How to connect an RCD: circuits, connection options, safety rules
The creation of a modern in-house electrical network is a responsible event related to calculations, the selection of wires and electrical installations, installation work. In this case, one of the main tasks remains to ensure the safety of residents and the safety of property. Do you agree?
If the protective devices are correctly selected and the connection circuit of the RCD and automatic devices is thought out, all risks are reduced to a minimum. But how to do that? What to consider when choosing? We will answer these and many other questions in our material.
You can also understand the principle of operation of the RCD and its connection options. Expert advice and installation nuances are collected in this material. In addition, videos are posted in the article, from which you will learn about the main errors when connecting and see how the RCD connects in practice.
The content of the article:
The purpose and principle of operation of the RCD
Unlike an automatic machine that protects the network from overloads and short circuits, RCDs are designed to instantly detect the presence of leakage current and response by disconnecting the network or a separate electrical line.
Since these two protective devices differ functionally, both must be present in the assembly diagram.
The principle of operation of the RCD is simple: comparing the values of the incoming and outgoing currents and tripping when a mismatch is detected.
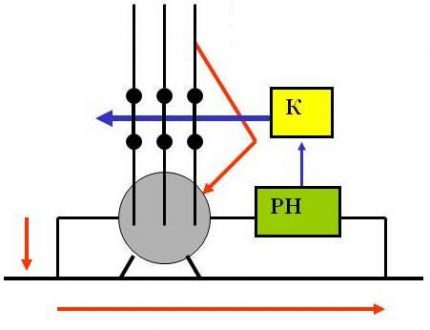
Inside the case of the automatic device there is a transformer with a core and windings with uniform magnetic flux directed in different directions.
When a leakage current occurs, the output magnetic flux decreases, as a result of which the electric relay is triggered and opens the power supply.This is possible if a person touches a grounded device and electrical circuit. On average, it takes from 0.2 to 0.4 seconds. More about the device and the principle of operation of the RCD we talked here.
There are various types of devices designed for direct or alternating current networks. One of the important technical characteristics that is necessarily present in the marking is the leakage current.
To protect the residents of the house, 30 mA devices are selected. Where there is an increased risk, for example, bathrooms with high humidity, children’s playrooms, install 10 mA RCDs.
A higher rating, such as 100 mA or 300 mA, is designed to prevent fire, as large current leaks can cause a fire. Such devices are mounted as a common introductory RCD, as well as in enterprises and large facilities.
Detailed information on choosing the right RCD set out in this article.

AEDT is more compact than a bunch of protective devices and takes up less space in the control cabinet, but when it is triggered it is more difficult to find the cause of the trip.
The installation scheme is selected in accordance with the task and the type of network - 1-phase or 3-phase. If it is necessary to protect the house or apartment as a whole from current leaks, RCDs are installed at the input of the power line.
Single-Phase Protection Options
Manufacturers of powerful household appliances mention the need to install a set of protective devices. Often in the accompanying documentation for a washing machine, electric stove, dishwasher or boiler indicates which devices need to be additionally installed on the network.

Considering the number of different circuits, serving sockets, switches, equipment that loads the network as much as possible, we can say that there are an infinite number of RCD connection schemes. In domestic conditions, you can even install outlet with built-in RCD.
Next, consider the popular connection options, which are the main ones.
Option # 1 - general RCD for a 1-phase network.
The place of the RCD is at the entrance of the power line to the apartment (house). It is installed between a common 2-pole circuit breaker and a set of circuit breakers for servicing various power lines - lighting and socket circuits, individual branches for household appliances, etc.
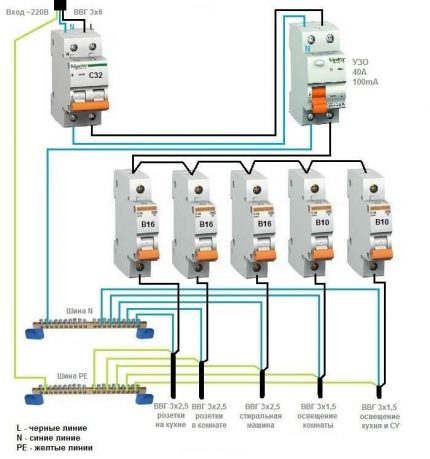
Suppose that a current leak has occurred due to the contact of the phase wire with a metal device connected to the network. The RCD trips, the voltage in the system disappears, and it will be quite difficult to find the cause of the shutdown.
The positive side concerns saving: one device is cheaper, and it takes up less space in the electrical panel.
Option # 2 - general RCD for a 1-phase network + counter.
A distinctive feature of the circuit is the presence of an electricity meter, the installation of which is mandatory.
Protection against current leakage is also connected to the machines, but on the incoming line a meter is connected to it.
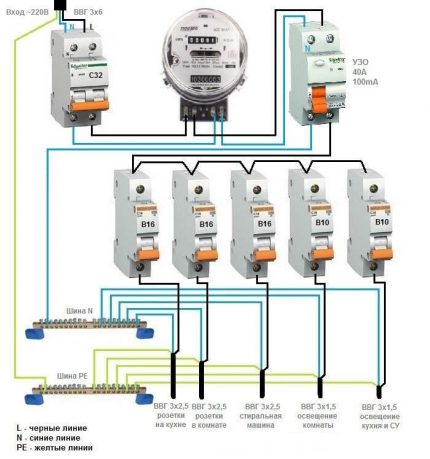
The advantages of this arrangement are the same as the previous solution - saving space on the electrical panel and money. The disadvantage is the difficulty of detecting a leakage current.
Option # 3 - general RCD for a 1-phase network + group RCDs.
The scheme is one of the more complicated varieties of the previous version.
Thanks to the installation of additional devices on each working circuit, protection against leakage currents becomes double. From a security point of view, this is a great option.
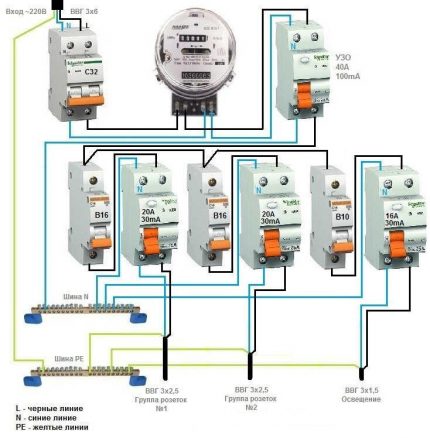
So that both devices (private and general) do not work immediately, it is necessary to observe selectivity, that is, when installing, take into account both the response time and the current characteristics of the devices.
The positive side of the circuit is that in an emergency one circuit will turn off. It is extremely rare that the entire network is disconnected.
This can happen if an RCD installed on a specific line:
- defective;
- out of order;
- does not match the load.
To avoid such situations, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with RCD verification methods on performance.
Cons - congestion of the electrical panel with a multitude of similar devices and additional expenses.
Option # 4 - 1-phase network + group RCDs.
Practice has shown that the circuit without mounting a common RCD also functions well.
Of course, there is no one protection insurance against failure, but this can be easily fixed by buying a more expensive device from a manufacturer you can trust.
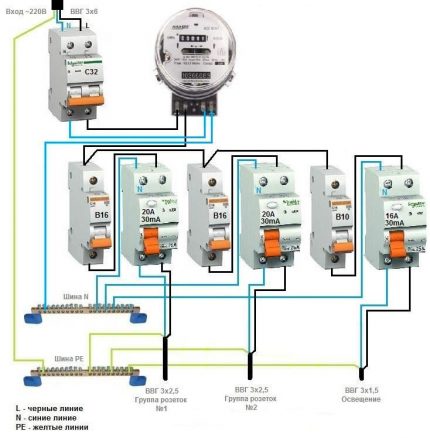
From the point of view of economy, the wiring of several devices loses - one common would cost much cheaper.
If the electrical network in your apartment is not grounded, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the schemes RCD connection without grounding.
3-phase circuitry
In houses, industrial premises and other structures, there may be a different option for arranging power supply.
So, for apartments, connecting a 3-phase network is uncharacteristic, but to equip a private house, this option is not uncommon. Here, other protection device connection schemes will be used.
Option # 1 - general RCD for a 3-phase network + group RCDs.
For a 380 V network, a 2-pole device is not enough, you need a 4-pole analog: you need to connect 1 zero core and 3 phase conductors.
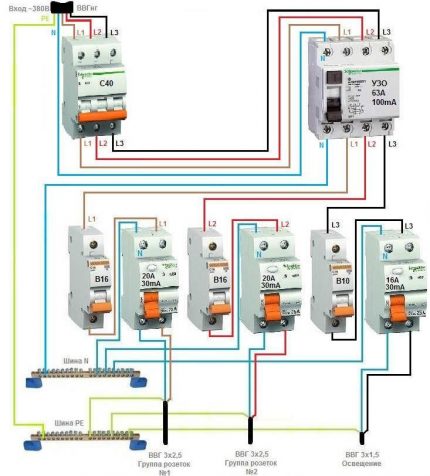
The type of wires is important. For a 1-phase network, a standard VVG cable is suitable, while for a 3-phase network, it is recommended to extend a more resistant to ignition VVGng. We wrote about choosing the right type of wire in our other article.
Option # 2 - general RCD for a 3-phase network + counter.
This solution completely repeats the previous one, but an electricity meter has been added to the circuit. Group RCDs are also included in the individual line service system.
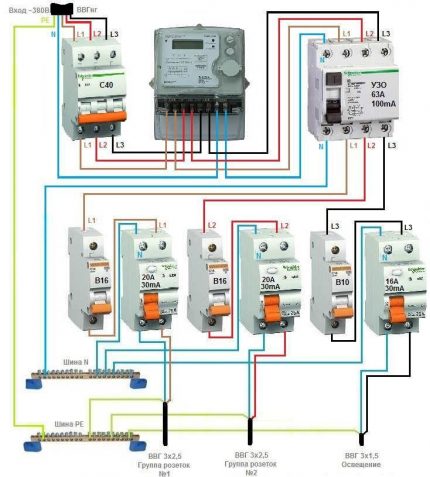
There is a nuance that applies to any of the presented schemes. If there are several lighting and outlet circuits in the apartment or house, several powerful household appliances requiring the arrangement of separate power lines, it makes sense to install double protection with a common RCD.
In the opposite case, either a common apparatus is sufficient, or one for each circuit.
Instructions for installing an RCD
First you need to choose a place to mount the device. 2 options are applied: a shield or a cabinet. The first resembles a metal box without a lid, mounted at a height convenient for maintenance.
The cabinet is equipped with a door that can be locked.Some types of cabinets have openings so that you can take readings of the meter without opening the door, and turn off the device.

A neutral wire is always connected to the left terminals at the input and output, and the phase wire to the right. One of the options:
- input terminal N (upper left) - from the introductory machine;
- output N (lower left) - to a separate zero bus;
- input terminal L (upper right) - from the introductory machine;
- output L (lower right) - to group machines.
By the time the protective device is installed, circuit breakers can already be installed on the switchboard. To streamline the arrangement of devices and wires, you may need to rearrange the devices in a specific order.
We present an example of installing an input RCD in an electrical cabinet, where a meter, an input circuit breaker and several circuit breakers for individual circuits - lighting, socket, etc.
Never connect an RCD at the input - it always follows a common introductory circuit breaker. If a counter is used, the residual current device switches to the third position from the input.
Connection process description:
- install the device on a DIN rail to the right of the machine - just attach it and push it with a little effort until it clicks;
- we stretch the cut and stripped wires from the machine and the zero bus, insert into the upper terminals according to the diagram, tighten the fixing screws;
- in the same way, insert the wires into the lower terminals and tighten the screws;
- test - first turn on the general machine, then RCD, press the "Test" button; when pressed, the device should turn off.
To make sure the connection is correct, the leakage current is sometimes staged. Take two working wires - the "phase" and "ground", at the same time lead to the base of the lamp. A leak appears and the device should instantly trip.
What mistakes should be avoided?
Before connecting, be sure to double-check the technical specifications of the devices. The rated current must be equal to or higher than the same parameter for the input machine. It is easy to determine the values by marking.
Electricians recommend choosing a protective device a step higher, that is, for a 50A machine, UZO 63A is suitable.
You can correctly calculate the parameters, choose a machine and RCD with the correct rating, but during installation, make a small mistake, as a result of which the system will be useless.
For example, newcomers often confuse tires. It should be remembered that I use different buses for the neutral conductor and the ground wire. In addition, for each device, a separate bus is required: for 5 RCDs - 5 buses.
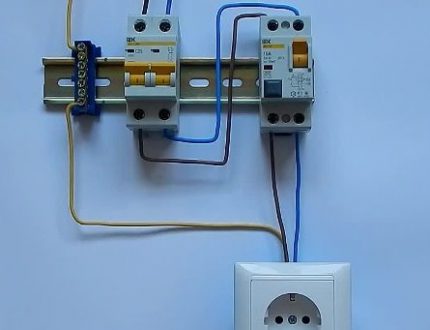
In no case should you confuse the poles N and L. They have lettering on the case, and the wires differ in color, so you need to be careful.
If a false alarm occurs or, on the contrary, the device does not respond, the possible reason is as follows:
- "Phase" and "earth" are connected after the RCD;
- incomplete connection - the N conductor is not inserted into the corresponding terminal;
- “Zero” and “earth” are connected at the outlet;
- confusion between connecting two or more RCDs to electrical installations.
In practice, there are many more errors, since different schemes are used. The more devices involved in the assembly of the electrical panel, the more carefully you need to be when connecting.
Safety rules during work
Most of the rules are general in nature, that is, they must be applied in the process of any electrical work.
If you decide to equip a distribution board yourself, before installing and connecting an RCD, do not forget:
- turn off the power - turn off the machine at the entrance;
- use wires with appropriate color coded;
- Do not use metal pipes or fittings in the apartment for grounding;
- install an automatic input switch first.
If possible, it is recommended to use separate devices for lighting lines, sockets, circuits for a washing machine, etc. In the opposite case, installing a common RCD is enough.

In addition to the characteristics of the devices themselves, the parameters of other wiring elements are also important, for example, wire cross section. It should be calculated taking into account the constant load.
It is better to connect the wires to each other with the help of terminal blocks, and for connecting to devices - use specially designed, marked terminals, as well as the circuit on the case.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
A few practical tips and explanations will help beginners figure out how to choose and connect an RCD in the house or apartment.
Errors when connecting outlets:
About the need and nuances of installing protective devices:
It is not always possible to call a qualified specialist for switchgear equipment. Sometimes machines or RCDs have to be installed independently.
Due to an oversight during installation, an electric shock can occur, therefore it is important to use wiring diagrams, correctly make calculations and follow safety rules.
Are you professionally engaged in electrical work and want to add useful tips or other RCD connection schemes? Maybe you want to supplement our article with recommendations on electrical safety? Write your comments in the block below - your comments will be useful to many home masters.

 How to connect a differential machine: possible connection schemes + step-by-step instructions
How to connect a differential machine: possible connection schemes + step-by-step instructions  RCD for a water heater: selection criteria + schemes and connection rules
RCD for a water heater: selection criteria + schemes and connection rules  Rules for connecting an RCD to a single-phase network without grounding: the best schemes + operating procedure
Rules for connecting an RCD to a single-phase network without grounding: the best schemes + operating procedure  Features of connecting automatic machines and RCDs in the shield: circuits + installation rules
Features of connecting automatic machines and RCDs in the shield: circuits + installation rules  Fire RCD: selection recommendations, rules and installation diagrams
Fire RCD: selection recommendations, rules and installation diagrams  Rules for connecting RCDs to a single-phase network with grounding: briefing on the work
Rules for connecting RCDs to a single-phase network with grounding: briefing on the work  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements