Underground gas storage facilities: suitable ways of storing natural gas
It would seem that knowledge of how underground gas storages are arranged has no practical value for the average user. But humanity is too dependent on "blue" fuel and so I want to be sure that there will never be interruptions in its supplies. Is that right?
And each compatriot can be reassured by information about gas storages located underground (UGS) - as long as they are full of problems with gas supply there will be no. Read more about storage device and storage features in our article.
The content of the article:
Underground gas storage facilities
If for the storage of gas for domestic needs, owners of private houses use gas holders, then on a national scale we are talking about completely different storage options. So, officially underground gas storages are complexes of engineering facilities that serve for pumping, storage and selection of “blue” fuel. They consist of ground and underground components.
TO ground relate:
- gas distribution point, which serves to distribute the gas stream into several process ones;
- compressor shopwhere the fuel is prepared (by increasing pressure) for injection into wells;
- gas treatment plants.
Underground UGS components are: wells, production, capacity. And the last item (capacity) is the most interesting - on how the “blue” fuel is stored depends on how the gas storage itself is arranged.

Overview of gas storage tanks
With the same weight, gas occupies much larger areas than any solid bodies.And since it is used in huge quantities, the same containers are needed for its storage.
Moreover, specialists refused to store gas in man-made land tanks a century ago.
The reason is that this would require:
- occupy vast areas of the planet with complexes for storing low-pressure blue fuel;
- Use expensive and explosive high pressure gas tanks.
As a result, in order to neutralize the negative points listed above, the choice was made in favor of underground storage facilities, and those located at a considerable depth are considered as such. Which, in most cases, is from 300 to 1000 meters. And you can store fuel there in tanks created by nature.
In total, engineers learned to successfully use 7 types of natural gas storage tanks:
- formed in water-saturated porous formations;
- preserved after the production of carbohydrates, namely the same gas, oil;
- formed in rock salt deposits;
- created in the mine workings of mines;
- Created in durable permafrost;
- with a low temperature ice breed shell;
- formed after underground atomic explosions.
Although there are many options, only the first 4 methods of gas storage differ in practicality. The remaining tank options are only theoretically suitable.

The reason for the impracticality of the remaining three options is as follows:
- Gas can be stored in frozen rocks, and several existing storages in the northern regions of the planet confirm this. But their volumes are extremely insignificant, therefore, they have no industrial value today.
- Capacities formed by underground nuclear explosions are quite suitable for storing significant gas reserves, which has already been experimentally proven. But the bottom line is that powerful weapons were tested away from people's places of residence. Therefore, there are usually no consumers, utilities.
As a result, these types of containers are simply unsuitable for use.
Although UGS facilities are called storage facilities, in reality, gas conservation is not their primary concern. Since what is in them is mostly used to smooth out unevenness and consumption. Which happens daily, weekly, seasonal. Only in the last turn UGS facilities are created to mitigate the consequences of force majeure circumstances.
Next, we consider in more detail each of the options for storing gas underground.
Option # 1 - storage in saturated reservoirs
Storage facilities in water-saturated formations are designed to mitigate the effects of seasonal unevenness when using gas. And also to create strategic reserves.
An important feature of the construction of such storages is the minimum human participation - most often at the stage of creating the wells necessary for pumping gas.
The indicated containers are sought in artesian strata. Gas storages are created where the rock structure is permeable, porous. The remaining liquid is removed by gas, which compresses it, and then squeezes it.
The so-called tanks for storing fuel themselves, in fact, are not. More precisely, they do not exist at all - they use as a place for storage voids in porous layers. And the whole procedure for creating a gas storage consists in displacing part of the water to the periphery.They do this in order to create space for "blue" fuel.
Perform the procedure described above will only succeed if a number of factors contribute to this:
- The porous permeable layer is covered with a dome (cover) of gas-tight rocks, which are usually extruded clays.
- The aquifer extends from the boundaries of the repository for tens of kilometers. Better yet, if it has access to the surface. All of the above enables the gas to successfully squeeze out the water in the reservoir.
- The length of the dome is sufficient to provide the ability to store significant volumes of gas.
- The porosity and permeability of the rock provides an acceptable gas capacity and the ability to give it during development.
If at least one of the conditions is not met, then it will be impossible to create an underground storage.
The principle of operation of modern underground storage is simple. Features can be considered by the example of large UGS facilities used to smooth out seasonal irregularities.
So, usually in the warm season they pump the right amount of gas. Which begin to be selected only with the onset of the heating season. Moreover, not some huge amount of gas is sent to the main pipe, but the average one, known from the experience of operation in past winters.
And, if suddenly the temperature drops sharply and the daily consumption becomes an order of magnitude higher, then a large underground gas storage facility will not increase the volumes of extraction anyway. And the shortage will be covered by small storages designed to smooth out daily, weekly consumption. The reason is that it is easier and faster to select from them.

The advantage of underground gas storage in water-saturated formations is substantial capacity. A disadvantage is that geologists, when studying the characteristics of an aquifer, may not identify and take into account some important factor. As a result, the storage will be unusable.
And the worst thing is that it is often revealed after a huge investment in the construction of ground and underground infrastructure. Quite often, less significant troubles are also encountered, from which the operation of underground gas storage in water-saturated rocks is accompanied by significant unplanned costs.
Option # 2 - Capacities after hydrocarbon production
Engineering complexes that belong to this type serve to smooth out seasonal fluctuations in the consumption of “blue” fuel. And also to create strategic reserves.

The storage device of this type is the same as in the case with analogues created in water-saturated formations. That is, fuel is stored in the voids of porous rocks.
UGS facilities created in the rocks where hydrocarbons were once located are the most abundant in the world. So, their number reaches a significant 70%, the reason for this is a number of advantages.
Which include: significant capacity and savings on investment in exploration, the creation of infrastructure or at least part of it, and drilling - oil and gas have already been extracted at the place of creation of such underground storage facilities.

But the tanks that survived after hydrocarbon production cannot be called ideal.
They have many disadvantages:
- leakage problems of old wells - especially for former oil fields;
- insufficient porosity, permeability of rocks;
- mixing gas with oil residues - which sometimes leads to significant losses, since the resulting mixture can no longer be used.
And also often in oil fields, gas has a dangerous impurity in the form of hydrogen sulfide. Which is harmful to human health, and also destroys all kinds of steel structures, even those related to stainless ones.
The operation of underground gas storage facilities based on the locations of depleted hydrocarbon deposits is possible due to the fact that gas injects oil residues from the desired reservoir upon injection. In addition, it, like water, has the effect of compressibility and mobility, which facilitates the task of equipping the tank. Sometimes oil under pressure of gas is not squeezed out into the rock, but rises to the top, which becomes an additional source of profit.
Option # 3 - reservoirs in rock salt deposits
Such containers with gas serve to smooth the daily, weekly unevenness of its use, and also take part in leveling the seasonal. In addition, storage in salt formations successfully cope with the role of a backup source for important consumers.
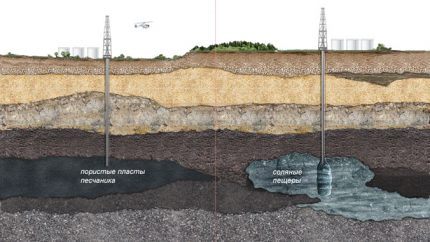
The indicated UGS facilities are created by washing out part of the salt deposits in order to create the cavity of the required size. Why initially several wells are drilled through which water is supplied for an extended period of time.
Although the described procedure is lengthy and costly, it pays for itself, since the storage of the injected natural gas takes place without loss. The reason is that salt caves are leakproof. In addition, they have the effect of self healing - tectonic and other cracks quickly become overgrown with salt deposits.
The advantage of the arrangement of such underground gas storages is that the selection of the required amount of fuel occurs with virtually no speed limits. Which is many times higher than when performing the same operations in containers of other types. An important advantage of underground storage facilities built in salt caves is the high percentage of gas withdrawal - one of the highest among all its types.

But the number of caverns in salt formations does not exceed 2% of the total number of storages.
This indicator is affected by a number of negative points:
- The presence of a huge amount of salt water after leaching the caves to save gas. As a result, if there is no sea nearby or at least salt processing plants, there is nowhere to put the liquid. What is the main reason for the small amount of this kind of underground gas storage.
- Net volume reduction during operation. This phenomenon is caused by evaporation of salt in places with higher pressure and accumulation where it is lower.
- The appearance in the gas of impurities, which often become the remains of the liquid previously used to wash the cave.
- Insignificant volumes, which does not allow to create reserves in sufficient quantities.
As a result, salt storage facilities are usually used only where it is not possible to use the types of containers listed above.
Option # 4 - UGS in mining
Their volumes are insignificant. Nevertheless, the Swedes and Norwegians keep part of their strategic gas reserves in tanks of this kind.
Mining PVC is the only gas storage facility fully equipped by man. So, in one of the mines, explosions create a container, which is then sheathed with steel sheets.

Although it is profitable to operate underground gas storage facilities in abandoned mines due to the high percentage and speed of extraction, their number will not increase significantly in the near future. The reason is that the described repositories are difficult to build. Since it is not always possible to achieve complete tightness, which leads to significant losses.
This happens due to the fact that during the operation of the mine they try to bring the maximum amount of air there. What is the purpose of creating a ventilation system with a mass of outcrops to the surface, which during the arrangement of the storage facility is not always possible to seal.
As a result, today, there are only a few successful examples of implementing the idea of storing gas in abandoned mines (in Sweden, Norway, Germany).
Are the vaults sealed?
Fuel leaks are common processes that cannot be avoided. Since there are too many reasons.
For convenience, they are divided into 3 categories:
- geological;
- technological;
- technical.
To group geological reasons include the heterogeneity of UGS tires, the presence of tectonic faults, as well as the features of hydrodynamics and geochemistry. For example, gas can simply migrate through the reservoir, and specialists will not affect it in any way.
Technological causes relate to the most frequent as errors regularly occur when evaluating any facts. For example, the effectiveness of hydraulic traps, gas reserves, ongoing physical and chemical processes.

Technical reasons most often associated with the state of the wells used, with the help of which gas is injected.
Features of creating UGS facilities
In 95% of cases, UGS facilities are created gas extrusion, oil residues from porous formations. Thus, “tanks” are created for storing “blue” fuel.
And the most important feature is that the volume of gas used to extrude liquids in the future cannot be used for delivery to consumers. Its task is to prevent the return of water, hydrocarbon residues to their old place. Otherwise, the repository simply ceases to exist.
That is, said gas is buffer. As a rule, it happens at least half of the total volume uploaded to the underground gas storage facility. And in some cases, the buffer gas is 3 times more than what can be used for delivery to consumers, which is called active.
It is interesting that the amount of buffer gas cannot be previously calculated. That is, everything is checked exclusively by an experimental method. Which in many cases takes years. But still, when the result is unsatisfactory, the buffer gas can be pumped out in full.
Storage Fill Order
After geologists have carried out studies of any reservoir and decided that a gas storage facility can be created in the right place, gas producers are building an engineering complex.

And then begins the injection of “blue” fuel into the future of the UGSF, which is supplied from the nearest trunk pipeline. And it enters the cleaning site, where all kinds of mechanical impurities are removed.
Clean fuel is supplied to the metering station. And after that, in the compressor shop, where compression is carried out - this is the name of the preparation of gas for pumping into the storage. It represents an increase in gas pressure to the desired value.
Then it is transported to gas distribution points. Where the total flow is divided into several and enters into different production lines. From where it is sent along the plumes to the wells for injection.
Throughout the process, experts control a number of parameters, including gas pressure and temperature, and productivity of each well.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video below is devoted to the topic of creating UGS facilities to smooth out uneven fuel consumption, which will be supplied by the Power of Siberia gas pipeline.
Underground gas storages are the most reliable and profitable way to level the uneven consumption of gas and its stable supply during force majeure. And the most interesting thing is that it is not human genius that needs to be thanked for, but nature, which has prudently created suitable strata of rocks.
Have you personally taken part in the creation of underground gas storage facilities and want to supplement the above material with useful information? Or noticed a discrepancy in the facts? Leave your comments and comments - the feedback block is located below the article.

 To which floor are gasified houses: legislative norms and rules for the gasification of high-rise buildings
To which floor are gasified houses: legislative norms and rules for the gasification of high-rise buildings  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements