
How to make a hydrogen generator for your home with your own hands: practical tips for manufacturing and installing  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Organic farming in our country is just beginning to gain momentum. More and more farms are abandoning chemical fertilizers in favor of biofertilizers.But in many farms, manure is really unprofitable because it is difficult to provide him with the right conditions for ripening. In this case, it may really make sense for large farms to switch to using manure as biofuel.
Hello. In 1940, the widespread spread of organic farming began. And in Russia since ancient times manure was used in fields and vegetable gardens. For biofuels, I can also say that this is not a novelty, but so far it is not entirely cost-effective. I read somewhere, even when my father was engaged in farming, which is on a farm of 50 thousand pigs, buying a biogas plant will pay off in about 7 years.
And how much did a cube of gas cost in 1940 ???
Greetings! My humble opinion: currently obtaining biofuels from manure is unprofitable, costly and even harms the environment. My opinion is based on visiting and studying the work of BS "Luchki" in the Belgorod region. The prime cost of 1 kW / h is 7 rubles. This is 2 times more than the average for Russia. So, the more such BS (biostations), the greater the losses! Calculations show that the ambitious Luchki project will pay off in 7 years, even taking into account 85% of state subsidies. There is nothing to talk about the payback of fully commercial projects.
In addition to this, purely economic aspect, there are other disadvantages that do not allow putting biogas production on stream:
- biogas is explosive - its main component is methane;
- production requires the participation of highly skilled workers - in rural areas it is very difficult to find such workers;
- after receiving biogas, the disposal of spent manure is required - this is expensive.
These are only the main problems faced by biofuel producers.
Greetings, I will comment on your humble opinion, otherwise suddenly someone will really believe what you wrote.
I myself am engaged in autonomous gasification (gas tanks) and I want to note that when a person has a choice to pay for equipment in 7? years, but tomorrow press a button and get home warm, hot water, a gas stove, paying for it, or continue to buy coal, firewood, chop, wear, heat, heat up in the evening, and freeze in the morning, he will choose the first, having a budget less than connecting to the gas pipeline in most cases.
As for your “study” and visit ... Cost of 1 kW-7 rubles ... kW of what? As I understand it, electricity (??), do you mean that there is an industrial gas generator? So it costs from 4 million rubles (Kamaz), or do you confuse a legal entity and an individual?
So for legal entities, kW of electricity on average is 9 rubles, and for individuals from 4 in regions.
What are these calculations? Give the capacity of the installation, its cost, the cost of heating, delivery and other things, gas output?
The so-called cons:
-Biogas is explosive, this is the greatest discovery since the days of the bicycle, I will not comment, and so it is clear to everyone.
- Do not believe it, “highly qualified specialists”, but as a matter of fact ordinary gas workers with tolerances in the fields a dime a dozen, just give the job as a person in the subject speak.
-Disposal ?? In fact, the big point is not even gas, but the sale of high-quality fertilizer, which for some reason you call waste manure.
It is only in a few words that I described the main problems that a thinking person who has read your comment will encounter.
When I was on an exchange in the Netherlands, where agriculture and livestock are very developed, in particular, I saw a lot of mesophilic plants. There they are megapopular and enjoy subsidies from the state.
Since the Netherlands, like all of Europe, is ecologically obsessed, 99% of farmers, both private owners and individual farms, firms and companies, have long had both mesophilic and thermophilic plants (depending on the size of the farm). It would also be nice for us to pay attention to this, but so far, I think, only private owners will be able to realize this, moreover with a well-functioning and profitable business, since we will not have subsidies in the near future, as in Europe.
I read about examples of using biogas plants in Russia.Moreover, both fully artisanal, which work only in the warm season, and full-fledged, producing gas year-round. But you need to understand that all these are enthusiasts. We have no subsidies for this business and will not be in the foreseeable future. And large farms that have their own money operate according to a well-established scheme and categorically do not like innovations.
Agree with you. In Russia, with a clearly debugged biogas system, there are about 5 households in total, as far as I know (I could be wrong). All why ... so a man decided to go into farming. He went, allocated him AKKOR land (this is real), the bank gave support for small businesses. The first sowing is scarcely enough for equipment (it is more profitable for cattle to grow their own grain), and of course, a small population. While the business develops, loans pay off ... for the most part, farms are now working on a small payback.
I looked at a low-performance methane generator based on a regular (!) Barrel - clearly and clearly, but a number of questions arose.
As shown - around winter, the barrel is thermally insulated from the outside (covered with a fur coat). Is there enough natural heat to keep the temperature inside the barrel at 30 - 35 degrees Celsius? Can heating be required sometimes? It can be automated.
Then another moment - when loading organic matter and unloading waste (fertilizer), air (oxygen) can get into the barrel! Gas may be explosive! There is an upper explosive limit for the gas mixture (almost pure methane and some oxygen), as well as a lower explosive limit (air and some methane). Therefore, I think on the top of the barrel it is necessary to provide a safety valve that relieves the occasional excess pressure of methane.
I am interested while studying, but I’ll start in the spring. If there is anyone, then help with advice.
In the small barrel shown, the waste pipe and the recycled pipe are almost nearby and at the same height! And in the installation explanations it is clearly indicated that these two pipes should be located opposite, moreover, the pipe with the spent raw materials should come out almost at the very bottom! Boot db at least 50 cm higher than the previous one! Question - will the proposed option work?