Insulation for the floor in a wooden house: materials for thermal insulation + advice on choosing insulation
Good thermal insulation provides a reduction in heat loss by 20–40%, and in some cases more. At the same time, a properly selected insulation for the floor in a wooden house not only reduces heating costs, but also directly affects the microclimate in the rooms. You need to know how to pick it up. Do you agree?
You will learn all about the thermal insulation options acceptable for arranging a wooden floor from our article. We will tell you what criteria influence the choice and how to take them into account. Our recommendations will help to correctly equip the lower floor in a structure of timber or logs.
The content of the article:
Thermal insulation of floors in wooden houses
There is no universal heat-insulating material for all cases. To insulate each structure in a private house (foundation, load-bearing walls, ceiling), you should choose your best option.
And even in the same cottage, floors in different rooms often have to be insulated with various thermal insulation. The requirements for the thermal conductivity of the floors in them often vary.
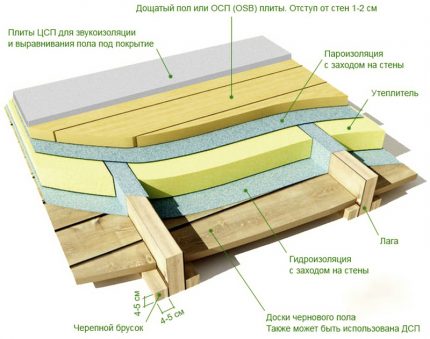
It should distinguish between floors in a wooden house between:
- basement and ground floor;
- residential floors.
In the second case, insulation is usually not produced. Above and below are heated rooms with approximately the same microclimate parameters. It is not necessary to distinguish between them with additional thermal insulation.
But the floor above the basement will have to be insulated in a wooden house in any situation. And it doesn’t matter - the basement is used somehow or the wind is walking from below between the supports of the pile foundation.
Only the insulation option and its thickness will change.But thermal insulation will have to be laid anyway, otherwise heat loss through an uninsulated ceiling will be quite noticeable.
The floor in the wooden house on the ground floor is mounted:
- on the ground;
- on lags or on a coupler;
- on the beams.
The first option is usually used with a low strip foundation. The second - with a foundation basis in the form of a monolithic plate. And the third - in all other situations.
And in each case, the insulation should be selected individually. For example, it is impossible to put mineral wool on the ground, it will quickly dampen and deteriorate with such installation.

The main reason for the damage to the “cake” of the insulated floor on the ground floor above the basement is excess humidity. The heat insulator and the construction of such a floor in a private wooden house are affected by moisture from the ground and condensate formed due to the temperature difference, as well as water spilled during cleaning.
To protect the insulation, polymer waterproofing films are used. But if the floor insulation system is designed without ventilation, then films that interfere with the free drainage of condensate can even do harm. When the insulation gets wet, it will lose its insulating characteristics, and it will become an excellent breeding ground for the fungus.
Possible materials for insulation
There are an incredible amount of heaters on the domestic market. But for floor insulation devices in a low-rise house of logs or timber, not all of them are suitable.
On the one hand, it is necessary to take into account the compatibility of the selected heat-insulating material and the wood from which the residential building was built. And on the other hand, do not forget about the environmental friendliness of all used building materials.

The main advantage of a cottage made of wood is environmental friendliness. Insulate the floor in it with synthetics should only be a last resort.
Among the whole variety of heaters for a wooden house, the following are recommended:
- stone wool;
- cellulose ecowool;
- expanded clay;
- sawdust;
- fibrolite.
Also, in certain situations, you can use extruded polystyrene foam. But it is best to do without this material, preferring more environmentally friendly insulation from the above list.
Option # 1 - rock mineral wool
Mineral wool is made from fiberglass, slag from blast furnaces and rocks. In wooden houses, it is worth using the last of these types - cotton insulation from basalt fibers. It is the safest for humans and environmentally friendly - it has virtually no synthetic binders.
Stone wool has:
- low thermal conductivity of 0.034-0.04 W / (m * K);
- excellent vapor permeability;
- good noise reduction.
Basalt insulation is not subject to decay, does not burn and quietly withstands heating up to 700 °With no loss of performance.

Option # 2 - cellulose ecowool
This material is environmentally friendly, resistant to mold and incombustibility. In the manufacture of ecowool, cellulose (paper waste) is impregnated with antiseptics and flame retardants.
Fire and fungi are not afraid of her. At the same time, this heat-insulating material can absorb moisture up to 15% of its own weight.
Also, ecowool cannot be mounted near the bases of the main chimneys, foundations of stoves and fireplaces. Under the influence of high temperatures, cellulose will smolder. Due to the abundance of flame retardants, it will not light up.But the gradual smoldering of paper will inevitably thin out the insulation layer and lead to an increase in heat loss.

Option # 3 - sawdust
If you want to get the cleanest home from an environmental point of view, then insulate the floor in a wooden cottage can be sawdust. They are poured with a rammed layer with a thickness of 10–40 cm between the logs, which gives a sufficiently high-quality insulation without any chemistry.
Sawdust is the cheapest of the existing insulation. They are tested by time and long practice. However, this material, like any wood, is flammable. Whether it is worth adding a flammable fuel in a wooden house to a potential fire is an open question.

Option # 4 - expanded clay
The second line in terms of cheapness after sawdust can be deservedly given to expanded clay. This insulation is made of fired clay. It is in the form of granules with many air-filled voids inside.
Of the minuses of expanded clay, only its high hygroscopicity is worth mentioning. If the expanded clay granule is split, then it will absorb water like a sponge. Without an underlying waterproofing in the form of a thick polyethylene film, such a heater can not be poured.

Option # 5 - expanded polystyrene
This material is marketed by foam and slab. Penoplex (EPSP). If you take it, then for floor insulation only the second option is extruded polystyrene foam. It is denser and absorbs much less moisture.
Expanded polystyrene and wood are often called antagonists. The first does not allow moisture to pass, and the second, on the contrary, absorbs it well and then gives it to the air.
However, with proper installation, EPSS and foam can be combined with wooden structures. It is only necessary to leave a gap for ventilation between the polystyrene foam insulation and wood so that condensation does not accumulate there.

Option # 6 - fiberboard
Fiberboard slabs are made from wood chips and cement. This is an excellent insulation, which so far is not too widespread in Russia.
Fibrolite is characterized by rather high hygroscopicity. It dries quickly, which, however, is only possible with good ventilation. It is non-combustible, harmless to humans, not subject to decay and a breathable heat insulator. It is impossible to let it get wet and freeze.

Choosing the best insulation
If you need the most environmentally friendly material, then the choice should be stopped on sawdust, expanded clay or fiberboard. Basalt cotton wool is also in this regard ready to give a serious head start to expanded polystyrene.

The floors in the bathroom, toilet and kitchen are also recommended to be insulated with extruded polystyrene foam. These rooms are characterized by high humidity.The more moisture-resistant insulation will be used in them or under them, the longer this material will last.
However, if ventilation in the subfloor is well-organized, then ordinary mineral wool can also be used.
For comparison, the table below shows the main characteristics of insulation:
| Material | Thermal conductivity, W / (m * K) | Vapor permeability, mg / (m * h * Pa) |
| Stone mineral wool | 0,034—0,039 | 0,3–0,35 |
| Ecowool | 0,038–0,041 | 0,3–0,67 |
| Expanded clay | 0,1–0,18 | 0,25–0,27 |
| Sawdust | 0,05–0,08 | 0,3–0,8 |
| Fibrolite (with a density of 300–500 kg / m3) | 0,07–0,1 | 0,18–0,3 |
| Eps | 0,029–0,032 | 0,003–0,005 |
Choosing what is better to insulate the floor in a wooden house, you should compare the available options for:
- thermal conductivity;
- vapor permeability;
- flammability;
- environmental friendliness;
- durability (resistance to moisture and fungus);
- the price.
The lower the thermal conductivity of the insulation, the better. Vapor permeability affects the ability to breathe and conduct condensate out.
Expanded clay and sawdust are considered the cheapest heat insulators. More expensive are fiberboard, ecowool and EPS.
With the schemes of the device of the system of insulation of floors, built on logs, will introduce next article. We recommend reading very useful information.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video # 1. The nuances of warming a wooden floor in a house made of timber:
Video # 2. Thermal insulation of the subfloor on the logs with mineral wool:
Video # 3. Analysis of possible errors during floor insulation:
When choosing a heater for the floor, you should focus on the features of the insulated room, the type of foundation and the available budget.
In most cases, the best option is environmentally friendly and non-combustible basalt mineral wool. But if the floor is equipped on the ground, it is better to use expanded clay. And if there is high humidity in the basement, then polystyrene foam should be preferred.
Tell us about how you insulated the floor in a wooden building with your own hands. Share which insulation option you prefer and why. Please leave comments in the block below, ask questions and post photos on the topic of the article.

 Insulation for walls of the house outside: an overview of options + tips for choosing an external insulation
Insulation for walls of the house outside: an overview of options + tips for choosing an external insulation  Floor insulation by logs: materials for thermal insulation + insulation schemes
Floor insulation by logs: materials for thermal insulation + insulation schemes  Floor insulation in a wooden house: work procedure + popular heaters
Floor insulation in a wooden house: work procedure + popular heaters  Insulation of the ceiling in a private wooden house inside and out: choosing the best material and the nuances of installation
Insulation of the ceiling in a private wooden house inside and out: choosing the best material and the nuances of installation  Warming of a wooden floor: popular insulation technologies + expert advice
Warming of a wooden floor: popular insulation technologies + expert advice  Extruded polystyrene foam as insulation: material pros and cons + application tips
Extruded polystyrene foam as insulation: material pros and cons + application tips  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
We bought a small cottage near Novosibirsk, he’s about 20 years old, we are wintering the first winter. At the first frost, the floor becomes icy. How people lived in this house is unclear. I collect information about heaters and in general about what methods of insulation exist. One question torments me - and rodents will not settle in these warm and cozy heaters? From everything that I learned today, I am inclined to use basalt wool, most likely, it is better suited in our case.
Just in basalt wool, rodents practically do not settle. There are exceptions, but rarely.