What is a water protection zone + norms for determining its boundaries
All of us cannot but worry about the quality of water in the water supply system, which we drink and use for domestic needs. Cleanliness should be taken care of both at headquarters where water is drawn and in water supply networks.
It is not only water intake that must be protected from pollution; the water protection zone along its entire length should fully fulfill its function. Let's try to figure out what the security zone is and what responsibility is provided for non-compliance with sanitary standards.
The content of the article:
Three zones of the sanitary protection zone
For the purpose of environmental protection, a sanitary protection zone (ZSanO) is created around all water supply facilities.
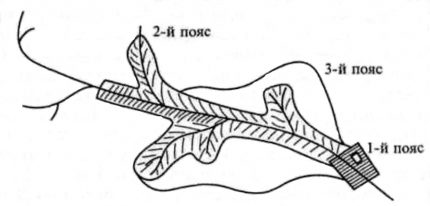
Sanitary-protective zoning involves the formation of 3 zones:
- strict regime - No. 1;
- restrictive - No. 2;
- Observational - No. 3.
In strict mode, the water intake facilities and the water intake site are protected from accidental or intentional harm. The second restriction belt is designed to protect the water source from microbial contamination, and the third observation belt is needed to control the level of chemical pollution.
If the first belt can be outlined manually, using a small number of normative digits, then the second and third zones are determined as a result of complex hydrodynamic calculations by a difficult method.
It’s much more convenient to master a computer program.AmwellsIn the meantime, we will consider the general principles for constructing sanitary protection zones in several ways.
#1. For open source water supply
Suppose the water in the water supply comes from a river - this is an open (or surface) source. The first belt is determined by the location of the water intake facilities (head elements of the water supply system). We add to them 180-200 meters upstream and 90-100 meters downstream.
The water intake and the adjacent water area are controlled by paramilitary guards, it is forbidden to find strangers here.
Having decided on the length, let's find out the width of the coastal strip that falls into the ZSanO. There may be 50 and 200 m with the capture of the opposite bank, which depends on the power of the river itself. Along a large and deep channel with an intensive current, no more than 50 m of the coast is isolated on both sides. And if the river is small - in total up to 150 m and more. This includes the width of two coastal edges and the river itself.

When taking water from a large lake, reservoir, when it is very far from the opposite shore, they measure 100 m in all directions. It looks like a circle with such a radius, and some part of it passes through the water. The water border of the zone is marked with buoys and beacons with backlight.
The second belt is the territory that immediately follows and adjoins the first belt. There are severe restrictions on it: factories and industrial production, farmland, construction, the arrangement of beaches and places of mass out-of-town recreation are prohibited.
To know where to place the boundary of the second belt upstream, it is necessary to study the ability of river water to self-purify.
On average, a river processes pollution that has got into it from 3 to 5 days. During this time, the river flow should not have time to bring polluted water to the point of intake, self-purification should occur earlier. If you translate into mileage, then including in the second belt 20-35 km of the channel for large and 35-60 km for small rivers above the intake is quite enough.
And downstream the border will pass at a distance of 250-300 m from the water intake. Here it is required to exclude the reverse movement of water against the flow due to wind.
The third belt - it includes cities, towns, villages that are supplied with water from this source, the territory needs constant monitoring, but there are no such restrictions as in the first and second.
# 2 For water supply from an underground source
In the variant with an underground source, a sanitary protection zone is also needed. For shallow water wells, revealing the aquifers of sedimentary deposits, the strict regime zone is surrounded by a radius of 50 m, and for deep wells reaching aquifers in bedrock, this figure is half as much - 25 m.
There can be no unnecessary structures, except for the primary pumping station, water tower, a minimum of utility buildings.
Surface and drainage drains must be taken outside, and the territory itself should be landscaped, landscaped, fenced, while at the same time providing an unhindered access for special vehicles with service crews to eliminate possible sudden malfunctions, planned measures for maintenance and repair of equipment.

The second zone is determined so that pollution from outside it could not penetrate underground aquifers and reach water intake in a period of 100 to 400 days - a specific figure is calculated based on the laws of hydrodynamics, taking into account the characteristics of soils and climatic factors.
The third zone is a zone of active human activity. It is assumed that the movement of pollution from this territory towards the water intake will be slow and take longer than the planned life of the well (25-50 years).
Sanitary protection zones are drawn on the maps, information about them is published, and the strict regime belt is marked with all sorts of warning signs and signs on the ground, surrounded by a solid fence, barbed wire mesh, etc.
# 3 For structures and water pipelines outside the water intake
Outside the territories related to the abstraction of water from sources, there are strict security zones around such waterworks:
- spare tanks, filter stations - 30 m;
- water towers - 10 m;
- pumping plants, chlorine and reagent warehouses, sedimentation tanks, etc. - 15 m.
Along the water conduits, sanitary lanes must be laid on the left and right. Their width varies from 10 to 50 m and depends on how high the groundwater rises, what is the diameter of the water pipes.
If the cross-section of the pipe does not exceed 1 m, a strip of 10 m wide is sufficient, for a pipe with a diameter of more than 1 m, the width of the strip doubles, and with high groundwater - up to 50 m, regardless of the size of the pipe.
When a water conduit is laid in already built-up areas, the reduction of the area of protection zones is allowed, if the sanitary-epidemiological service does not mind.
The specificity of prohibitions within the framework of the ZSanO
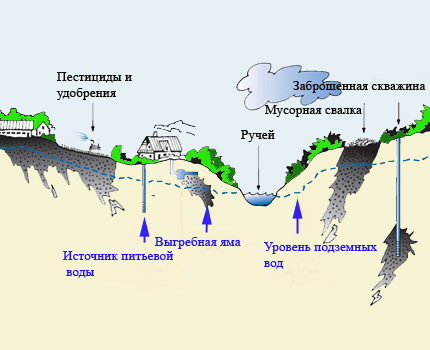
The most stringent requirements are imposed on strict security zones (first belt). In their territories it is impossible to erect buildings and structures, dig trenches or otherwise dig into the ground, store any materials, apply fertilizers, litter, cut down green spaces, graze livestock, go fishing, equip boat moorings, swim.

An extensive list of bans has been compiled for the second security zone. Construction and blasting, driving in piles and other actions creating vibration are prohibited.It is forbidden to discharge effluents, to develop the bowels of the earth, to cut forests, to place warehouses of toxic chemicals, fertilizers, fuels and lubricants, to plow virgin lands, to drain swamps.
It is not allowed to allocate places for cattle cemeteries, silo and dung pits, livestock and poultry complexes, etc. Excluded the use of the protected area for living, outdoor activities, sporting events. It is forbidden to pull water conduits through the territory of landfills, filtration fields, near cemeteries.
Subtleties of laying sewage
Accidents on sewer networks are a frequent occurrence, and this is not only due to the natural deterioration of pipes and systems. Sewerage, like water supply, has a security zone, but it is not customary to label it with signs and signs. The presence of sewer pipes and their location must be judged by the wells closed with massive metal covers marked “K” or “GK”.
Before starting excavation work in the security sewer zone, it is necessary to study the plans and schemes of engineering communications, get relevant recommendations and expert advice.
Otherwise, it is easy to break the sewer pipe with one careless push of the bucket of the excavator, and who will then calculate the losses and material costs of the restoration? And if there is a water supply nearby, then the damage and negative consequences increase many times.

The security zone of sewage networks is set in proportion to the pipe section:
- up to 0.6 m across - at least 5 meters in both directions;
- from 0.6 to 1.0 m or more - 10-25 meters each.
It is necessary to take into account the seismological characteristics of the terrain, climate and average monthly temperatures, humidity and freezing of the soil, especially the soil. The presence of adverse factors is an occasion to increase the security zone.
The distance to the sewer networks located underground from such objects is also regulated:
- from any foundations, the sewage system should be 3-5 meters apart (for pressure head the distance is greater than for gravity);
- from supporting structures, fences, trestles, the indent is from 1.5 m to 3.0 m;
- from the railway track - 3.5-4.0 m;
- from the road curb on the roadway - 2.0 m and 1.5 m (standards for pressure and gravity sewage);
- from ditches and ditches - 1-1.5 m from the near edge;
- street lighting poles, racks of contact networks - 1-1.5 m;
- pylons of high voltage power lines - 2.5-3 m.
The numbers are reference, accurate engineering calculations allow you to get more reasonable data. If the intersection of water and sewer pipes cannot be avoided, the water supply should be placed above the sewer. When it is technically difficult to carry out, a casing is put on the sewer pipes.
The space between it and the working tube is densely compacted with soil. On loam and clay, the length of the casing is 10 meters, on sand - 20 meters. Crossing communications for different purposes is better at right angles.
You can read more about the calculation of the slope of sewer pipes. in this our article.

When opening water and sewer pipes in connection with the repair, it is allowed to use equipment in earthwork to a certain depth. The last meter of earth thickness above the pipe is removed carefully by hand without using a tool with shock and vibration.
It is strictly forbidden to touch the sanitary zones of water pipes during installation, but in the city the requirements are less stringent.
In urban conditions, with forced parallel arrangement of the main water and sewer pipes, it is supposed to withstand the following distances:
- 10 m for pipes up to 1.0 m across;
- 20 m with a pipe diameter of more than 1.0 m;
- 50 m - on wet soil with any pipe diameter.
For thinner household sewage pipes, the distance to other underground utilities is determined by their standards:
- to the water supply - from 1.5 to 5.0 m, depending on the material and the diameter of the pipes;
- to rain drainage systems - 0.4 m;
- to gas pipelines - from 1.0 to 5 m;
- to cables laid underground - 0.5 m;
- to the heating plant - 1.0 m.
The final word on how to ensure the safe coexistence of the water supply and sewage systems remains with the specialists of the water utility enterprises. All controversial issues should be resolved during the design process and not emerge at the operational stage.
List of regulatory documents
The mandatory creation of a sanitary protection system with a breakdown into zones is provided for by the law “On the sanitary and epidemiological well-being of the population” (No. 52FZ, 03.30.99) According to this law, the development of a water supply system of a water supply system should be connected to the water supply project and drawn up as a separate project.
ZSanO design is based on SanPiN with cipher 2.1.4.1110-02 . This regulatory document defines how to calculate sanitary protection zones, and describes the requirements for them from the standpoint of sanitation and epidemiology. Ignoring the rules and regulations prescribed in SanPiN 2.1.4.1110-02, is fraught with a high probability of outbreaks of serious infectious diseases, mass poisoning, epidemics.
Abbreviated documents will also be useful. SNiP: 40-03-99 (new version 2.04.03-85), 2.07.01-89 *, 2.07.01-89 *, 2.05.06-85 *, 3.05.04-85 *, 2.04.02-84 (section 10 - Sanitary protection zones ) In building codes and codes with the indicated codes, you can find the necessary information on the design of water supply and sewer networks, on the development of settlements, on trunk pipelines.

Regulatory materials - the basis for the development of standards, taking into account local characteristics of a particular region. The approval and adjustment of the norms for ZSanO involved urban and rural administrative authorities.
Responsibility for non-compliance with protective rules
Security zones are a kind of guarantee of the purity of water and its protection from pollution. To comply with the rules in force in these zones, all business entities and private individuals are required. The following sanctions are provided for violation:
- indemnification - the perpetrator must compensate for the damage caused by unauthorized construction, storage and warehousing of materials, the accumulation of garbage and waste closer than 5 m from the water supply;
- administrative measures, i.e. fines - for neglect of building codes, rules, for the construction of buildings and any other construction without a project approved in advance;
- criminal liability for the seizure of land in sanitary protection zones.
It is foolish to say as an excuse that you did not know about the location of the protection zones - this does not exempt from liability.
Before performing any construction, land and other work, you should contact the water utility and familiarize yourself with where security zones are located in your village and its environs, and what actions cannot be carried out in the chosen place. This is the only way to avoid unpleasant and unexpected consequences.

Since the first zone of the ZSanO should be marked with warning signs, if they are absent, the responsibility for the order in the security zone lies with the operating organization, and there is no reason to make claims against those who accidentally invade the forbidden territory.
But if there are warnings, the violator will not be able to absolve himself of blame for illegally entering the sanitary zone and taking any actions there.

The legislation of the Russian Federation determines the degree of responsibility and punishment for those who violate sanitary standards and requirements. You can read about this in the Code of the Russian Federation “On Administrative Violations” (No. 195FZ, December 30, 2001) In particular, Article 8.13 deals with water bodies and their protection.
A fine of 500 to 1 thousand rubles can be fined for violations in the sanitary protection zones of water pipelines and water intakes of an ordinary person, an official - 1-2 thousand rubles. Penalties for legal entities range from 10 to 20 thousand rubles.
If the zone of sanitary protection of a reservoir, lake, river involved in water supply is harmed, then fines are higher - 1-2 thousand rubles, 3-4 thousand rubles and 30-40 thousand rubles, respectively. Compliance with the rules and regulations of the legislation of the Russian Federation is strictly checked.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
What does the strict security sanitary zone look like:
How does the program for calculating the sanitary protection zones of underground water intakes work:
To summarize ... Security zones are an important condition in creating water supply systems. And they must fully fulfill their functional purpose, if we want clean water to run from the water taps.
When the filtering stations on the water supply can not cope with the level of pollution, harmful chlorine is added to the water for disinfection. Isn’t it better to remember the environment and not upset the sanitary protection zones?
Want to ask a question about the topic of an article? Please leave your comments in the block below. Here you can express your opinion or tell interesting facts about the sanitary protection zones.

 Water supply and sanitation rules: balance calculation + norms of water supply and consumption
Water supply and sanitation rules: balance calculation + norms of water supply and consumption  Water pressure reducer in the water supply system: purpose, device, regulation rules
Water pressure reducer in the water supply system: purpose, device, regulation rules  Water leakage sensor: how to choose and install a do-it-yourself anti-flood system
Water leakage sensor: how to choose and install a do-it-yourself anti-flood system  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
I would like to hope that this is the case, and that the theory does not diverge from practice. I did not see, however, the cemeteries' directions in the text - how far can they be from the place of direct water intake (through the well) and, say, from natural sources?
Or at what depth should a well be laid to eliminate water pollution? Is it possible to take water from a source located 2 kilometers from the cemetery, but under the mountain, 15 meters below its level?
For the remoteness of the source of drinking water from the cemetery, there is a recommendation of the World Health Organization (WHO) - 250 meters. For complacency, you can take the water for analysis, in the laboratory they will say for sure whether there are any obstacles to eating it.
Hello. I read that by the standards of 500 meters. I think 15 meters in height and 2 km of distance is enough for a well anyway.
In reality, in practice, everything looks a little different. I am the owner of my own cafe, located on the banks of the river, from the edge of which is literally 50 meters. The old owners left the toilet in place, it is located at a distance of about 10 meters from the edge of the river. The environmental prosecutor’s office came several times, did not make any comments. Of course, we ourselves demolished it and processed it, we live for ourselves and our children, it’s a pity for nature.
Unfortunately, this is only in words. At least with us. In the summer, people like to come to such places. One such thing is in our area. Of course, they know that they should drink this water, but all is useless. The supervisory authorities know about this, but do nothing.All hope is only for treatment facilities. Fortunately, the water after the fence goes through several stages before getting into the house. Although we still dug a well, and our family takes water from there. Of course, there is no harm from chlorinated water, but I see no benefit in this.
Hello. In my opinion, this is not just an inconvenience, but a serious problem that threatens your health and the health of your loved ones. It’s not worth putting up with it and looking for workarounds, file a complaint with the Federal Service for Supervision of Consumer Rights Protection and Human Welfare and higher authorities. A waste of time will not be waste, if sanitary standards are not observed, the problem should be eliminated, and this can be achieved quite realistically.
Poor water can lead to serious illness.
Hello. We want to buy a land plot in SNT, which is located in the water protection zone. Behind the site there is a seasonal groove with a width of about 15-20 m. The distance from the proposed construction site of the residential house to the groove is about 50 m. No one will pollute the security zone, on the contrary, we want to ennoble.
How to remove the “security zone” in a given place, are there any actions in terms of evidence that this zone will be kept clean?