How to arrange a filtering field for a septic tank: typical schemes + design rules
The suburban sewage system has some features that affect the sanitary condition of the entire land plot. The efficiency of filtering sewage depends on the design of autonomous treatment facilities.
As the last stage of purification, a filtration field for a septic tank is often used, which is necessary for the post-treatment of the liquid. We will figure out how to make the calculations and build the field with your own hands.
The content of the article:
Filtration field as part of the sewage system
Without the main part that performs the initial processing of sewage waste, that is, a septic tank, the filtration field is not used, since its purpose is the post-treatment of the already purified liquid. To make it clearer, consider how VOC works.
The cleaning process begins in the drive, where sewage is divided into different fractions: solid mineral waste precipitates, fat floats and forms a film, some of the substances remain in the water as a suspension. If air supply is not provided, the process of decomposition of some part of the waste occurs due to the vital activity of anaerobic bacteria.
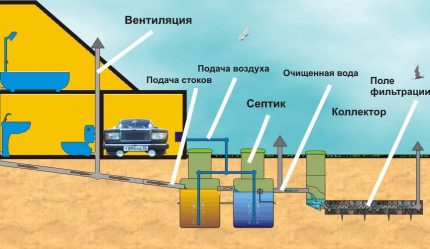
Further, the liquid flows into the next compartment, equipped with ventilation, where aerobic microorganisms are involved in the treatment of wastewater. They form activated sludge, which can later be used as fertilizer. The result of two-stage cleaning is a slightly turbid liquid that is not yet suitable for use.
It turns into industrial water or simply falls into the ground (ditch, pond) after undergoing post-treatment, which is carried out in the following way:
- on the filtration field;
- in the infiltrator;
- directly in the ground;
- in the filter well.
A typical multi-stage system, with dozens of options, is good because it effectively cleans sewer waste, minimizes cooperation with sewage trucks and maintains a clean ecology of the garden. And now we will dwell in more detail on the design of the filtration field.
Design features of PF
Filtration field - a relatively large area of land on which secondary purification of the liquid occurs.
This cleaning method is exclusively biological, natural in nature, and its value in cost savings (no need to buy additional devices or filters).

A typical device of a filtration field is a system of parallel-laid drainage pipes (drains) that extend from the collector and are placed at regular intervals into ditches with a thick sand and gravel layer.
Previously used asbestos-cement pipes, now there is a more reliable and economical option - plastic drains. A prerequisite is the presence of ventilation (vertically installed risers that provide oxygen access to the pipes).
The design of the system is aimed at ensuring that the liquid is evenly distributed over the allocated area and has the maximum degree of purification, therefore there are several important points:
- the distance between the drains - 1.5 m;
- the length of the drainage pipes is not more than 20 m;
- pipe diameter - 0.11 m;
- intervals between ventilation risers - not more than 4 m;
- risers height above ground level - at least 0.5 m.
To ensure the natural movement of the fluid, the pipes have a slope of 2 cm / m. Each drain is surrounded by a filtering “pillow” made of sand and pebbles (gravel, gravel), and is also protected from land by geo-cloth.

There is one condition, without which the installation of a septic tank with a filtration field is impractical. Special throughput properties of the soil are required, that is, on loose coarse and fine clastic soils that do not have a bond between the particles, a post-treatment system can be constructed, and dense clay soils, the particles of which are bonded in a consolidated manner, are not suitable for this.
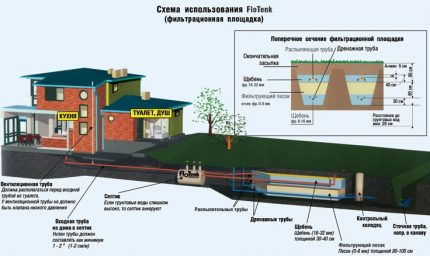
Typical device diagram
Whatever the overall dimensions of the filtration field, its design consists of the following parts:
- collector (control well, distribution well);
- a network of plastic drains (drainage pipes with holes);
- vent risers;
- filtering "pillow".
Traditionally, the drainage layer is poured from sand and gravel (gravel, pebbles). Geotextiles are used to protect drains. Sewer system with PF looks like this:
When constructing a filtration field with your own hands, it is not necessary to build a collector yourself - on sale you can find plastic sewage tanks of the required volume.
Often they do without a distribution well, connecting a septic tank and a pipe system directly - but this is convenient for small-sized PFs.
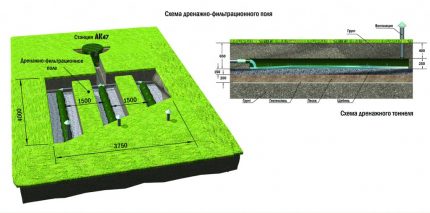
Sometimes, instead of PF, ready-made plastic devices are used - infiltrators.They help out when there is a shortage of free area, and the soil does not have layers of loam with sandy loam and has sufficient flow properties.
If desired, you can install several infiltrators connected by pipes in series.

Next, we consider how to properly design and install PF.
Filter Field Design
Designing is an obligatory stage before any serious construction. It is necessary to accurately markup, make calculations, knock estimates, prepare materials, take into account all the nuances.
A professionally designed project will save you from mistakes that are common to inexperienced beginners.
How to choose a scheme and choose a place?
The choice of scheme depends on three factors:
- type of septic tank;
- availability of free territory;
- cleaning requirements.
The fact is that the degree of purification in different septic tanks is different. For example, biological treatment plants (Topas, Astra, Eurobion) do not need a filtration field at all: water purified by 98% immediately enters the drainage trench or reservoir.
Septic tanks, constructed independently from concrete rings, bricks or tires, on the contrary, are not in themselves effective treatment facilities, therefore, the liquid leaving them requires additional post-treatment.
We recommend that you read the instructions for self-installation of various types of septic tanks:
- Septic tank made of concrete rings: device, schemes + step-by-step installation process
- How to build a drain pit of brick: options and methods of the device
- How to arrange a septic tank from tires with your own hands: step-by-step instructions
- How to make a two-chamber septic tank from concrete rings: a building instruction
As a rule, all sewerage elements are located in one line, that is, they are arranged alternately in the same direction from the house - first a septic tank, then a filtering field.
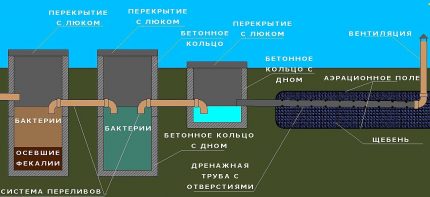
This means that when installing a septic tank, it must be borne in mind that part of the free territory behind it will be required for the construction of the PF (or, at a minimum, the installation of an infiltrator).
With a volume discharge of sewage, the principle works: the “branchier” and longer the drainage pipe network, the more effective the treatment.
It is worth initially paying attention to the specifics of the filtering field device:
Sizing and costing
In order to correctly calculate the size of the field, it is necessary to take into account the daily amount of runoff and soil composition. If you know exactly the features of the soil, you can push off from the volume of the septic tank.
The table will help in calculating the filtering field.
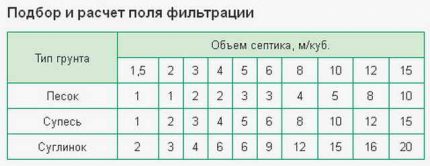
But these are approximate estimates. There are tables to more accurately determine the size of the "working" area. They are based on accounting for such qualities as the permeability of soils.
Here is a variant of such a table, which may be useful to owners of suburban areas with clay or sandy soils.
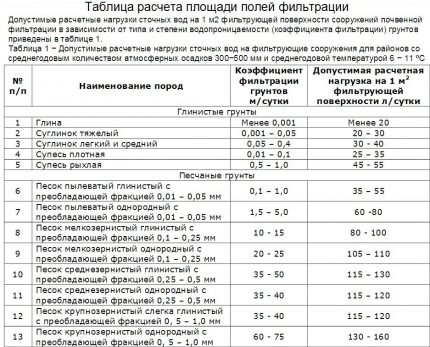
Peat indicators correspond to the data on dusty sand, and pebble and gravel have the maximum water permeability: their filtration coefficient is 100-200 m / day. For them, there are no permissible load standards, since such a loose composition is able to pass any volume of liquid.
Having determined the size of the field, you can calculate the number of pipes, ventilation risers (on average 1-2 for each drain), backfill (gravel, pebbles, gravel, sand), geotextiles, and then derive the approximate cost of all materials.
Installation Instructions PF
In addition to these materials, you will need a tool for excavating (shovels, buckets, wheelbarrows). The trenches intended for drainage are not as deep as the foundation pit for a septic tank, so construction equipment can be omitted. However, a few pairs of hands will speed up the process.
The cycle of work on the device of the filtering field is conditionally divided into a number of standard steps:
Stage No. 1 - the device of trenches
At the first stage, it is necessary to prepare a place for laying perforated pipes. There are two ways: you can dig one large pit, and then it will be more convenient to arrange drainage and assemble the structure from pipes, or you can make several trenches (according to the number of drains), which will significantly reduce the construction time.
The depth of the pit should be such that the liquid in the pipes does not freeze during the cold season, that is, the branched pipe system must be placed below the level of freezing of the soil. When installing the ditches, you need to remember about a slight bias that allows the fluid to move naturally - by gravity. The slope is 1.5-2 cm / meter pipe.

During the construction of PF adhere to strict geometry. The foundation pit, as a rule, has a square or rectangular shape, and the trenches are the same in length. Suppose you need a total pipe length of 60 m - you can make 4 branches of 15 m or 6 branches of 10 m. The length of one drain is the distance from the inlet pipe (or collector) to the last ventilation “fungus”.
The lower part of the trenches is covered with coarse sand (from 10 cm to 1 m), then 0.4-0.5 m with gravel (crushed stone, pebbles).If drainage drains are needed, they are placed in the ground under the sand, but not less than 1 m above the groundwater.
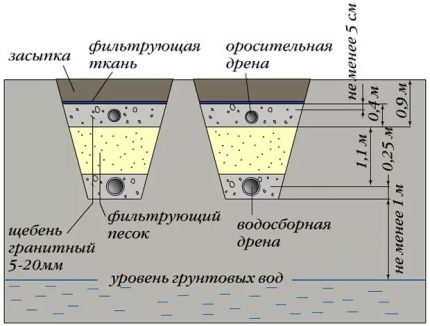
Drainage pipes lead to a storage tank located on the opposite side of the septic tank.
Stage number 2 - laying perforated pipes
On the prepared base lay drainage pipes made of plastic. The process itself is quite simple, the main thing is to choose the right pipes.
You can buy ready-made ones - smooth or corrugated, with perforation and a textile layer, or you can take ordinary sewers and drill holes in them with a drill. The recommended diameter of the drain is 100-110 mm.

Together with the pipes, it is necessary to purchase a set of fittings for connecting different elements. Need corners and tees. The process of laying drainage pipes is described in more detail in this material.
Stage 3 - ventilation device
The ventilation system is necessary for oxygen to enter the pipes, without which aerobic bacteria lose their viability. For ventilation risers, you can use ordinary gray sewer pipes, covering them with lids on top to protect them from debris.

The minimum height of ventilation pipes above the ground is 0.5 m. Usually they try to make them more accurate or decorate in order to maintain the aesthetic appeal of the garden landscape.
Stage 4 - backfill and further maintenance
After laying the perforated pipes, backfill is necessary. From the sides and from above, each branch is covered with gravel (the top layer is about 50 mm), then it is covered with a layer of geotextile and a finishing thick layer of soil. Geotextiles are used to prevent siltation of pipes. The ground above the drains must be compacted, but so as not to damage the pipes.
The filtering field is included in the work with the septic tank. Special actions for servicing drains are not provided. It is believed that the PF has been functioning smoothly for 6-7 years, after which it is necessary to disassemble the structure and replace the gravel filter. To increase the filter service life, geotextiles are also laid under a layer of gravel (crushed stone).
As a convenient installation alternative to the traditional filtration field, a modern version has been developed - a cartridge of infiltrators, the installation of which will be introduced to the following photo selection:
Are there other solutions?
Not everyone can use the filtration field as a way of post-treatment of sewage. What to do to those who own a clay land or have built a house in an area with a high level of groundwater?
Recommendations for the selection of septic tanks for high AHW are described. in this article.
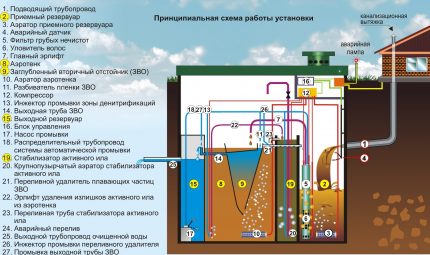
You can also create a sewer system with filter well, but for its installation a number of conditions are also necessary (for example, non-clay soil and the location of groundwater a meter below the conditional bottom of the well).
If you simply install a septic tank without additional treatment, insufficiently clarified and disinfected water will enter the soil and an unpleasant odor may appear.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Videos with useful information about the design of treatment facilities.
Septic Rostock with PF:
Theory of arrangement of a septic tank with filtering fields in pictures:
You can build a filtration field with your own hands, if you correctly perform the calculations and fulfill all the installation conditions. To determine the type of soil or choose a septic tank, you can contact specialists. A complete wastewater treatment system is a guarantee of environmental cleanliness, therefore, and comfort.
After studying our article, there were questions about arranging the filtering field, please write them in the comments box and we will try to respond to them promptly.

 Do-it-yourself monolithic concrete septic tank: schemes and rules for arranging a concrete septic tank
Do-it-yourself monolithic concrete septic tank: schemes and rules for arranging a concrete septic tank  The device of a septic tank: the principle of operation and basic organization schemes
The device of a septic tank: the principle of operation and basic organization schemes  Overview of the septic tank “Sunrise”: characteristics, model range, installation rules
Overview of the septic tank “Sunrise”: characteristics, model range, installation rules  Compressor for septic tank: principle of operation, how to choose + operating rules
Compressor for septic tank: principle of operation, how to choose + operating rules  Installation of the septic tank "Topas": DIY installation + service rules
Installation of the septic tank "Topas": DIY installation + service rules  Rules for servicing a septic tank in winter: cleaning and maintenance
Rules for servicing a septic tank in winter: cleaning and maintenance  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
It is best, of course, to have an engineer education in order to arrange a septic tank with soil post-treatment systems on its site. But what if there are no crusts and experience? How to make the project as convenient as possible for yourself, and even not offend the neighbors in the site !? Maybe it’s better to order a project with calculations in a specialized organization specializing in autonomous sewage systems or make a calculation according to this information? Maybe someone has already tried to do it on their own and will give practical advice.
Ideally, of course, attract specialists to do all the work: from design to installation of a septic tank and filtration fields. But the implementation of such a project exclusively by experts will cost a pretty penny, in simple terms. Therefore, many are guided by standard designs of septic tanks and filtration fields, adapting them to soy conditions.
The article is an excellent introduction, plus you can use the site search and find more suitable options for your site and home.
As for the comments above regarding the fact that geotextiles do not have a place in the filtering fields, I disagree with Alexander and Sergey here. This material does not directly contact the filtration fields, but is located behind layers of gravel and sand. Therefore, geotextiles will not become clogged with suspension, which excludes the propagation of harmful microorganisms in this material.
There is no place for geotextiles in the filtration field.
I agree. The pores of the geotextile will quickly become clogged with suspension and various microorganisms will begin to multiply in them. The process of colmatization will occur. Geotextiles are good material, but not for this purpose.