Floor boiler gas consumption: daily standard consumption + calculation example with formulas
When choosing boiler equipment for the heating system, a very worrying thought persistently drills my head - but how much will the unit be voracious? Surely the answer will appear when the heating is working, and the meter will begin to calculate the gas consumption of the floor boiler, regularly winding revolutions. However, it will be too late to lament if the amounts payable for gas do not please ...
Competent sales consultants, of course, answer most of the questions that arise, you can always turn to a competent engineer for help, but it's good to have at least basic knowledge yourself.
Learn from this article as much as possible about the methods for calculating energy consumption and factors that must be taken into account in the calculations. Below you will find not only boring formulas, but also examples. In the end, what can be done to reduce gas consumption.
The content of the article:
What affects gas flow?
Fuel consumption is determined, firstly, by power - the more powerful the boiler, the more intensively the gas is consumed. At the same time, it is difficult to influence this dependence from the outside.
Even if you muffle a 20-kilowatt device to a minimum, it will still consume more fuel than its less powerful 10-kilowatt counterpart, turned on at maximum.
Secondly, we take into account the type of boiler and the principle of its functioning:
- open or closed combustion chamber;
- convection or condensation;
- ordinary chimney or coaxial;
- one circuit or two circuits;
- the presence of automatic sensors.
In a closed chamber, fuel is burned more economically than in an open chamber. The efficiency of the condensing unit due to the built-in additional heat exchanger for condensing the vapors present in the combustion product is increased to 98-100% compared with 90-92% of the efficiency of the convection unit.
WITH coaxial chimney the value of efficiency also increases - cold air from the street is heated by a heated exhaust pipe.Due to the second circuit, there is, of course, an increase in gas consumption, but in this case, the gas boiler also serves not one, but two systems - heating and hot water supply.
Automatic sensors are a useful thing, they capture the external temperature and set the boiler to the optimal mode.
Thirdly, we look at the technical condition of the equipment and the quality of the gas itself. Scale and scale on the walls of the heat exchanger significantly reduce heat transfer, it is necessary to compensate for its lack by increasing power.
Alas, the gas may be water or other impurities, but instead of making claims to suppliers, we switch the power regulator by several divisions towards the maximum mark.

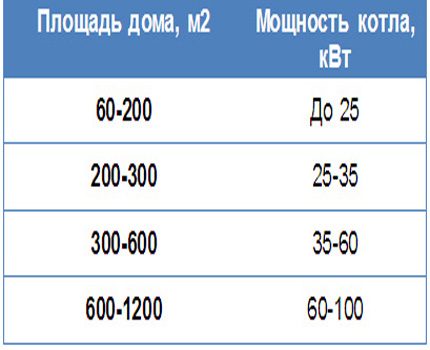
And, fourthly, the area of heated rooms, the natural decrease in heat, the duration of the heating season, weather features. The larger the area, the higher the ceilings, the more floors, the more fuel it will take to heat such a room.
We take into account some heat leakage through windows, doors, walls, roof. Year to year is not necessary, there are warm winters and crackling frosts - you can’t predict the weather, but cubic meters of gas used for heating depend on it directly.
Quick preliminary calculation
It’s pretty easy to figure out how much gas your gas boiler will consume.
We will be repelled either from the volume of the heated room, or from its area:
- in the first case, we use the standard of 30-40 W / cu. m;
- in the second case - 100 W / sq. m
The standards are taken taking into account the ceiling height in the room up to 3 meters. If you live in the southern regions, the numbers can be reduced by 20-25%, and for the north, on the contrary, increase one and a half times or twice. Those. take in the second case, for example, 75-80 W / sq.m or 200 W / sq.m.
Multiplying the relevant standard by volume or area, we get how many watts boiler power necessary for heating the room. Further, we proceed from the standard statement that modern gas equipment consumes 0.112 cubic meters of gas to generate 1 kW of thermal power.
We multiply again - this time the gas consumption standard (number 0.112) by the boiler power obtained in the previous multiplication (do not forget to convert watts to kW). We get the approximate gas flow per hour.
The boiler usually runs 15-16 hours a day. We consider the daily gas consumption. Well, when the daily consumption is already known, we easily determine the gas consumption for a month and for the entire heating season. The calculations are approximate, but sufficient to comprehend both the principle of calculation and the expected gas flow.

Example.
Let's say the area of the room is 100 m².
We calculate the boiler power: 100 W / sq. m * 100 m² = 10,000 W (or 10 kW).
We calculate the gas consumption per hour: 0.112 cubic meters. m * 10 kW = 1.12 cubic meters m / hour.
We calculate the gas consumption per day (16 hours of operation), per month (30 days), for the entire heating season (7 months):
1.12 cc m * 16 = 17.92 cubic meters m
17.92 cc m * 30 = 537.6 cubic meters m
537.6 cc m * 7 = 3763.2 cubic meters m
Note: you can immediately determine the monthly and seasonal power consumption of the boiler in kW / h, and then convert it to gas consumption.
10 kW * 24/3 * 2 * 30 = 4800 kW / hour - per month
0.112 cubic meters * 4800 kW / h = 537.6 cubic meters m
4800 kW / h * 7 = 33600 kW / h - per season
0.112 cubic meters * 33600 kW / h = 3763.2 cubic meters m
It remains to take the current gas tariff and translate the total into money. And if in the project the installation of a dual-circuit system that will not only heat the house, but also heat water for domestic needs, add to the power of the equipment and, accordingly, to the gas flow floor gas boilers heating another 25%.

The boiler is connected to the main gas pipeline
Let's analyze the calculation algorithm, which allows to accurately determine the consumption of blue fuel for the unit installed in a house or apartment with connection to centralized gas supply networks.
Calculation of gas flow in formulas
For a more accurate calculation, the power of the gas heating units is calculated by the formula:
Boiler power = Qt * K,
Where
Qt - planned heat loss, kW;
K - correction factor (from 1.15 to 1.2).
The planned heat loss (in W), in turn, is considered as follows:
Qt = S * Δt * k / R,
Where
S is the total area of the enclosing surfaces, sq. m;
∆t - difference of internal / external temperatures, ° C;
k is the dispersion coefficient;
R is the value of thermal resistance of the material, m2• ° C / W.
The value of the dispersion coefficient:
- wooden structure, metal construction (3.0 - 4.0);
- masonry in one brick, old windows and roofing (2.0 - 2.9);
- double brickwork, standard roof, doors, windows (1.1 - 1.9);
- walls, roof, floor with insulation, double-glazed windows (0.6 - 1.0).
The formula for calculating the maximum hourly gas consumption based on the received power:
Gas Volume = Qmax / (Qр * ŋ),
Where
Qmax - equipment power, kcal / hour;
QR - calorific value of natural gas (8000 kcal / m3);
ŋ - boiler efficiency.
In order to determine the consumption of gaseous fuel, you just need to multiply the data, some of which must be taken from the boiler data sheet of your boiler, and some from building directories published on the Internet.
Using formulas as an example
Suppose we have a building with a total area of 100 sq m. The building is 5 m high, 10 m wide, 10 m long, twelve windows 1.5 x 1.4 m in size. Indoor / outdoor temperature: 20 ° C / - 15 ° C.
We consider the area of the enclosing surfaces:
- Paul 10 * 10 = 100 sq. m
- Roofing: 10 * 10 = 100 sq. m
- Windows: 1.5 * 1.4 * 12 pcs. = 25.2 sq. m
- Walls: (10 + 10 + 10 + 10) * 5 = 200 sq. m
Beyond the windows: 200 - 25.2 = 174.8 square meters. m
The value of thermal resistance of materials (formula):
R = d / λ, where
d - material thickness, m
λ is the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the material, W / [m • ° C].
We calculate R:
- For the floor (concrete screed 8 cm + mineral wool 150 kg / m3 x 10 cm) R (gender) = 0.08 / 1.75 + 0.1 / 0.037 = 0.14 + 2.7 = 2.84 (m2• ° C / W)
- For the roof (sandwich panel from mineral wool 12 cm) R (roof) = 0.12 / 0.037 = 3.24 (m2• ° C / W)
- For windows (double-glazed windows) R (windows) = 0.49 (m2• ° C / W)
- For walls (sandwich panels from mineral wool 12 cm) R (walls) = 0.12 / 0.037 = 3.24 (m2• ° C / W)
The values of thermal conductivity coefficients for different materials were written out from the reference book.

Now let's calculate the heat loss.
Q (floor) = 100 m2 * 20 ° C * 1 / 2.84 (m2* K) / W = 704.2 W = 0.8 kW
Q (roof) = 100 m2 * 35 ° C * 1 / 3.24 (m2* K) / W = 1080.25 W = 8.0 kW
Q (windows) = 25.2 m2 * 35 ° C * 1 / 0.49 (m2* K) / W = 1800 W = 6.3 kW
Q (walls) = 174.8 m2 * 35 ° C * 1 / 3.24 (m2* K) / W = 1888.3 W = 5.5 kW
Heat losses of building envelopes:
Q (total) = 704.2 + 1080.25 + 1800 + 1888.3 = 5472.75 W / h
You can also add heat loss to ventilation. To heat 1 m3 air from –15 ° С to + 20 ° С requires 15.5 W of thermal energy. A person consumes about 9 liters of air per minute (0.54 cubic meters per hour).
Suppose there are 6 people in our house. They need 0.54 * 6 = 3.24 cubic meters. m of air per hour. We consider the heat loss for ventilation: 15.5 * 3.24 = 50.22 watts.
And the total heat loss: 5472.75 W / h + 50.22 W = 5522.97 W = 5.53 kW.
Having spent heat engineering calculation, we first calculate the boiler capacity, and then the gas flow per hour in a gas boiler in cubic meters:
Boiler power = 5.53 * 1.2 = 6.64 kW (round up to 7 kW).
To use the formula for calculating gas consumption, we translate the resulting power indicator from kilowatts to kilocalories: 7 kW = 6018.9 kcal. And we take the boiler efficiency = 92% (manufacturers of modern gas floor-standing boilers declare this indicator within 92 - 98%).
Maximum hourly gas consumption = 6018.9 / (8000 * 0.92) = 0.82 m3/ h
The boiler is powered by a gas tank or cylinder
The formula Gas volume = Qmax / (Qр * ŋ) is suitable for determining the need for various fuels, incl. and liquefied gas. We take from the previous example the obtained boiler power indicator - 7 kW. If 0.82 m is required for such a boiler3/ h of natural gas, how much propane-butane will be required then?

To calculate, you need to know what its calorific value is. Beats calorific value (this is the calorific value) of liquefied hydrocarbons in megajoules - 46.8 MJ / kg or 25.3 MJ / l. In kilowatt hours - 13.0 kW * h / kg and 7.0 kW * h / l, respectively.
We leave the efficiency of the gas boiler equal to 92% and calculate the hourly gas demand:
Gas volume = 7 / (13 * 0.92) = 0.59 kg / h
One liter of liquefied gas weighs 0.54 kg, per hour the boiler will burn 0.59 / 0.54 = 1.1 l of propane-butane. Now we consider how much liquefied gas is consumed by a gas boiler per day and per month.
If the boiler will work for 16 hours, then per day - 17.6 liters, per month (30 days) - 528 liters. A typical 50 liter bottle contains about 42 liters of gas. It turns out that on our house with an area of 100 m2 528/42 = 13 cylinders per month will be required.

Installing a gas tank is much more convenient than replacing empty cylinders with full ones. It is enough to refuel the gas holder for the entire heating season 2-3 times.
How to minimize gas consumption
In order to give less money for gas consumed by the floor boiler and not to round your eyes in amazement at the sight of the next payment, follow these recommendations.
First, pay attention to condensing boiler - the most economical today. Its efficiency reaches 98-100% and higher. The price is high, but it will pay off and will soon pay off. For each model, read customer reviews.
If you do not need water heating, take a single-circuit boiler. In a dual-circuit system, 20–25% are additionally not needed for the gas demand.
Secondly, conscientiously insulate not only the walls, but also the roof, the floor with the foundation and basement. Install energy-saving double-glazed windows on windows. Use a thermal imager. All points of cold should be found and eliminated. At the entrance to the house (corridor, hall, hallway) build a warm floor.
Third, use timers and sensors. The temperature you set for heating the air in the room will be automatically adjusted - for example, the batteries will heat up by night and cool slightly during the day.
If you decide to leave the house for a week, you can set the heating system for the period of absence to a minimum with the return to normal operation at the time of arrival. Once a year, inspection is necessary with the cleaning of blockages and scale from the heat exchanger, traces of soot from the burner, soot from the chimney.

Fourth, install a buffer storage in the heating system, in which there will be a certain supply of coolant (hot water). Due to this “thermos” feeding the battery for a while with the boiler turned off, it is possible to save up to 20% of fuel.
Fifth, do not ignore proper ventilation. A constantly ajar window sash will take out more heat to the street than a window wide open for five minutes.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video below is about gas consumption for floor standing boilers.
Heating with liquefied gas (propane). Fuel consumption, personal experience:
Gas consumption of a floor gas boiler HOT SPOT 12 kW (user review):
Gas is a popular energy resource, the problem of saving both the resource itself and the means to pay for it does not lose its relevance.
Reasonable gas consumption is a good economical boiler, and professional installation of the heating system, and the fight against heat loss. The high efficiency of the unit is a guarantee of long-term savings on gas costs.
If you doubt the accuracy of independent calculations, ask for help from a qualified specialist who knows the smallest nuances of formulas. His authoritative opinion will save you from mistakes both at the stage of designing the heating system and during its operation.

 How to reduce the power of a gas boiler: the best options to reduce gas consumption by the boiler
How to reduce the power of a gas boiler: the best options to reduce gas consumption by the boiler  Do-it-yourself installation of a floor gas boiler: technical standards and algorithm of work
Do-it-yourself installation of a floor gas boiler: technical standards and algorithm of work  How to increase the efficiency of a gas boiler with your own hands: the best ways to increase the efficiency of the boiler
How to increase the efficiency of a gas boiler with your own hands: the best ways to increase the efficiency of the boiler  Gas boiler power consumption: how much electricity is needed to operate standard equipment
Gas boiler power consumption: how much electricity is needed to operate standard equipment  Beretta gas boiler malfunctions: how to decrypt the code and eliminate the malfunction
Beretta gas boiler malfunctions: how to decrypt the code and eliminate the malfunction  Installing a solid fuel boiler: do-it-yourself nuances of installing a boiler
Installing a solid fuel boiler: do-it-yourself nuances of installing a boiler  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
I’m thinking about moving the house to gas heating. Many people write that this is much more profitable, but almost anywhere else is how much “much”, with numbers. Useful stuff.
Hello Leonid. And how do you heat a house now: a solid fuel boiler, a stove, or using electricity? I ask this question in order to understand with what to nevertheless compare, to carry out calculations. It would be nice if you also indicated the area of your house, it is also very important to provide you with accurate data.
Let's compare heating with gas and electricity. I’ll give you a ready-made example for an apartment of 36 m², and there you yourself will make the necessary calculations, substituting your data.
There is an apartment of 36 m² in which electric convectors are installed in each room for heating. The monthly energy consumption for heating alone was 750 kW.
As for a similar apartment in area, it has a gas non-condensing single-circuit gas boiler with a coaxial chimney. The maximum power of the equipment is 7 kW. For a month, such a boiler consumes 190 m3 of gas.
Now calculations, tariffs of the Moscow region:
1) The apartment is electrically heated - 3.89 x 750 = 2917.5 rubles .;
2) The apartment is on gas heating - 5.7 x 190 = 1083 rubles.
As you can see, heating with gas comes out almost three times cheaper. I will also attach a table on the cost of materials, equipment and installation.