Vacuum solar collector: principle of operation + how to assemble yourself
A lot of money is spent on hot water and space heating. But there is an alternative source of energy - a vacuum solar collector. Have you heard about this? It allows you to significantly reduce financial costs for maintaining comfort, providing maximum heating effect with minimal heat loss.
This device can be bought from manufacturers of household equipment or assembled independently at home. To choose a suitable model, a lot of information remains to be studied. We will help you determine the main criteria for the purchase.
The article will focus on the principle of operation and the design of the vacuum manifold. We will talk about the design features of various models, consider the pros and cons of these installations. In addition, we will describe in detail how to make and install a vacuum solar collector yourself.
The material is accompanied by videos from which you will learn about the important features and principles of operation of vacuum collectors.
The content of the article:
- The principle of operation of the vacuum unit
- How is a vacuum-type collector arranged?
- Structural Nuances and Classification
- Comparison of various modifications
- What should be the heat sink?
- Pros and cons of vacuum type collectors
- DIY assembly
- How to place the device?
- Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The principle of operation of the vacuum unit
The vacuum solar collector differs from conventional solar systems in the way solar energy processing. A classic battery simply receives light and converts it into electricity. The collector consists of glass tubes with a vacuum recreated inside. They are combined into a single system through special docking nodes.
Inside each tube is a channel of one or two copper rods with a coolant. By capturing the sun's rays, the active element heats the heat-transfer material, thus ensuring the operation of the collector.
Due to this design, the level of energy transfer increases significantly, and heat loss is significantly reduced, since the vacuum layer allows you to save about 95% of the captured solar energy.

In addition, the dependence of reservoir productivity on seasonality, ambient temperature and various weather conditions, such as gusts of wind, variable cloud cover, precipitation, etc., decreases.
How is a vacuum-type collector arranged?
Modern vacuum devices that provide premises with heat and hot water due to solar energy are technologically different.
Collectors are divided into the following types:
- tubular without a glass protective coating;
- module with reduced conversion;
- standard flat version;
- device with transparent thermal insulation;
- air unit;
- flat vacuum manifold.
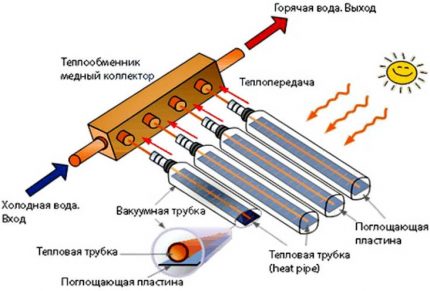
All of them have a common structural similarity, so they consist of:
- external transparent pipefrom where air is completely pumped out;
- heated pipelocated in a large pipe where the liquid or gaseous coolant moves;
- one or two prefabricated valvesto which pipes of a larger caliber are connected and a circulation loop of thin tubes placed inside is included.
The whole design is somewhat reminiscent of a thermos with transparent walls, in which an unprecedentedly high level of thermal insulation is maintained. Due to this feature, the housing of the inner tube acquires the ability to warm up efficiently and fully give the energy resource to the coolant circulating inside.
Structural Nuances and Classification
Vacuum-type collectors are classified by the type of glass tubes installed in the structure, or by the characteristics of the heat channels. Tubes are usually coaxial and feather, and heat channels are U-shaped straight-through and heat pipe types. .
Coaxial tube characteristic
Coaxial tubes are a double glass thermos flask with a vacuum space artificially created between the walls.The inner surface of the tube has a layer of special heat-absorbing coating, so the actual heat transfer occurs directly from the walls of the glass bulb.

As an absorbing element, a copper tube containing an ether composition is soldered into a glass tube. In the process of heating, it evaporates, effectively gives off its heat, condenses and drains to the bottom of the tube. Then the cycle repeats, thus creating a continuous process of heat transfer.
Feather Tube Features
Vacuum pen tubes have a greater wall thickness than coaxial and do not consist of two, but one flask. The internal copper absorption element is provided along the entire length with a strong amplifier - a corrugated plate with a high-level energy-absorbing coating.
Due to this design feature, the vacuum is located directly in the heat channel, part of which, together with the absorbent, is integrated directly into the flask.

Collectors made on the basis of feather vacuum tubes are considered to be the most efficient in their class, perfectly cope with the tasks and reliably serve for many years.
Principle of operation of the heat pipe heat pipe
The heat channels of a heat pipe consist of closed tubes containing an easily volatile liquid composition. Under the influence of sunlight, it warms up, passes into the upper region of the channel and concentrates there in a special heat collector (manifold).
The working fluid at this moment gives off all the accumulated heat and again drops down to resume the process.
The heat-pipe heat exchanger sleeve is connected to the manifold’s heat exchanger through a special socket soldered into the 1-pipe heat exchanger itself or bent around by a 2-pipe heat exchanger.

The heat carrier selects the released energy from the heat reservoir and transfers it further through the system, thus ensuring the availability of hot water in taps and radiators. The heat pipe system is easy to install and demonstrates high efficiency during operation.

In the event of a breakdown or failure without any difficulties, it is possible to replace the damaged unit with a new one without resorting to reconstruction of the entire system.
Repair work can be easily carried out right at the location of the collector, without dismantling the unit and without applying unnecessary efforts to the work.
Description of a U-shaped in-line heat exchanger
The tube of the direct-flow heat exchanger has the shape of the letter U. Water or the working fluid of the heating system circulates inside. One part of the element is intended for cold coolant, and the second correctly discharges the already heated one.
During incandescence, the active composition expands and enters the storage tank, thus creating a natural circulation of fluid in the system. A special selective coating applied to the inner walls increases the heat-absorbing ability and increases the efficiency of the system as a whole.

U-type tubes demonstrate high performance and give solid heat transfer, but at the same time they have one significant drawback. They form one integral construction with manifold’s and are always mounted together with it.
Replace a single single tube that failed, will not work. For repair, you will need to dismantle the entire complex and put a new one in its place.
Comparison of various modifications
In the manufacture of solar units, heat channels and vacuum glass tubes for solar collectors are combined in a variety of combinations.
The most popular among consumers are coaxial models with a heat pipe heat pipe. Buyers are attracted by the loyal price of devices and a very simple, affordable service throughout the entire life cycle.

Vacuum devices with heat pipe channels demonstrate high reliability and have no restrictions on use, even in high-pressure solar thermal complexes.
Devices with a coaxial flask containing direct-flow U-shaped channels are also included in the list of popular ones. They are characterized by such parameters as low heat loss and efficiency from 70% and above.

The situation is somewhat spoiled: a complex repair process, specific maintenance during operation and the inability to replace a single damaged unit. If something happens to the device, it is dismantled and a completely new collector is put in place.
Fountain tubes are structurally a single cylinder made of glass with thickened strong walls (depending on the manufacturer, from 2.5 mm and above). The pen-absorbent insert contained within fits tightly on a working channel made of heat-conducting metal.
Almost perfect insulation creates a vacuum space inside the glass container. The absorbent transfers the absorbed heat without loss and provides the system with an efficiency of up to 77%.

Models with a feather element are somewhat more expensive than coaxial ones, but due to their high efficiency they provide full-fledged comfort in the room and quickly pay off.
The most effective and efficient are feather flasks with internal direct-flow channels. Their actual efficiency sometimes reaches record levels of 80%.

The price of the products is quite high, and during the repair it is necessary to drain the entire coolant from the system and only then proceed with troubleshooting.
What should be the heat sink?
The heat collector is another very important working element of the vacuum manifold. Through this node, the accumulated heat is transferred from the tubes to the coolant.
The heat collector is located at the top of the device. One of its components, the copper core, receives energy and transfers it to the main heat carrier circulating in the closed system “tank-collector heat exchanger”.
Correct operation is guaranteed when connected to the system circulation pump. The automation controlling the heating complex clearly monitors the temperature level in the channels and, if it falls below the permissible critical minimum (for example, at night), stops the pump.
This allows you to avoid reverse heating when the coolant begins to collect the heat of the hot water collected in the storage tank.
Pros and cons of vacuum type collectors
The main advantage of the units is the almost complete absence of heat loss during operation. This provides a vacuum environment, which is one of the highest quality natural insulators. But the list of benefits does not end there.
Devices have other pronounced advantages:
- work efficiency at low temperature indicators (up to -30 ° С);
- the ability to accumulate temperatures up to 300 ° C;
- the maximum possible absorption of thermal energy, including the invisible spectrum;
- operational stability;
- low susceptibility to aggressive atmospheric manifestations;
- low windage due to the structural features of tubular systems capable of passing air masses of different densities through themselves;
- high level of efficiency in regions with a temperate and cool climate with a small number of clear and sunny days;
- durability subject to the basic rules of operation;
- availability for repair and the ability to change not the entire system, but only one failed fragment.
The disadvantages include the inability of the collectors to self-clean from hoarfrost, ice, snow and the high price of components needed to assemble the unit at home.

DIY assembly
The process of assembling a vacuum manifold begins with the manufacture of a substrate frame for work items. It is mounted immediately in the place that is allocated for the unit.
The size and dimensions of the frame entirely depend on the model that you plan to make, and are usually prescribed in the instructions, which is located among the supporting documents for the components.

I fix the places where the frame adjoins the roof surface with sealant, so that in the future water will not enter the house through openings. Then, the storage tank is delivered to the installation site and it is fixed with screws on the upper part of the frame.
The next step is to collect the heater, temperature sensor and automated air vent. All auxiliary units and related parts are placed on the supplied softeners. To fix the temperature sensor use a socket wrench.
Next, equip the supply of water communications. For this purpose, pipes are taken from any material resistant to low temperature indicators and capable of withstanding up to 95 ° C. Well proven polypropylene pipes and fittings.

By connecting the water supply, the storage tank is filled with water and tested for leaks. If leaks are detected somewhere within 3-4 hours, they are repaired.
At the end, heating elements are installed. To do this, the copper tube is wrapped in aluminum sheet and placed in a vacuum tube made of glass. From below, a fixing cup and anther of durable, flexible rubber are put on the flask.
The upper copper tip of the tube is pushed all the way into the brass capacitor. Viscous thermal contact grease is not removed from the pipes. The locking mechanism is latched onto the bracket and all the remaining glass tubes are mounted on the same principle.

A mounting block is placed on the structure, a 220 volt power supply is supplied to it, and three auxiliary units are connected to the system - a heating element, an air outlet, and a temperature sensor.
The last to connect the controller, designed for the correct management of the complex. The desired operating parameters are entered into the controller menu and the system is started in standard mode.
A step-by-step instruction on the construction of a solar collector is given in this article.
How to place the device?
In order for the vacuum collector to fully work and effectively provide the living room with the necessary energy, it is necessary for him to find the most suitable place and correctly orient the device relative to the parts of the world.

For settlements of the northern hemisphere, it is important to place the collector in the southern part of the roof of the house or on the sunny side of the site. It is desirable to ensure a minimum deviation for the plane of the device.
If there is no possibility to direct the surface to the south, it is worth choosing among the west and east the most light angle in open space.

The energy solar complex should not cover chimneys, decorative fragments of roofing, spreading branches of trees and tall residential or technical buildings. This will reduce the efficiency and reduce the level of heating of the active elements.
If the unit is located correctly, it will provide almost the same heat transfer throughout the year, regardless of the season.
If there is no much experience in the implementation of complex repair, installation and locksmithing work, vacuuming the tubes at home is irrational. This process is very laborious and requires special knowledge and specialized equipment.
In addition, self-made vacuum-type elements have a much lower level of efficiency than factory parts. Therefore, it is most reasonable to purchase products from a specialized manufacturer, and then try to assemble several sections at home.
The site has a selection of articles on the arrangement of the solar heating system, we recommend that you read:
- Solar heating systems: analysis of heating technology based on solar systems
- Heating a private house with solar panels: schemes and device
- Flexible solar panels: types, characteristics + connection features
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
A detailed, detailed description of the vacuum tube, the principle of its operation and the features of the functioning of the solar collector as a whole. The author talks about some interesting nuances and shows that the installation can be a real alternative to a gas boiler.
Interesting information about the work of the solar collector in the winter.
How to mount a vacuum solar collector with your own hands at home. All the nuances of the process, recommendations and useful tips.
Knowing the basic principle of operation of a tubular vacuum solar collector, you can assemble the unit yourself. The installation will fully meet personal individual requirements and needs.
This is not a difficult task, however, it requires increased attention, scrupulousness and certain skills, otherwise the risk of damaging the integrity of the flask and breaking its tightness increases significantly.
All interested in the matter of choice, installation or self-assembly of the solar collector are invited to leave comments and ask questions. The contact form is located in the lower block.

 Plastic Bottle Solar Collector: A Step-by-Step Guide to Helio Assembly
Plastic Bottle Solar Collector: A Step-by-Step Guide to Helio Assembly  How to make a solar collector for DIY heating: a step-by-step guide
How to make a solar collector for DIY heating: a step-by-step guide  Solar charge controller: circuit, principle of operation, connection methods
Solar charge controller: circuit, principle of operation, connection methods  The principle of operation of the solar battery: how the solar panel is arranged and works
The principle of operation of the solar battery: how the solar panel is arranged and works  Solar charger: device and principle of operation of charging from the sun
Solar charger: device and principle of operation of charging from the sun  Solar panels for summer cottages and houses: types, principle of operation and calculation procedure for solar systems
Solar panels for summer cottages and houses: types, principle of operation and calculation procedure for solar systems  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
A good alternative to adsorption solar panels. Anyway, most of the electricity is spent on heating: heating, hot water. And here everything is very simplified and cheapened - heating occurs directly from the Sun, bypassing the stage of electricity generation, where, precisely, the biggest losses of efficiency are. In the middle lane (for example, N. Novgorod) it works very effectively.
The husband in our house installed a vacuum solar collector.We bought the finished version, but installed it myself, and it didn’t take much time. I don’t understand why they asked for such an amount for the installation ... And they are very happy with the unit, it’s enough even on not sunny days, it functions without problems in winter at minus 15-20. Only periodically need to be cleaned.
Anna, where did you buy it?
Where in the summer to put warm ??? How to convert it to electrical energy ???)
Dmitry, if the water temperature in the summer goes beyond 80 degrees, you can consider the option of dumping excess heat into the pool. If you want easier, you can sew strips of fabric with a length of 150-160 cm and a width equal to the circumference of the tube + 2 cm. Along the long side, on one side, sew on one part of Velcro (textile fastener), on the other - on the other. With such a simple case, you can wrap as many tubes for the summer as give extra energy. Take off before the fall :)))