How to make a heat pump for heating a house with your own hands: the principle of operation and assembly scheme
The first versions of heat pumps could only partially satisfy the demand for thermal energy. Modern varieties are more effective and can be used for heating systems. That is why many homeowners are trying to mount a heat pump with their own hands.
We will tell you how to choose the best option for the heat pump, taking into account the geo-data of the site on which it is planned to be installed. The article proposed for consideration describes in detail the principle of the use of “green energy” systems, the differences are listed. Based on our advice, you will no doubt focus on the effective type.
For independent masters, we present the technology of assembling a heat pump. The information presented for consideration is supplemented by visual diagrams, photo selections and detailed video training in two parts.
The content of the article:
What is a heat pump and how does it work?
The term heat pump refers to a set of specific equipment. The main function of this equipment is the collection of thermal energy and its transportation to the consumer. The source of such energy can be any body or medium with a temperature of + 1º or more degrees.
There are more than enough sources of low-temperature heat in our environment. These are industrial wastes of enterprises, thermal and nuclear power plants, sewage, etc. For the operation of heat pumps in the field of home heating, three independently restored natural sources are needed - air, water, and land.

The three potential energy suppliers listed are directly related to the energy of the sun, which, by heating, moves air with the wind and transfers thermal energy to the earth. It is the choice of source that is the main criterion according to which heat pump systems are classified.
The principle of operation of heat pumps is based on the ability of bodies or media to transfer thermal energy to another body or medium. Recipients and suppliers of energy in thermal pumping systems usually work in pairs.
So distinguish the following types of heat pumps:
- Air is water.
- Earth is water.
- Water is air.
- Water is water.
- Earth is air.
- Water - Water
- Air is air.
In this case, the first word defines the type of medium in which the system removes low-temperature heat. The second indicates the type of carrier to which this thermal energy is transmitted. So, in heat pumps water - water, heat is taken from the aqueous medium and liquid is used as a heat carrier.
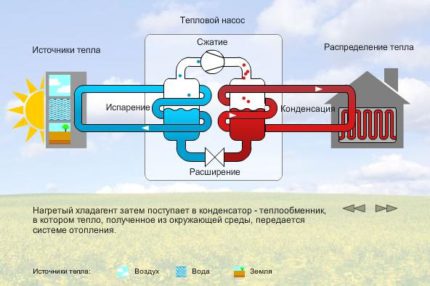
Modern heat pumps use three main heat source. This is soil, water and air. The simplest of these options is air heat pump. The popularity of such systems is associated with their rather simple design and ease of installation.
However, despite such popularity, these varieties have a rather low productivity. In addition, the efficiency is unstable and dependent on seasonal temperature fluctuations.
With decreasing temperature, their performance drops significantly. Such options for heat pumps can be considered as an addition to the existing main source of thermal energy.
Options for equipment using ground heatare considered more effective. Soil receives and accumulates thermal energy not only from the Sun, it is constantly heated by the energy of the earth's core.
That is, the soil is a kind of thermal battery, the power of which is practically unlimited. Moreover, the temperature of the soil, especially at a certain depth, is constant and varies insignificantly.
Scope of energy generated by heat pumps:
The constancy of the source temperature is an important factor in the stable and efficient operation of this type of power equipment. Similar characteristics are possessed by systems in which the aquatic environment is the main source of thermal energy. The collector of such pumps is located either in the well, where it is in the aquifer, or in a reservoir.
The average annual temperature of sources such as soil and water varies from + 7º to + 12º C. Such a temperature is quite enough to ensure the effective operation of the system.
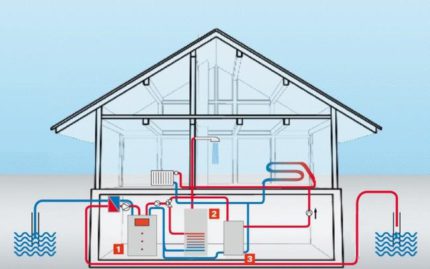
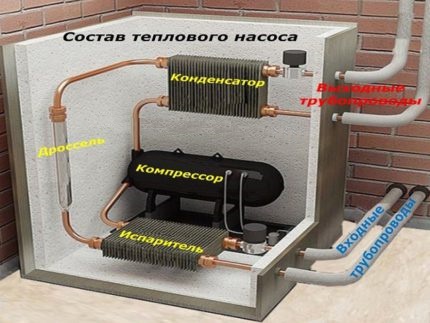
The main structural elements of heat pumps
In order for the power generation plant to work according to the principles of the heat pump, 4 main units must be present in its design, these are:
- Compressor.
- Evaporator.
- Capacitor.
- Throttle valve.
An important design element of the heat pump is the compressor. Its main function is to increase the pressure and temperature of the vapors resulting from the boiling of the refrigerant. For climate technology and heat pumps, in particular, modern scroll compressors are used.
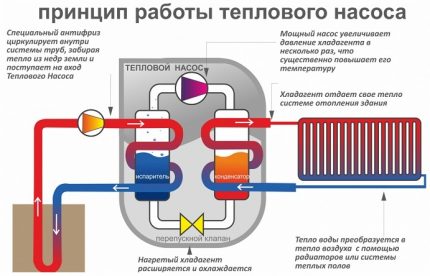
Such compressors are designed for operation at subzero temperatures. Unlike other varieties, scroll compressors produce little noise and operate both at low gas boiling points and at high condensation temperatures. The undoubted advantage is their compact size and low specific gravity.

The evaporator as a structural element is a container in which liquid refrigerant is converted into vapor. The refrigerant, circulating in a closed circuit, passes through the evaporator. In it, the refrigerant warms up and turns into steam. Low pressure steam is directed towards the compressor.
In the compressor, refrigerant vapors are exposed to pressure and their temperature rises. The compressor pumps the heated steam under high pressure towards the condenser.

The next structural element of the system is a capacitor. Its function is to transfer thermal energy to the internal circuit of the heating system.
Serial samples manufactured by industrial enterprises are equipped with plate heat exchangers. The main material for such capacitors is alloy steel or copper.

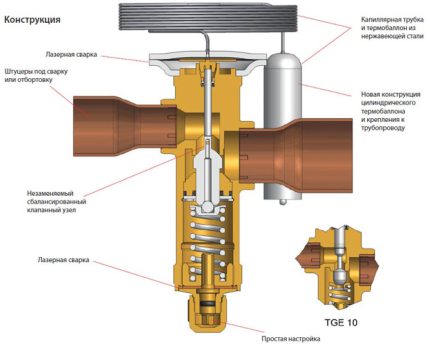
A thermostatic, or otherwise throttling, valve is installed at the beginning of that part of the hydraulic circuit where the circulating high-pressure medium is converted to a low-pressure medium. More precisely, the throttle paired with the compressor divide the heat pump circuit into two parts: one with high pressure parameters, the other with low.
When passing through an expansion throttle valve, the fluid circulating in a closed circuit partially evaporates, as a result of which the pressure decreases with temperature. Then it enters the heat exchanger in communication with the environment. There, it captures the energy of the medium and transfers it back to the system.
The throttle valve controls the flow of refrigerant towards the evaporator. When choosing a valve, system parameters must be considered. The valve must comply with these parameters.
Heat pump type selection
The main indicator of this heating system is power. First of all, the financial costs for the purchase of equipment and the choice of one or another source of low-temperature heat will depend on capacity. The higher the power of the heat pump system, the higher the cost of components.
First of all, it refers to the compressor capacity, the depth of the wells for geothermal probes, or the area for placing a horizontal collector. Correct thermodynamic calculations are a kind of guarantee that the system will work efficiently.
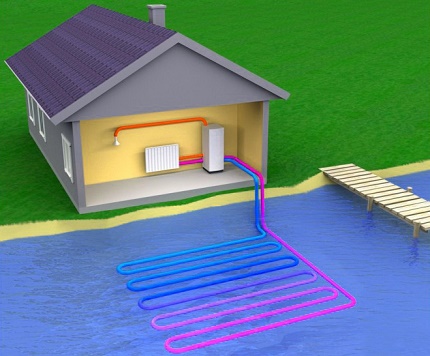
To begin with, you should study the area that is planned for the installation of the pump. An ideal condition would be the presence of a body of water in this section. Using water-water type options significantly reduce the volume of earthwork.
Using the heat of the land, on the contrary, involves a large number of works related to excavation. Systems that use the aquatic environment as low-grade heat are considered the most efficient.

There are two ways to use the thermal energy of the soil. The first involves drilling wells with a diameter of 100-168 mm. The depth of such wells, depending on the parameters of the system, can reach 100 m or more.
Special probes are placed in these wells. In the second method, a pipe manifold is used. Such a collector is located underground in a horizontal plane. For this option, a sufficiently large area is required.
For laying the collector, areas with wet soil are considered ideal. Naturally, drilling wells will cost more than the horizontal location of the reservoir. However, not every area has free space. For one kW of heat pump power, 30 to 50 m² of area is needed.

In the case of the presence of a high-lying groundwater horizon, heat exchangers can be arranged in two wells located at a distance of about 15 m from each other.
The selection of thermal energy in such systems by pumping groundwater in a closed loop, parts of which are located in wells. Such a system requires the installation of a filter and periodic cleaning of the heat exchanger.
The simplest and cheapest heat pump circuit is based on the extraction of thermal energy from the air.Once it became the basis for the installation of refrigerators, later, according to its principles, air conditioners were developed.
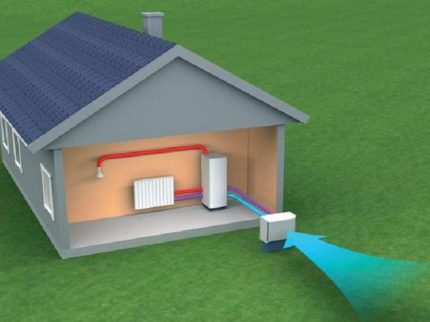
The effectiveness of the various types of equipment is not the same. The lowest indicators are pumps that use air. In addition, these indicators are directly dependent on weather conditions.
Soil varieties of heat pumps have stable performance. The efficiency coefficient of these systems varies between 2.8 -3.3. Water-water systems are most effective. This is primarily due to the stability of the source temperature.
It should be noted that the deeper the pump collector is located in the reservoir, the more stable the temperature will be. To obtain a system capacity of 10 kW, you need about 300 meters of the pipeline.
The main parameter characterizing the efficiency of the heat pump is its conversion coefficient. The higher the conversion coefficient, the more efficient the heat pump is.
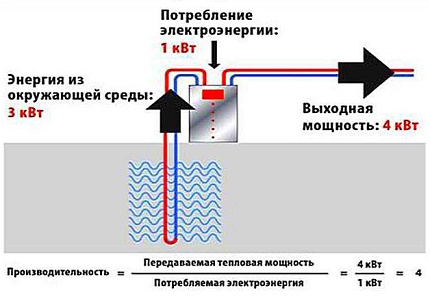
Do-it-yourself heat pump assembly
Knowing the action scheme and the heat pump device, assemble and install by yourself alternative heating system quite possible. Before starting work, it is necessary to calculate all the basic parameters of the future system. To calculate the parameters of the future pump, you can use software designed to optimize cooling systems.
The easiest option to build is air-water system. It does not require complex work on the device of the external circuit, which is inherent in water and soil varieties of heat pumps. For installation, only two channels will be needed, one of which will supply air, and the second one will discharge the spent mass.

In addition to the fan, you need to get a compressor of the required power. For such an unit, the compressor that ordinary equipment is equipped with is quite suitable split systems. It is not necessary to buy a new unit.
You can remove it from old equipment or use accessories for an old refrigerator. It is advisable to use a spiral variety. These compressor options, in addition to having sufficient efficiency, create high pressures that increase temperature.
To build a capacitor, you will need a capacitance and a copper pipe. A coil is made from a pipe. For its manufacture, any cylindrical body of the desired diameter is used. By winding a copper pipe on it, you can easily and quickly make this structural element.
The finished coil is mounted in a container previously cut in half. For the manufacture of containers, it is better to use materials resistant to corrosion processes. After placing a coil in it, the halves of the tank are welded.
The coil area is calculated using the following formula:
MT / 0.8 RT,
Where:
- MT - the power of thermal energy that the system produces.
- 0,8 - the coefficient of thermal conductivity in the interaction of water with the material of the coil.
- RT - the difference in temperature of water at the inlet and outlet.
Choosing a copper pipe for self-production of a coil, you need to pay attention to the wall thickness. It should be at least 1 mm. Otherwise, when winding, the pipe will deform. The pipe through which the inlet of the refrigerant is located in the upper part of the tank.

The heat pump evaporator can be made in two versions - in the form of a container with a coil located in it and in the form of a pipe in a pipe. Since the temperature of the liquid in the evaporator is small, the capacity can be made from a plastic barrel. In this capacity is placed a circuit that is made of a copper pipe.
Unlike a condenser, the coil of the evaporator coil must correspond to the diameter and height of the selected tank. The second variant of the evaporator: pipe in pipe. In this embodiment, the refrigerant pipe is placed in a plastic pipe of a larger diameter, through which water circulates.
The length of such a pipe depends on the planned pump capacity. It can be from 25 to 40 meters. Such a pipe is coiled.
Thermostatic valve refers to shut-off and control pipe fittings. A needle is used as a locking element in the expansion valve. The position of the valve shut-off element is determined by the temperature in the evaporator.
This important element of the system has a rather complicated design. It includes:
- Thermocouple.
- Diaphragm.
- Capillary tube.
- Thermoball.
These elements may become unusable at high temperatures. Therefore, during soldering work, the valve should be insulated with asbestos cloth. The control valve must match the capacity of the evaporator.
After carrying out work on the manufacture of the main structural parts, a crucial moment comes of assembling the entire structure into a single unit. The most crucial step is refrigerant injection process or coolant into the system.
Independently conducting such an operation is unlikely to be affordable for a simple layman. Here you will have to turn to professionals who are engaged in the repair and maintenance of HVAC equipment.
Workers in this area, as a rule, have the necessary equipment. In addition to charging refrigerant, they can test the system. Self-loading of refrigerant can lead not only to breakdown of the structure, but also to serious injuries. In addition, special equipment is also needed to start the system.
When the system starts, a peak starting load occurs, which is usually about 40 A. Therefore, starting the system without a start relay is not possible. After the first start-up, the valve and the refrigerant pressure must be adjusted.
The choice of refrigerant should be taken seriously. After all, it is this substance that is essentially considered the main “carrier” of useful thermal energy. Of the existing modern refrigerants, freons are the most popular. These are derivatives of hydrocarbon compounds in which part of the carbon atoms is replaced by other elements.
As a result of these works, a closed loop system was obtained. The refrigerant will circulate in it, ensuring the selection and transfer of thermal energy from the evaporator to the condenser. When connecting heat pumps to the heat supply system of a house, it should be noted that the temperature of the water at the outlet of the condenser does not exceed 50-60 degrees.
Due to the low temperature of the thermal energy generated by the heat pump, specialized heating appliances should be selected as the heat consumer. It can be a warm floor or volume low-inertia radiators made of aluminum or steel with a large radiation area.
Home-made versions of heat pumps are most appropriate to consider as auxiliary equipment that supports and complements the work of the main source.
Every year the designs of heat pumps are being improved. Industrial designs designed for domestic use use more efficient heat transfer surfaces. As a result, system performance is constantly growing.
An important factor that stimulates the development of such a technology for the production of thermal energy is the environmental component. Such systems, in addition to being quite effective, do not pollute the environment. The absence of an open flame makes its operation absolutely safe.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video # 1. How to make the simplest home-made heat pump with a heat exchanger from PEX pipes:
Video # 2. Continued briefing:
As alternative heating systems, heat pumps have long been used. These systems have reliability, a long service life and, importantly, are environmentally friendly. They seriously begin to be considered as the next step towards the development of efficient and safe heating systems.
Want to ask a question or talk about an interesting method of building a heat pump, not mentioned in the article? Please write comments in the block below.

 DIY geothermal heat pump for home heating: device, design, self-assembly
DIY geothermal heat pump for home heating: device, design, self-assembly  How to make a heat pump with your own hands from an old refrigerator: drawings, instructions and assembly tips
How to make a heat pump with your own hands from an old refrigerator: drawings, instructions and assembly tips  Water-water heat pump: device, principle of operation, rules for arranging heating on its basis
Water-water heat pump: device, principle of operation, rules for arranging heating on its basis  How to make an air-water heat pump: device diagrams and self-assembly
How to make an air-water heat pump: device diagrams and self-assembly  Frenett heat pump: device and principle of operation + can you assemble it yourself?
Frenett heat pump: device and principle of operation + can you assemble it yourself?  Air-to-air heat pump: principle of operation, device, selection and calculations
Air-to-air heat pump: principle of operation, device, selection and calculations  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
In our city there was a creamery, from which hot water and steam were regularly discharged. So our neighbor, apparently with an engineering mindset, adapted this energy to heat his greenhouses. And only today I learned how to do this. The principle of operation is clearly stated, and there are schemes. But I doubt that I can do everything right with my own hands to make it work.
I read the material, did not learn anything new. This technology has long been used in the countries of Northern Europe (in Denmark, Sweden, Norway). It is especially popular in the construction of energy-saving and passive houses.
I wonder what will happen if a well drilled for a pump becomes clogged with silt? As far as I know, well owners clean them every five years.
And what happens in wells designed for heat pumps?
Read carefully - the wells are dry.
“In the case of the presence of a high-lying groundwater horizon, heat exchangers can be arranged in two wells located at a distance of about 15 m from each other.”
If you haven’t learned anything new, then there shouldn’t be any questions at all 🙂 If you carefully read the article, you may notice that we are talking about the need to install filters, plus periodic cleaning of the heat exchangers is an inevitable phenomenon.
Yes, in Western countries, these technologies are widely used, systems are expensive, but then they pay off and you essentially use a free heat source.
Regarding the wells. This is not the same technology that is used for water supply at home, so it is incorrect to compare in this case.
MT / 0.8 RT, where:
MT is the power of thermal energy that the system gives out.
0.8 is the coefficient of thermal conductivity during the interaction of water with the material of the coil.
RT - the difference in water temperature at the inlet and outlet
Ambiguities with the formula. MT - power in what units? Kilowatts, BTU / hour, Watts? Power like the letter P is indicated. 0.8 what dimension does it have? The temperature difference is also denoted as Delta t, and RT. And finally, the area in which it is measured, sq.m. or sq. cm? For example, it would be good to give a specific calculation, and not a strange kind of formula.