Starter for fluorescent lamps: device, principle of operation, marking + subtleties of choice
A starter for fluorescent lamps is included in the package of an electromagnetic ballast control (EMPR) and is designed to ignite a mercury lamp.
Each model released by a specific developer has different technical characteristics, but it is used for lighting technology that is powered exclusively from AC power, with a limit frequency not exceeding 65 Hz.
We offer to understand how the starter for fluorescent lamps is arranged, what is its role in the lighting device. In addition, we will outline the features of different starting devices and tell you how to choose the right mechanism.
The content of the article:
How is the device arranged?
Optionally, the starter (starter) is quite simple. The element is represented by a small discharge lamp capable of forming a glow discharge at low gas pressure and low current.
This small glass bottle is filled with an inert gas - a mixture of helium or neon. Movable and fixed electrodes of metal are soldered into it.
All electrode spiral bulbs are equipped with two terminal blocks. One of the terminals of each contact is connected in the circuit. electromagnetic ballast. The rest are connected to the cathodes of the starter.
The distance between the electrodes of the starter is not significant, therefore, by means of the mains voltage it can easily be punched. In this case, a current is generated and the elements entering the circuit with a certain share of resistance are heated. It is the starter that is one of these elements.
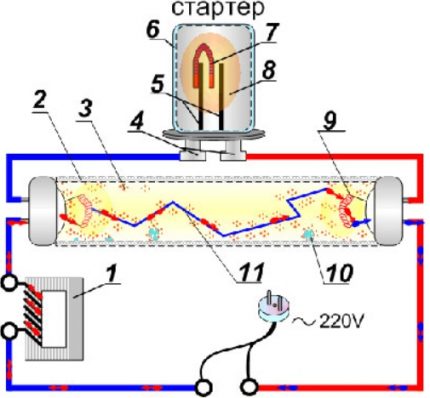
The flask is placed inside a housing made of plastic or metal, which acts as a protective casing.In some samples, there is an additional inspection hole on top of the lid.
The most popular material for block production is plastic. Constant exposure to high temperature conditions allows you to withstand a special composition of the impregnation - phosphor.
Devices are available with a pair of legs that act as contacts. They are made of different types of metal.
Depending on the type of construction, the electrodes can be symmetric movable or asymmetric with one movable element. Their findings pass through the lamp holder.
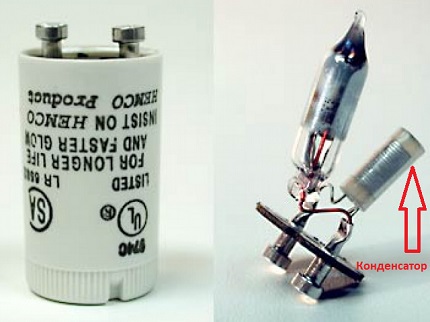
A mandatory part in the device is a capacitor that can smooth out extracurrents and at the same time open the electrodes of the device, by extinguishing the arc that arises between the current-carrying elements.
Without this mechanism, there is a high probability of soldering of contacts when an arc occurs, which significantly reduces the life of the starter.

The correct operation of the starter is determined by the supply voltage. When reducing the nominal values to 70-80%, the fluorescent lamp may not light up, because not enough heating of the electrodes.
In the process of selecting the right starter, given the specific model fluorescent lamps (luminescent or LL), it is necessary to further analyze the technical characteristics of each type, as well as determine the manufacturer.
The principle of operation of the apparatus
Having supplied mains power to the lighting device, the voltage passes through the turns throttle LL and a filament made of tungsten single crystals.
Then it is brought to the contacts of the starter and forms a glow discharge between them, while the glow of the gas medium is reproduced by heating it.
Since the device has one more contact - bimetallic, it also reacts to changes and begins to bend, reshaping its shape. Thus, this electrode closes the electrical circuit between the contacts.
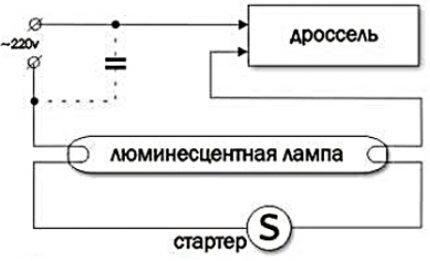
The closed loop formed in the electrical circuit of the luminescent device conducts current through itself and heats the tungsten filaments, which, in turn, begin to emit electrons from their heated surface.
Thus, thermionic emission is formed. At the same time, the heating of mercury vapor in the cylinder is reproduced.
The generated electron flow helps to reduce the voltage applied from the network to the contacts of the starter by about half. The degree of glow discharge begins to fall along with the temperature of the glow.
A bimetal plate reduces its degree of deformation, thereby breaking the chain between the anode and cathode. The current flow through this section stops.
A change in its parameters provokes the appearance of an electromotive force of induction inside the choke coil, in the conductive circuit.
The bimetallic contact instantly reacts by producing a short-term discharge in a circuit connected to it: between LL tungsten filaments.
Its value reaches several kilovolts, which is quite enough to break through an inert atmosphere of gases with heated mercury vapor. An electric arc is produced between the ends of the lamp, producing ultraviolet radiation.
Since such a spectrum of light is not visible to humans, the lamp design has a phosphor that absorbs ultraviolet light. As a result, the standard luminous flux is visualized.

However, the voltage on the starter connected in parallel with the lamp is not enough to form a glow discharge, respectively, the electrodes remain in the open position during the period of illumination of the fluorescent lamp. Further, the starter is not used in the working scheme.
Since the current indicators must be limited after producing a glow, electromagnetic ballast is introduced into the circuit. Due to its inductive resistance, it acts as a limiting device that prevents lamp breakdowns.
Types of starters for fluorescent devices
Depending on the operation algorithm, starting devices are divided into three main types: electronic, thermal and with a glow discharge. Despite the fact that the mechanisms have differences in the structural elements and in the principles of operation, they perform identical options.
Electronic starter
The processes reproduced in the starter contact system are not controllable. In addition, a significant impact on their functioning has a temperature environment.
For example, at temperatures below 0 ° C, the heating rate of the electrodes slows down, respectively, the device will spend more time on the ignition of light.
Also, when heated, the contacts can be soldered to each other, which leads to overheating and destruction of the lamp spirals, i.e. her spoilage.

Even properly functioning devices tend to wear out over time. They keep the glow of the lamp contacts longer, thereby reducing its production resource.
It was precisely to eliminate such shortcomings in the semiconductor microelectronics of starters that complex structures with microcircuits were used. They make it possible to limit the number of cycles of the process of simulating the closure of the electrodes of the starter.
In most samples on the market, the electronic starter circuitry is composed of two functional units:
- management scheme;
- high voltage switching unit.
An example is the microcircuit of an electronic ignitor UBA2000T from the company PHILIPS and high-voltage thyristor TN22 production STMicroelectronics.
The principle of operation of the electronic starter is based on opening the circuit by heating. Some samples have a significant advantage - the option of standby ignition mode.
Thus, the opening of the electrodes is carried out in the necessary phase voltage and subject to optimal temperature parameters of the heating contacts.
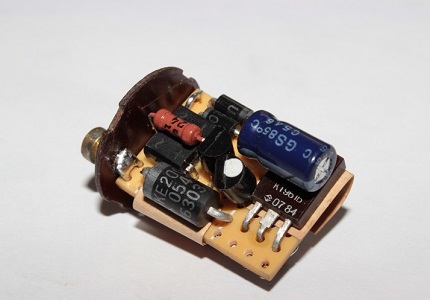
It is important that when the lamp breaks and unsuccessful attempts to start this type of mechanism, the mechanism turns off if their number (attempts) reaches 7. Therefore, there is no question of early failure of the electronic starter.
As soon as the lamp is replaced with a working one, the device will be able to resume the process of starting the LL. The only negative of this modification is the high price.
In a circuit with a starter, as an additional method of reducing radio interference, symmetrical chokes can be used with a winding divided into identical sections, with an equal number of turns wound onto a common core device.

All areas of the coil are connected in series with one of the lamp contacts. When turned on, both of its electrodes will work under the same technical conditions, thereby reducing the degree of interference.
Thermal view of the starter
A key distinguishing feature of heat ignitors is the long start-up period of the LL. Such a mechanism in the process of functioning uses a lot of electricity, which negatively affects its energy-consuming characteristics.

As a rule, this type is used in low temperature conditions. The algorithm of work differs significantly from analogues of other types.
In the event of a power failure, the electrodes of the device are in a closed state, when applied, a pulse with a high voltage is formed.
Glow discharge mechanism
Triggers based on the principle of glow discharge have bimetallic electrodes in their construction.
They are made of metal alloys with different linear expansion coefficients when the plate is heated.

The possibility of lighting the lamp is determined by the duration of the previous heating of the cathodes and the current flowing through the lighting device at the time of opening the starter contact circuit.
If during the first jerk the starter does not light the lamp, it will automatically try again until the lamp lights up.
Therefore, such devices are not used in low temperature conditions or in adverse climates, for example, in high humidity.
If the optimum heating level of the contact system is not provided, the lamp will spend a lot of time on ignition or will be disabled. According to GOST standards, the ignition time spent by the starter should not exceed 10 seconds.
Launchers that perform their functions through the thermal principle or glow discharge are necessarily equipped with an additional device - a capacitor.
The role of the capacitor in the circuit
As noted earlier, the capacitor is located in the casing of the device parallel to its cathodes.
This element solves two key tasks:
- Reduces the degree of electromagnetic interference generated in the radio wave range. They arise as a result of contact of the starter electrode system and formed by the lamp.
- Affects the ignition process of a fluorescent lamp.
Such an additional mechanism reduces the magnitude of the pulse voltage generated by opening the cathodes of the starter, and increases its duration.

Since the use of a suppressing device does not allow complete leveling of electromagnetic interference, two capacitors are introduced at the input of the circuit, the total capacitance of which is at least 0.016 microfarads. They are connected in series with the midpoint ground.
The main disadvantages of starters
The main disadvantage of starters is the unreliability of the design. Failure of the triggering mechanism provokes a false start - several flashes of light are visualized before the start of a full-fledged light stream. Such problems reduce the life of the tungsten filaments of the lamp.

In fluorescent lamps, an increase in operating voltage is observed over time, while in a starter, on the contrary, the longer the service life, the lower the ignition voltage of a glow discharge. Thus, it turns out that the lamp turned on can provoke its operation, due to which the light goes out.
The open contacts of the starter again light the light. All these processes are carried out in a split second and the user can observe only flicker.
The pulsating effect causes retinal irritation, and also leads to overheating of the throttle, reducing its life and lamp failure.
The same negative consequences are expected from a significant spread in the time of the contact system. It is often not enough to fully preheat the cathodes of the lamp.
As a result, the device lights up after a series of attempts, which is accompanied by an increased duration of the transition processes.
If the starter is connected to the single-lamp circuit, in this case there is no way to reduce the light pulsation.
In order to reduce the negative effect, it is recommended to use this type of circuit only in rooms where lamp groups are used (2-3 samples each), which must be included in different phases of the three-phase circuit.
Explanation of marking values
There is no generally accepted abbreviation for starter models of domestic and foreign production. Therefore, we consider the basis of the notation separately.
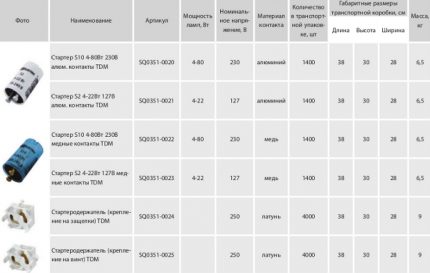
According to GOST, the decoding of the alphanumeric values [XX] [C] - [XXX] applied to the device’s case is as follows:
- [Xx] - numbers indicating the power of the light-reproducing mechanism: 60 W, 90 W or 120 W;
- [WITH] - starter;
- [Xxx] - voltage used for work: 127 V or 220 V.
To implement the ignition of lamps, foreign developers produce devices with various designations.
Electronic form factor is produced by many companies.
The most famous in the domestic market - Philipsproducing starters of the following types:
- S2 rated for power 4-22 W;
- S10 - 4-65 watts.
Firm OSRAM It is focused on the release of starters both for a single connection of lighting devices, and for serial. In the first case, it is the S11 marking with a power limit of 4-80 W, ST111 - 4-65 W. And in the second, for example, ST151 - 4-22 watts.
The produced starter models are presented in a wide assortment. The key parameters taken into account in the selection are proportional to the characteristics of the fluorescent lamps.
What to look for when choosing?
In the process of choosing a trigger, it is not enough to rely on the name of the developer and the price range, although these factors should be taken into account, as indicate the quality of the device.
In this case, reliable devices that have proven themselves in practice are winning. It is worth paying attention to such companies: Philips, Sylvania and OSRAM.

The most basic operational parameters of the starter are the following technical features:
- Ignition current. This indicator should be higher than the operating voltage of the lamp, but not lower than the power supply.
- Base voltage. When connected to a single-tube circuit, a 220 V device is used, and a two-lamp circuit uses 127 V.
- Power level.
- The quality of the housing and its fire resistance.
- Operational period. Under standard conditions of use, the starter must withstand at least 6,000 starts.
- Duration of cathode heating.
- Type of capacitor used.
It is also necessary to take into account the inductive resistance of the coil and the rectification coefficient, which is responsible for the ratio of reverse resistance to direct at constant voltage.
Additional information on the device, operation and connection of the ballast mechanism of fluorescent lamps is presented in this article.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Help in choosing the necessary ballast for a fluorescent lamp:
Starter for luminescent devices: fundamentals of marking and device design:
Theoretically, the operating time of the starter is equivalent to the life of the lamp that it ignites. Nevertheless, it is worth considering that over time, the intensity of the glow discharge voltage decreases, which affects the operation of the luminescent device.
However, manufacturers recommend changing both the starter and the lamp at the same time. To acquire the desired modification, it is initially worth studying the main indicators of the devices.
Share with your readers your experience in choosing a starter for fluorescent lamps. Please leave comments, ask questions about the topic of the article and participate in discussions - the feedback form is located below.

 Inductor for fluorescent lamps: device, purpose + circuit for connecting
Inductor for fluorescent lamps: device, purpose + circuit for connecting  Electronic ballasts for fluorescent lamps: what it is, how it works, wiring diagrams for lamps with electronic ballasts
Electronic ballasts for fluorescent lamps: what it is, how it works, wiring diagrams for lamps with electronic ballasts  Ballast for fluorescent lamps: why is it needed, how it works, types + how to choose
Ballast for fluorescent lamps: why is it needed, how it works, types + how to choose  Replacing fluorescent lamps with LEDs: the reasons for the replacement, which are better, replacement instructions
Replacing fluorescent lamps with LEDs: the reasons for the replacement, which are better, replacement instructions  LED lamp bases: types, marking, technical parameters + how to choose the right one
LED lamp bases: types, marking, technical parameters + how to choose the right one  Disposal of fluorescent lamps: where should you dispose of spent appliances
Disposal of fluorescent lamps: where should you dispose of spent appliances  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
I work as a manager at a state institution. We have fluorescent lamps in all rooms. They provide for a thermal starter. However, this element often fails. I asked the management several times to change the existing light fixtures to LED ones, but they refused me - there is not enough funding. I am no longer a boy, and it’s hard for me to climb the ceiling several times a week. In this regard, I would like to know: how to extend the life of thermal starters? Is it possible to replace them with devices with a glow discharge mechanism? If so, will something need to be changed in the device of the lamp itself?