Drainage scheme around the house: the nuances of designing drainage systems
The removal of ground and storm water from the foundation will significantly increase the service life of both the capital building and the country house. A simple drainage system in the device will protect underground concrete structures from gradual erosion, and basements from flooding. But it is extremely important to prevent the destruction of the foundation of the structure, right?
A well-designed drainage scheme around the house will help to build an effectively functioning system for collecting and discharging natural water. We suggest you familiarize yourself with carefully selected and verified information, based on regulatory documents and the actual experience of builders of low-rise buildings.
We will tell in detail about the types of drainage systems, the features of their device, the specifics of operation. We will argue in favor of choosing a certain type of drainage. The useful information presented to your attention is supplemented by photos, diagrams and video instructions.
The content of the article:
Types of drainage facilities for drainage sites
When designing a drainage system, they primarily determine the goals that are planned to be achieved. They can consist in draining the entire site, in protecting the foundation and basement of the house from excess moisture.
Of the existing drainage systems, two main types can be distinguished - open and deep (closed). The first can be used for agricultural needs, for wastewater from cultivated areas. Indoor drainage is used to drain water in cottages and cottage areas, to protect buildings from the negative effects of high water pollution.

Combined drainage systems are also used. They are often supplemented by storm sewer branches designed for utilization of atmospheric water.Subject to their competent design, they can significantly save on the construction of each system separately.
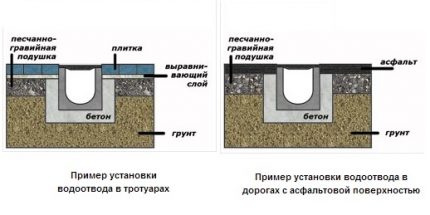
# 1: open drainage device
Open drainage is the easiest and most economical way to drain water, which can be used under the following conditions:
- clay soils underlying the soil layer, poorly transmitting water, due to which the fertile layer, located 20-30 cm from the earth's surface, is waterlogged;
- the site is located in a lowland, into which rainwater naturally flows during a period of heavy rainfall;
- there is no natural bias in the relief of the site, providing the movement of excess water in the direction of the street.
Open drainage is arranged in areas with high water supply, the mark of which is most often due to the location of the land allotment in the lowland or clay composition of soils that do not pass or pass water very weakly into the underlying layers.
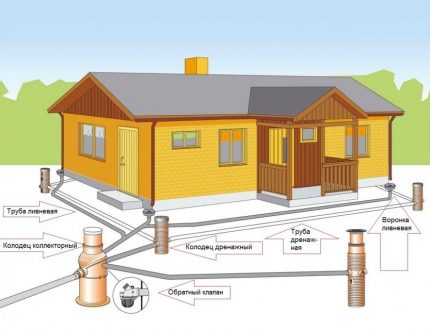
Planning a drainage scheme is best done at the design stage of the house. This will tie the work gutter system and place the storm water inlet under the gutters to the blind area.
Open drainage is considered the simplest and does not require a drawing up of a scheme. It is a trench 0.5 m wide and 0.6-0.7 m deep. The sides of the trench are positioned at an angle of 30 °. They encircle the territory around the perimeter and direct the wastewater into a ditch or foundation pit, into a storm sewer.
Territories with a slope towards the street are easier to drain. To do this, in front of the house, a gutter is dug across the slope, which will hold water from the garden. Then they dig a ditch, it will direct the drains towards the street, into the ditch.
If the site has a slope in the opposite direction from the road, then a transverse drainage ditch is dug in front of the facade of the fence and another longitudinal one is made to the end of the site.

The length of the lines for water flow, the number of wells and sand collectors depends on the area of the site, its topography, and the intensity of precipitation in a particular area.
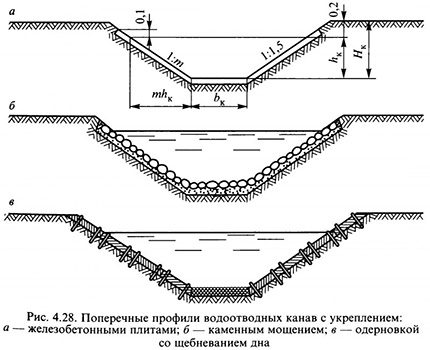
If the site is considered more or less even, and its level of bogging is not too high, then you can get by with the simplest drainage system.
Along the foundation of the fence, at the lowest point of the site, they dig a ditch 0.5 m wide, 2-3 m long and 1 m deep. Such a drainage system, although it protects against high water pressure, can cope with precipitation.

Over time, this simplest drainage system may lose operability due to gradual siltation. To prevent this from happening, it can be protected by a geo-strip. It is laid on the ground, after filling the ditches with an overlap, they drain the drainage layer. From above, to hide the ditch, it is sprinkled with a layer of fertile soil.
# 2: Building an Effective Storm
Storm sewage is necessary for the accumulation and removal of water from a portion of water falling in the format of precipitation. It is equipped with point and linear drainage devices.
The first type of water collectors is installed under the risers organized gutter system. The second type of catchment is located under the slopes of the roofs with an unorganized drain.
Water entering the catchment flows through an open or closed pipeline. It is diverted either to a common catchment well, or to a collector well, from which it moves to a centralized sewer network or a gutter.
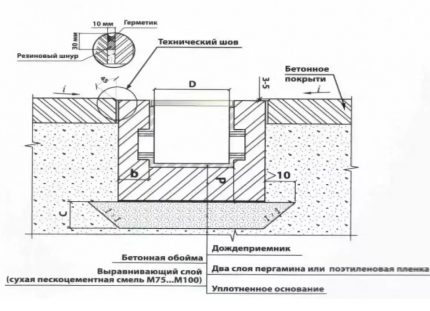
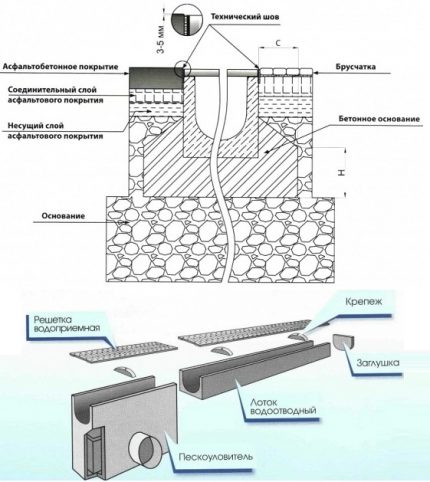
Elements of a storm system with point water collectors are also drainage drains, drains, dampers. Some manufacturers provide for the possibility of connecting storm water inlets with roof gutters, as well as with underground drainage systems.
In addition, off-the-shelf production models include sand traps and waste bins that simplify system maintenance.

This is a system of gutters made of plastic or concrete, which are installed on the site in those places in which the accumulation of water is most likely, but extremely undesirable.

Designing storm pattern with linear water inlets, the first thing they plan is to place a catchment or collector well. Next, determine the location of the rotary and inspection wells. Their arrangement will depend on the placement of storm water inlets-gutters and closed sewer branches.
To prevent water from entering the courtyard from the street, gutters are installed along the line of gates leading to the courtyard, garage doors, as well as in the gate area. When choosing the elements of the system that will be installed on the roadway, take into account the future load on them.
To prevent moisture from entering the building, the slope of the coating in the garage is done towards the intake grille. So water, when washing a car or thawing snow on a vehicle, will drain into the gutter.
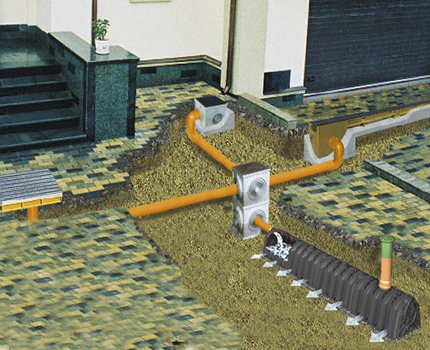
To give the shower a neat appearance, special trays made of polymer concrete, plastic, which are closed with metal or plastic grates, are used. At the entrance to the house use a special tray for cleaning shoes.
The grate for the gutter installed near the pool is chosen plastic, white, to avoid burns on a hot summer day.
Gutters and water intake points are connected to the drainage tank sewer pipes. At the junction of the gutters and pipes provide inspection wells. They are designed to facilitate access to the system and its cleaning from possible clogging.
Revision wells are made mainly of plastic. In order to obtain the necessary depth, their design provides for the possibility of building with the help of special extension elements.

A wide range of system elements allows the most rational design drainage scheme around the house, which will be optimal from a technical and financial point of view.
# 3: Construction of enclosed drainage options
Underground, closed drainage is used if the open system device takes up too much space on the land or it does not fit into the landscape picture of the territory. The conditions for its construction of a closed drainage system are similar to the prerequisites for organizing a network of open drainage ditches and ditches.
It is mandatory to organize underground drainage on the site if:
- it is located in a lowland, in a swampy area;
- near the buildings is a natural reservoir;
Its device is recommended if the house has an exploited basement (garage, basement, cellar).
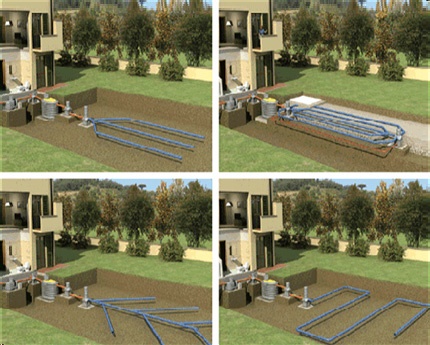
Underground drainage can be divided into two types:
- wall drainage;
- trench (reservoir) drainage.
Both types of underground drainage are carried out at the construction stage of the building. If it was decided to start the problem of water disposal after the construction of the house, then a trench ring system is used. There are restrictions for the use of trench drainage. It can be used if there is no basement in the house.
The fact is that, after bookmarks draene, filling the pit with sand or soil creates a more friable environment between the bedrock and the foundation. As a result, the water enters the environment and then even the presence of a clay castle does not protect the building from moisture.
Therefore, if the house has a basement, for effective drainage it is best to do wall drainage.It is used for drainage of groundwater directly from the foundation of the building, to protect basements, cellars, basement floors from flooding.

Wall drainage system limits the increase in water level, preventing its rise above the drainage pipes - drain lines. It is believed that a drainage pipe with a length of 1 m is capable of draining an area of about 10-20 m2.
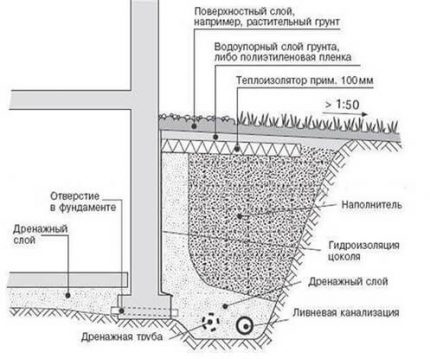
The distance from the drainage pipe to the foundation depends on the placement. inspection wells. They are laid in each corner (or through one corner) of the building, as well as in places of turns and pipe connections.
Revision wells are also located in places with a large level difference of the site and with a long pipe length - the distance between the wells should be no more than 40 meters.

The whole system closes to the last well. It should be located in the lowest place. Next, the water flows into a normal sewer or open water. If it is not possible to divert water from the house by gravity, then the pumping equipment is installed and it is pumped out forcibly.
To ensure gravity drainage of water, pipes are laid with a slight bias towards the prefabricated collector. The slope should be two centimeters per meter of drainage pipe. The depth of the pipe should be greater than the depth of freezing of the soil.

To save on geocomposite materials and prevent their mixing with the soil, use geotextiles. It freely passes water to drains and at the same time retains particles that lead to siltation. The pipe itself must also be wrapped in protective material before backfilling. Some models of drain are produced with ready-made filters from geotextiles.
It is possible to increase the efficiency of wall drainage with the help of a profiled polymer membrane, which can be two- or three-layer. One of its layers is a polyethylene film with formed protrusions, the second layer of the membrane is geotextile fabric.
The three-layer membrane is equipped with an additional layer of smooth polyethylene film. The membrane helps to filter water from the soil and at the same time serves as a waterproofing layer for the foundation of the building.
Indoor trench drainage protects the building from flooding and moisture. It is a filter layer, which is poured into the trench at a distance of 1.5-3 m from the wall of the house.
It is better that the depth of the drainage is 0.5 m deeper than the base of the foundation - so the water will not exert pressure on it from below. Between the trench with drainage and the foundation of the house remains a layer of clay soil, which serves as the so-called clay castle.

As with the installation of a wall drainage system, the drains are laid on a layer of gravel or small gravel. Both pipes and gravel are protected by geotextiles from clogging.
# 4: Step-by-step wall drainage construction
In order to get a visual representation of the drainage process around a country house, consider an example.The plot provided therein required the installation of a groundwater discharge system, as loam and sandy loam occur under the soil and plant layer, which transmit water extremely poorly due to the low filtration capacity.
The collector well in the example is intended for the partial discharge of collected water into the underlying soil strata and for the partial removal of excess from the site into the public gutter. Connected to it will be drains from a septic tank, stormwater and drainage. To drain excess water, a drain pipe located below all will be installed.
Having successfully dealt with the bulk of the work, we proceed to the final improvement:
# 5: Organization of combined systems
On the site near the house, you can also organize a combined drainage system. For example, drainage and stormwater runoff can accumulate in one collector well. In this case, the collector for collecting wastewater should be constructed taking into account the load from both systems. In addition, storm sewers may include point and linear water collectors.

It must be remembered that the mistakes made during the mixed type of water disposal can even lead to an increase in water storage, flooding of basements and cellars. The main drawback is the discharge of water from the drainage system into the underground drainage system.
When these two systems are combined, water from the roof enters the drains and seeps into the ground. This is especially active during heavy and prolonged precipitation. As a result, water, instead of leaving the system, seeps into the soil and saturates it with moisture.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video # 1. The scheme of surface drainage and its installation:
Video # 2. Do-it-yourself trench drainage system around the house:
Video # 3. Nuances of design and construction of a sewage system:
When designing a drainage system around a private building, it is very advisable to first obtain the advice of a hydraulic engineer. Failure to comply with the rules and conditions of water reduction can lead to subsidence of the soil, home, road.
This is especially important to consider when installing deep drainage. Therefore, it is better to draw up a drainage diagram around the house at the stage of drawing up the plan, then all the nuances of construction and water disposal will be taken into account in one project.
Those wishing to tell about their own experience in the drainage device are welcome to post comments. You can write them in the block below. Here you can ask questions and publish a photo on the topic of the article.

 Drainage device around the house: design and installation of a drainage system with your own hands
Drainage device around the house: design and installation of a drainage system with your own hands  Slope of the drainage pipe: calculations, standards and features of the installation of drainage on the slope
Slope of the drainage pipe: calculations, standards and features of the installation of drainage on the slope  Site drainage project: selection of location, slope, depth, drainage system elements
Site drainage project: selection of location, slope, depth, drainage system elements  Do-it-yourself site drainage: features of the construction of various types of drainage
Do-it-yourself site drainage: features of the construction of various types of drainage  How to make your own foundation foundation drainage: step-by-step instruction on arrangement
How to make your own foundation foundation drainage: step-by-step instruction on arrangement  DIY drain pipe installation: step-by-step instruction + analysis of nuances
DIY drain pipe installation: step-by-step instruction + analysis of nuances  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Hello, I am very interested in the topic of the drainage system, because when arranging my own summer cottage, I ran into the problem of choosing a drainage. Due to the fact that the terrain is swampy, a simple ditch along the perimeter cannot be dispensed with, apparently. So this is the problem for this case: you need to use underground drainage. The questions immediately ripened: what type? What is more effective: trench or wall?
Good afternoon, Ivan. Need a wall.
Wonderful article, cool photos, understandable and accessible, thank you very much for the material☕
Hello. Please tell me which is better to choose drainage, if the house is on a pile-screw foundation? Loamy soil on the site, the site was lifted with “clay soil” - this is 30-40 cm imported (sand + clay).
Good afternoon, Julia. Since the house stands on stilts, the only and most important requirement for drainage is efficiency. There is no trench or near-wall difference, it will not work to wash the foundation. For the calculation and the project, I advise you to contact the specialists, and I also recommend that you additionally familiarize yourself with article on our website about drainage design.
Honestly, I do not think that the site was raised with clay, otherwise you yourself created a problem. Clay, as you know, does not really let water through. For planning, apply: sand, fertile soil, chernozem, peat / sand mixtures.
Hello. Nikolay, you are not quite right. They create a filling with materials having a density due to binding components - a sandy loam mixture (denser than pure sand, but still loose, used for roughing roads, filling pits), loam (mainly clay, used to equip sites), coarse soil (stone rocks from 2 mm, suitable as a material for road works, rough scattering of sites).
Loam is the best option for creating compacted embossed soil. It has good enough throughput characteristics, which makes it possible not to provide a swamp on the site, and yet, it retains a sufficient amount of moisture to ensure soil fertility and hinder its drying out.
Hello! If you apply the recommendation and dig a ditch in front of the fence (in a section with a slope from the road), then where do you think the accumulated groundwater should be diverted?
Hello. Check out local, regional land use and development regulations. If you don’t have one or more points in the region according to the rules for groundwater abstraction, use the nearest sewage system, catchment ditches and so on.
Hello. We are faced with a monstrous problem - the dampness in the house. Walls were just plastered in it, wallpaper was glued, and in the very first winter mold appeared from below. They added the foundation and isolated it in the spring - it did not help. Next winter is the same.
They decided that due to the fact that the former owners raised the level of the slope too much and laid the tiles, and now all the water goes under the house. We made a canopy, but again, alas, the smell of dampness and mold in the middle of the house. What should we do, please advise? I have small children, I am afraid for their health.
Hello, Catherine. Have you visually examined the fact of water flow under the house? Just mold in the house is not a guarantee of improper drainage, there are another million possible reasons. What to do is to remodel everything, dismantle the tiles, the correct bias and all that sort of thing. Accurate to say without a photo and additional information is simply unrealistic.BUT! I repeat, exclude all possible causes, in addition to this, the most real one. It’s just that if this is not only the case, as long as you struggle with the slopes, the mold will grow and poison you even more.