Slope of the drainage pipe: calculations, standards and features of the installation of drainage on the slope
An impeccably designed and well-designed drainage will collect and divert groundwater from the site. It will protect the foundation from premature destruction, ensure normal growth of cultivated plants. In order to ensure spontaneous drainage of the collected water system, it is necessary to ensure the slope of the drainage pipe. And for his device you need accurate information, right?
You will learn all about the angle of drainage pipes and how to properly organize the drainage system from our article. Following our technical recommendations, you can design and accurately calculate the drainage network. The basis for the data are construction standards.
To help independent masters, the technology of designing a water drainage system is described in detail, the specifics of calculating and laying its components are thoroughly analyzed. For a clear perception of information attached photos and videos.
The content of the article:
Design features of drainage
There are three types of drainage systems, each of which has its own design features: horizontal, vertical, combined.
The working elements of horizontal drainage can be:
- tubular drains;
- gallery drains;
- trays and trenches.
The system of drainage pipes in combination with a filtering dusting (multilayer) - this is a tubular drain.
A multilayer filtering dusting, in this case, is done in order to prevent leachable soils from entering the system. By standards, the drainage circuit is always equipped manholes.

Unlike tubular drains, gallery drains are arranged from pipes of a larger cross section. On the walls of the pipes there are openings for collecting wastewater.
The process of arranging gallery drains also involves sprinkling with additional filtering with geotextiles.
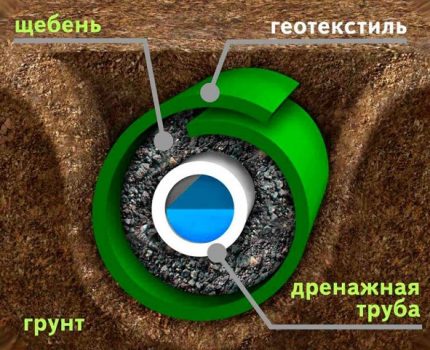
A drainage system with trays and trenches is usually done in such conditions when the groundwater level is allowed up to the level of 1.3-1.5 m. On stable soils, trenches are performed with slopes, on unstable soils the trenches are reinforced with reinforced concrete structures.
The vertical drainage system consists of a set of wells (wells) connected by a reservoir. A sewer is discharged through a collection line using a pumping station. Also, drainage on vertical drainage can be carried out by discharge into the lower layers of the soil.
The combined drainage system combines horizontal and vertical schemes. It is characterized by specialists as a complex drainage scheme and is usually arranged in areas where highly efficient drainage of soils is required.
Surface and depth diagrams
Based on the calculated parameters of the drainage deepening, distinguish between surface and deep drainage schemes. The purpose of the surface scheme is the collection and removal of precipitation products, as well as nearby groundwater.
The purpose of the in-depth scheme is to reduce the level of groundwater, their collection and diversion beyond the boundaries of the site where the construction site is located.

The scheme of water receivers of storm sewer systems supports point or linear execution. In the first case, sewage is diverted from local sources (gutters, pit pits, collections of input groups).
The linear scheme provides water drainage throughout the entire facility. As a rule, a combined solution with the implementation of both schemes is used at residential construction sites.
Deep drainage is mandatory in almost all cases of private housing construction and improvement of economic plots. This is an effective protection of those elements of building structures that are located below the zero level (foundation, basement, plant root system).
To exclude the construction of deep drainage is permissible on hills where the groundwater level does not exceed 1.5 m, where effective drainage of the soil is noted.

Designing a deep drainage scheme requires the execution of high precision calculations. Even a small calculation error can cause a low system efficiency.
The practice of installing such circuits often indicates a common mistake - an inaccurate calculation of the depth of the drain tab. The result is an uneven drainage of water from the site or, even worse - flooding of fertile land, basements.
There are other articles on our site where we examined in detail the construction of various drainage options. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with them:
- Drainage device around the house: design and installation of a drainage system with your own hands
- How to make your own foundation foundation house drainage: the secrets of proper organization
- How to competently do the drainage of the garden site with your own hands: we disassemble the correct arrangement technology
Design and drainage construction standards
The estimated values that will be required for the construction of a drainage system, as a rule, are:
- diameter of pipelines;
- pipeline laying level;
- pipe slope values;
- density geotextile filter.
And more about each item.
Value # 1 - estimated diameter of pipelines
The required diameter of the pipelines is calculated with emphasis on the design parameters of the intensity of water disposal.
For private housing construction, pipes with a diameter of 100 mm are usually optimal. Their throughput according to the standard is about 7 l / s, which is fully consistent with design standards in most cases.
Meanwhile, increasing the diameter of the drain allows you to cover a large working area, to strengthen the efficiency of the system.
Value # 2 - system bookmark depth
The level of laying of drainage pipelines, according to existing standards, is determined taking into account two criteria:
- The level of freezing soil.
- Depth of foundation.
The degree of soil freezing is directly related to the climatic properties of the area. Therefore, for each individual territory this parameter may differ.
But in any case, the calculation of the laying depth of drainage pipes is carried out from the end point of freezing of the soil with the addition of at least 300-500 mm of additional deepening to this value.
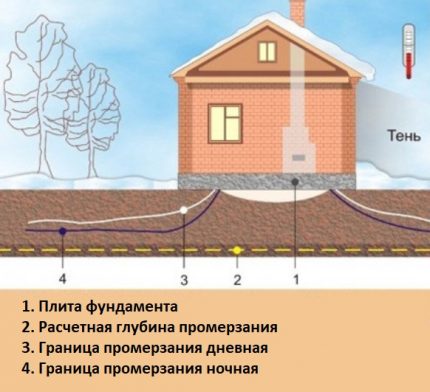
Using the same algorithm, the foundation drainage is calculated, but from the end point of the foundation.
Value # 3 - drain pipe slope
Under what slope to mount the pipes of the drainage system, SNiP standards clearly indicate. According to these standards, the minimum values of the drainage slope must be taken into account with the allowable minimum flow rate of wastewater.
In addition, it is stipulated that for pipes with a diameter of 150 mm the minimum allowable slope should be at least 8 mm per meter of length, and for pipes with a diameter of 200 mm - at least 7 mm per meter of length. In some sections of the networks it is allowed to underestimate these parameters to 7 mm and 5 mm, respectively.
The permissible maximum slope of the drainage pipes per meter length is 150 mm. More than this value, allowable slope only on the branches from plumbing fixtures with a branch length of up to 1.5 m.
On uncreated drain areas where pipes with a diameter of 40-50 mm are used, a slope of up to 30 mm per meter of length is permissible. And for pipes with a diameter of 85-100 mm and under the same conditions, the slope level can be made no more than 20 mm per meter length.

If trays are used as drainage elements, the slope level is taken with an eye to a sink rate at which the effect of self-cleaning of the liquid is ensured. Permissible filling of the trays is not higher than 80% with a tray width of at least 20 mm.
The value of the width of the trays is calculated based on the results of hydraulic calculations and depends on the design features of the elements. However, if the height of the tray is greater than 50 mm, the width value cannot be less than 70 mm.
Value # 4 - required density of geotextiles
When the design of the drainage system involves the use of perforated corrugated pipes as drainage, it is recommended to use a geotextile filter sheath (geotextile) along with sprinkling such pipes.
The geotextile web acts as a filter element, prevents the clogging of the highway with small particles of soil. To obtain the maximum filtering effect, a calculation of the density of the geotextile filter is required. The optimal design value for household drainage systems is considered to be a density of 100-150 g / m2.
Features of installation of drainage on a slope
Drainage systems provide drainage due to the slope of the drains. It would seem that, given the location of the site on the slope, water should be diverted from the site naturally, and there is simply no need for a drainage system.
However, the situation in such cases is completely different, and the drainage of the site on the slope becomes the same relevant measure as for sites with a slope horizon of less than 8%.

Of course, the drainage of territories on the slopes accompany their own characteristics. Often, the soil on steep slopes has a heterogeneous structure. At different horizons, a different level of groundwater may be noted.
Therefore, it is often necessary to use combined types of drainage to ensure the necessary degree of drainage of the entire territory of the site.
Meanwhile, in the construction of drainage systems on slopes with a level of more than 8%, the standards allow the absence of drainage inspection wells.
System layout and order
The organization of drainage on a site with a slope level of more than 8% begins with geological surveys. Based on the results of surveys, aquifers and groundwater levels are determined. Based on the information received, a project is being developed for the drainage of the site on the slope, and construction work is underway.
Ultimately, the task of eliminating the possibility of soil erosion by a chaotic natural drainage due to the steepness of the slope should be solved.
In a simple version, this is done approximately like this:
- At the upper elevation of the site, the first horizontal surface drain is created.
- A second horizontal surface drain is created at the lower elevation of the site.
- Both drains are connected by perpendicular trenches.
- From the horizontal drain of the lower level, they tap into drainage well.
If the landscape of the site has a stepwise complex shape and the project of the object provides for the construction of retaining walls, stairs, transitional areas, for each of the project elements it is necessary to construct point drainage systems that pass into the linear drainage system.
Plots of large area located on the slopes, as a rule, are equipped not with single surface drains, but with full-fledged herringbone-type water collection and drainage systems.
A branched drain is arranged on the upper horizon and combined with a collector drainage circuit surrounding the construction site. From the circuit, the effluents are sent to a collection tank outside the site or to storm sewer.
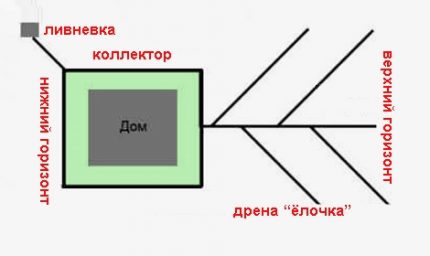
This circuit design is called ring drainage. Thanks to the construction of a protective circuit located around the perimeter of the facility, it is possible to take control of the groundwater level. In turn, the "herringbone" ensures the collection of water from the surface of the site and its effective removal.
Installation of ring drains is carried out at some distance from the construction site. This factor allows you to build an annular drainage system directly at the stage of operation of household facilities.
It should be noted that the effectiveness of lowering the groundwater level within the inner part of the circuit directly depends on the following parameters:
- pipe deepening level;
- the depth of the galleries;
- level of well deepening (if any).
The effectiveness of the protection is also influenced by the dimensions of the circuit.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
A few practical tips for laying drainage pipes will help you independently cope with the drainage device in the suburban area.
Protection of sites (territories) from oversaturation with moisture is an urgent task that has to be solved in almost every construction case. Existing drainage systems allow solving such problems.
The main point is to calculate and choose the option of a drain device that would be ideally suited in each particular case.
Are you planning to equip the site with drainage on your own, but have encountered difficulties at the design stage? Ask your questions in the comments section - we will try to help you.
Or have you successfully built a drainage system and want to share your experience with other owners of private households? Write your recommendations, add a photo under our article - your experience will be useful to many users.

 Site drainage project: selection of location, slope, depth, drainage system elements
Site drainage project: selection of location, slope, depth, drainage system elements  Drainage device around the house: design and installation of a drainage system with your own hands
Drainage device around the house: design and installation of a drainage system with your own hands  DIY drain pipe installation: step-by-step instruction + analysis of nuances
DIY drain pipe installation: step-by-step instruction + analysis of nuances  Do-it-yourself site drainage: features of the construction of various types of drainage
Do-it-yourself site drainage: features of the construction of various types of drainage  Drainage scheme around the house: the nuances of designing drainage systems
Drainage scheme around the house: the nuances of designing drainage systems  How to make your own foundation foundation drainage: step-by-step instruction on arrangement
How to make your own foundation foundation drainage: step-by-step instruction on arrangement  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Good afternoon. I would like the information to be supplemented with a more detailed description of the pipes used for drainage. The choice is now huge: plastic, asbestos-cement, ceramic ... And it is quite difficult for a simple layman to choose, especially since each manufacturer advertises his own products. Therefore, it is advisable to familiarize yourself with at least a brief description of the material and recommendations for its use.
Good day, Andrey.
Asbestos-cement and ceramic have almost identical characteristics. Rarely used for several reasons:
1. The complexity of installation. Due to the large weight, it is problematic to unload at the facility. The material is quite fragile. It requires careful preparation of the base and backfill.
2. The service life is 20-30 years.
3. The cost of the material itself, especially ceramics, is significantly more expensive than analogues.
PVC pipes, subject to the technology of the drainage system, have no drawbacks. They occupy leading positions in sales for the following reasons:
1. Easy to install. Unlike the previous two options - flexible and light in weight. They go in bays of 40-50 meters, which makes it easy to deliver and lay in a trench.
2. Different strengths. Two-layer, naturally, are more rigid than single-layer. The stiffness class is indicated by the letters SN, the higher the number after the more rigid the pipe. The maximum SN16.
3. Plastic is not subject to decomposition and destruction. Service life not less than 50 years.
4. Low cost of pipes.
Regarding the application:
- two-layer are applied in case of a large depth;
- pipe diameter is the absorption area. The higher the swampiness of the site, the larger the diameter required.