A furnace with a water circuit for heating a house: features of furnace heating + selection of the best option
Firewood and coal remain in many regions the most affordable types of fuel, with the help of which private cottages are heated. However, stove heating is chosen not only because of the cheapness and general availability of energy, but also because of the low cost of its arrangement.
Moreover, in addition to many advantages, a stove with a water circuit for heating a house has a lot of minuses. Not always this option is optimal. Let's try to understand the nuances of such a heating system.
The content of the article:
Features of heating based on the stove
Stove heating is the norm for Russian villages, the reliability and practicality of which has been tested for centuries. And today in many village houses there are stoves with a stove for cooking and a hearth for baking bread.
Some of them are equipped with a water circuit of the heating system, while others are not. But the landlords are not in a hurry to throw them out and change them to modern boilers. A more trouble-free and trouble-free method of heating has not yet been invented.
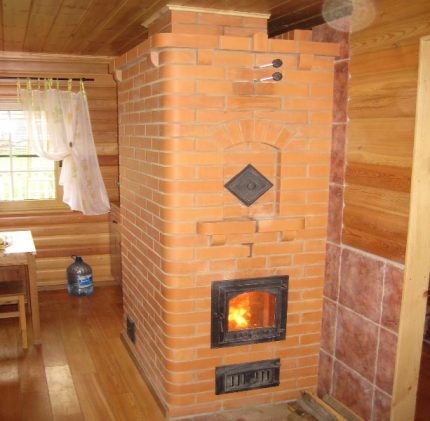

As fuel in such village stoves, they burn:
- coal;
- peat;
- firewood;
- briquettes (eurowood).
There is no fundamental difference between these types of fuel in terms of the arrangement of the stove inside and the wiring of the water heating system in a private house. Some of them give more heat, while others burn out longer. But the design of the furnace and the layout of the piping with the coolant in the rooms are the same in all cases.
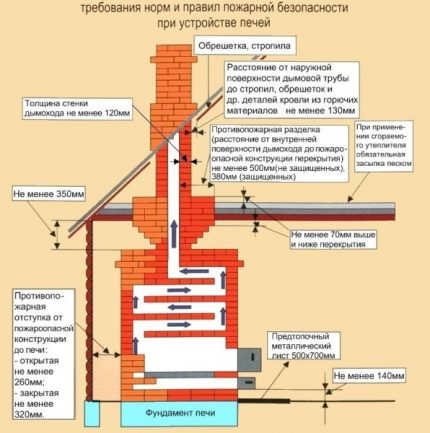
Among the advantages of stove heating are:
- lack of dependence on the availability of electricity in the network;
- the relatively low cost of the heating system;
- low cost of solid fuel and the possibility of using its different types;
- extreme ease of use;
- long-term heat transfer (for brick structures);
- universality - suitable for heating and cooking at the same time.
If a private house cannot be connected to the main gas, then a wood stove will be the best choice for heating it.
The only exception is when coal or firewood is not available in a particular area. But such an option in Russia is the exception rather than the norm.
Also, from the shortcomings of furnace heating, it should be mentioned:
- long warm-up of the system before the start of heat transfer;
- loss of mass of usable space in the house due to the massiveness of the furnace;
- heavy weight of brick kiln construction;
- low efficiency due to the departure of a significant amount of heat into the pipe;
- high fire hazard with improper use.
Brick heating and cooking stove for a private house with water heating, depending on the design and number of rows can weigh from 1.5 to 10 tons. Plus, the weight of the pipe is added here.
The foundation for such a mass requires a powerful and expensive cost, which can also be called a minus of the heating systems under consideration.
Heater water heating device
The furnace for the heating system under consideration should ideally be calculated and built simultaneously with the house. If a residential building has already been erected, then it will be difficult to install a brick construction in it. And often this is completely impossible because of the need to make a solid foundation and rebuild the rafter system.

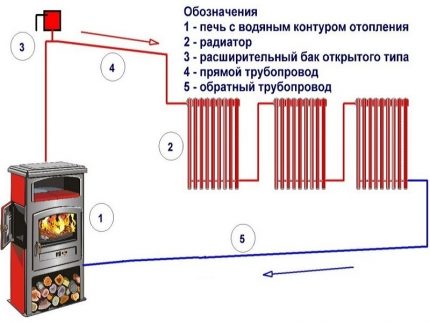
Furnace-based water heating consists of:
- directly stove (metal or brick);
- a heat exchanger in or around the furnace furnace, as well as in the form of a coil around the chimney;
- home circuits with coolant and an expansion tank in the attic.
Also, in some cases, this heating system is supplemented by a circulation pump and a hydraulic accumulator. However, such an extended version is used extremely rarely, as it requires uninterrupted power supply and leads to an increase in the cost of the entire circuit.
And the main plus of water heating stoves is the cheapness of the device. It is not worth complementing it with expensive and prone to breakage elements.
Circuit water circulation
The water heating system in houses is built with natural (gravitational) or forced circulation of the coolant. If it is done on the basis of a wood stove, it is best to give preference to the first option.
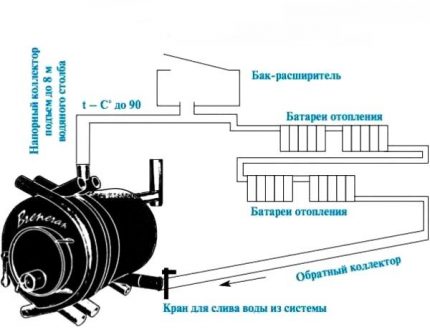
It is recommended to equip water heating stoves only in one-story houses with an area of up to 150 m2. In this case, it can be made gravitational without additional pumps.
If it is necessary to heat a cottage in a couple or more floors, then it is better to implement this on the basis of a more powerful boiler. The furnace for such buildings will have to be built simply huge, which is expensive to implement. And the amount of fuel will have to be poured into it every time considerable. And doing so is highly discouraged because of the increased risk of fires.
The classic stove heating system with natural circulation of water consists of:
- heat exchanger as part of the stove;
- contour from a metal pipeline;
- radiators (usually replaced with thick pipes in rooms);
- expansion tank.
If it is decided to do water heating in a country house with your own hands, then it is better to design it according to this scheme. Installation and calculation of this option is easier to perform than with forced water movement.

If the boiler is automated and the water is constantly heated as needed, then the wood-burning stove is heated once or twice a day. It is at these moments that the coolant in the furnace is heated to give off heat in the rooms. After chasing it with a pump through the pipes of the circuit is pointless. Anyway, nothing in a cold firebox will warm up.
When opting for a wood or charcoal stove, owners of private homes usually expect to get an autonomous heating system. If you put in it pumping equipment that requires power from the mains for operation, then it will be difficult to talk about autonomy.
Oven - brick or metal
A brick stove heats up longer, but also longer gives off heat to the space around it. The analogue of steel, on the contrary, quickly heats up and also cools quickly after burning fuel. This problem is partially solved due to the presence of large volumes of coolant in the water circuit.
However, the more water you have to store in the system, the more expensive it comes from materials.

A steel furnace for water heating with a power of 5-15 kW - without fuel and water, this is a structure weighing 100-300 kg. Such a potbelly stove can be safely put on reinforced lags. The furnace foundations must be poured when the stove weighs more than 700-800 kg. Now, if it is brick, then concrete work is definitely not enough.
Compared to metal, a brick stove weighs more, costs more and is more difficult to install. However, it has higher efficiency and less risk of freezing the circuit with a pipe rupture due to the formation of ice inside. If everything is decided to be done thoroughly for yourself and permanent residence, then it is recommended to stop the choice on the brick option.
Pipes - stainless steel or metal plastic
If the heating system is built on the basis of a hot water boiler, then it can be strapped not only with steel pipes, but also with plastic and polypropylene pipes. However, if the wood-burning stove will heat the water, then the circuit with the coolant from it should be created only from stainless steel.

Metalloplastik is designed to work with a coolant heated to 90–95 ° С. For a short time, it is able to transfer and heating to 110–120 ° С. At the same time, the automation of boilers and boilers initially does not allow heating of water to such degrees. For warm floors, it heats up to 30–45 ° С, and for batteries up to 60–65 ° С.
However, in the case of a wood stove, temperatures under a hundred are not just possible, but far from uncommon. Risking and playing Russian roulette, tying this oven using plastic pipes, is not recommended. It is best to give more reliable stainless steel.
In addition, the branch pipes leaving the furnace from the coil for connecting the pipes of the circuit will definitely heat up to very high temperatures. Less than half a meter separates them from open fire. It is dangerous to connect any plastic pipes to them because of the risk of the latter melting.
Heat dissipation - radiators or register
Heat is supplied from the stove to the heating circuit in portions for several hours, while firewood or coal burn in the furnace. If there is little water in the heating system, the house will quickly stand up. Therefore, in villages such heating is usually made of thick steel pipes, and not on the basis of radiators more familiar to citizens.The heating register for wood stoves is just perfect.

A stainless steel pipe with a diameter of 80–120 mm laid around the house is a heating register consisting of a supply from the furnace and a return to it. In the room farthest from the furnace, these lines are connected together, and in the rest of the rooms they are laid in the form of two pipelines along the external walls.
The register does not look as aesthetically pleasing as the radiator. But the first option is much cheaper and easier to do independently, than the second. For its implementation it is only necessary to have experience in handling the welding machine.
The heat transfer area for such a circuit is calculated by multiplying the number of PIs by the diameter and length of the pipe. Plus, in the calculations it is necessary to take into account the heat pressure in the supply and return, as well as the distance between the pipelines vertically.
However, often, such calculations are not performed, but a pipe with a diameter of 80–100 mm is taken and laid along the perimeter of the entire residential building with a loop in the back room. At the same time, the heat transfer is adjusted “by eye” and experimentally as a result of applying one or another volume of fuel to the furnace.
No wonder the contours from the registers, coupled with water furnaces, are so common. They do not even need to be counted, just take a suitable pipe and weld.
We select a heat exchanger for the furnace
The heat exchanger in the stove can be made of copper, steel or cast iron. The copper option is immediately better to exclude because of the high price. Soldering such a device on its own is extremely problematic.
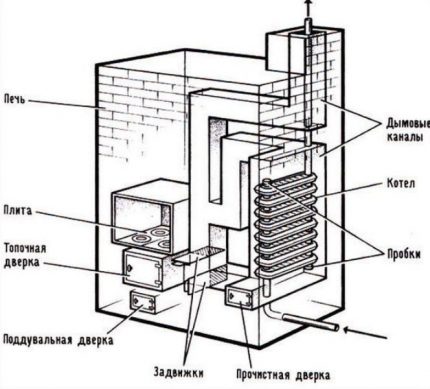
Cast iron outperforms steel in technical parameters. However, to make a heat exchanger for a wood stove with it yourself is problematic. You can only take an old battery for this. But here it must be taken into account that the seal between its sections will burn out in the furnace. And this is a direct way to the loss of tightness and the release of water into the combustion chamber.
If the heat exchanger is decided to be made of a cast-iron battery, then it is best to take MS-110-300 or MS-90-300 for this model. They are small and quietly fit in a firebox. The surface area of heating for each rib will be of the order of 0.14–0.16 m2.
Based on these numbers, we can estimate how many sections are needed for a particular circuit. For every 10 squares of the house, you need 1 kW, which will be approximately 0.1 m2 cast iron heat exchanger heating area.

Another point of using a cast-iron battery as a heat exchanger is the difficulty of cleaning it from soot from the inside of the furnace. From time to time, the combustion chamber needs to be cleaned, and the relief ribs “cast-iron” will greatly interfere with this.
The most optimal variant of the heat exchanger is steel in the form of:
- a coil of several tubes;
- shirts made of sheet steel.
They are made of low-carbon steel St10 ... St20 with a thickness of 4-5 mm. If you take the tube, then with a diameter of 30-50 mm.
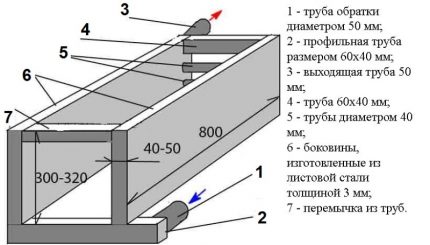
The tubular version in terms of heat transfer is more efficient, but it is also more laborious to manufacture.
To calculate the heat exchanger, use the formula:
Qy = K * (Tcp-Tk)
Where:
- K - heat transfer coefficient of the material (for low-carbon steels 15–20 is taken, and for gray cast iron - 50);
- Tcp - the average temperature of the heating medium in the furnace (Tmax + Tmin) / 2;
- Tk - average temperature of the heat carrier (T supply + Return) / 2.
If firewood is burned in the stove, then Tcp = (700 + 300) / 2 = 500 ° С and Tk = (80 + 60) / 2 = 70 ° С. As a result, Qy = 15 * (500-70) = 6450 kcal / hour. That is, about 7.5 kW / h will come out per square meter of the surface of the heat exchanger facing the fire.
For coal, the calculations are as follows - Tcp = (1000 + 600) / 2 = 800 ° С and Tk = 70 ° С. Qy = 15 * (800-70) = 10 950 kcal / hour = 12 734 W / hour. A square meter of the surface of the heat exchanger will produce about 12.7 kW / h.
Next, we divide the power necessary for heating a particular house by a calculated figure, depending on plans for the use of a particular type of fuel.
For example, for a cottage in 150 m2 need about 15 kW. If it will be heated with wood, then a heat exchanger with a heat exchange area of 15 / 7.5 = 2 m is required2. This is the surface that faces the flame and heats up.
If a tubular coil is selected, then its length is calculated by the formula:
S = 2 * 3.14 * D * L
Where:
S - estimated area;
D - tube diameter;
L - desired length.
The parameters of a steel sheet shirt are even easier to calculate; it usually consists of two rectangles on the sides of the combustion chamber.
Choosing the best option
It will be difficult to put a massive brick oven in an already built house. In this case, water heating is best organized on the basis of a metal potbelly stove, which is allowed to be placed on a reinforced wooden floor without pouring the foundation.
However, if it is possible to make the foundation as it should, then preference should be given to a more reliable brick kiln design.

Installing a circulation pump and / or accumulator in the heating circuit in question is a waste of money and zero additional benefit. They will only complicate the installation of the system. And when you turn off the light, these devices will create problems at all. Whereas the heating option without them, with problems in the mains, will continue to calmly heat the house.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Choosing the shape of a heat exchanger in a wood stove:
Overview of the brick furnace for water heating in the cottage:
The device of the heating and cooking stove made of brick with analysis of the design order:
It is difficult to call water heating based on a wood stove ideal and highly efficient. But this option of heating a private house is the most reliable, as well as cheap and easy to implement. It is not necessary to supplement such a circuit with a circulation pump and automation. They work from the mains and make the entire system offline, leveling it one of the main advantages.

 Brick stove for the home: guidelines for choosing the optimal type and examples of routines for independent masters
Brick stove for the home: guidelines for choosing the optimal type and examples of routines for independent masters  How the Russian stove works: design features and an overview of popular types of Russian stoves
How the Russian stove works: design features and an overview of popular types of Russian stoves  Wood stoves for heating a private house: rating of popular models + benchmarks for the buyer
Wood stoves for heating a private house: rating of popular models + benchmarks for the buyer  How to make stove heating in a private house with air or water circuits
How to make stove heating in a private house with air or water circuits  Russian bath stove: TOP-10 and guidelines for choosing the best model of a sauna stove
Russian bath stove: TOP-10 and guidelines for choosing the best model of a sauna stove  Gas bath stove: TOP-10 rating of sauna stoves for Russian and Finnish baths
Gas bath stove: TOP-10 rating of sauna stoves for Russian and Finnish baths  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
If I have a two-story house 6 × 8, is it possible to make a furnace with a water circuit, but without a circulation pump? It is clear that it is better with a pump - more uniform heating of the batteries, etc., but I would like to save.
Yes, that’s quite real. In my country house such a system has been functioning for more than five years. Furnace, expansion tank in the attic, four batteries (two on the first, two on the second floor), one-pipe system, metal-plastic, filled with antifreeze. If you have a house, then you can even fill the water, it will be even better. Both in terms of fluidity and heat capacity. So it’s quite possible to do without a pump.
Forgot to add that in such an oven, as a rule, a water boiler is also built in. So she solves two problems at once.