Amount of air for burning natural gas: formulas and calculation examples
The efficiency of all kinds of gas equipment depends on the quality of the combustion process. What directly affects the amount of air for burning natural gas, which is not difficult to calculate. Why not take care of the fuel efficiency and increase the efficiency of the equipment by doing the necessary calculations on your own, right?
But how to do it right and where to get data for calculations? To understand this topic, let's look at the theory of air consumption for gas combustion in our article, get acquainted with the simplest formulas for calculating the required air volume. And also talk about the practical benefits of these calculations.
The content of the article:
Theory of air consumption for gas combustion
The procedure for obtaining thermal energy directly affects the duration of operation, the frequency of work on maintenance of gas equipment. It should be understood that an optimal gas-air mixture is the key to safety. Let’s talk in more detail about the air consumption for gas combustion.
To burn one methane molecule, which is the main component of natural gas, exactly 2 oxygen molecules are required. If translated into understandable volumes, then in order to oxidize a cubic meter of the specified fuel, you will have to use 2 times more oxygen.
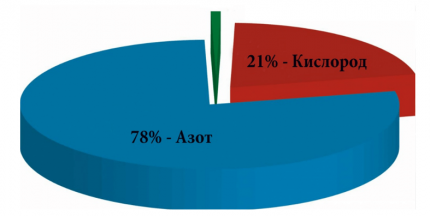
But in real conditions, everything is more complicated. Since air is used as an oxidizing agent to carry out the chemical-physical combustion process, it contains only one fifth of the oxygen necessary to maintain combustion. And, to be precise, then 20.93% - it is such a percentage that is customarily used for all kinds of technical calculations. That is, 9.52 times more air is needed.
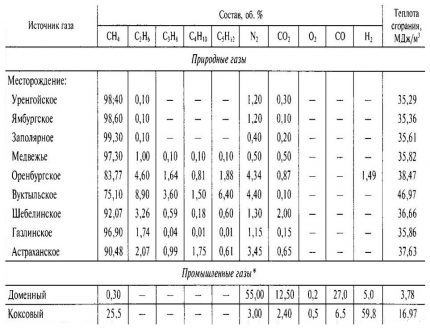
It will turn out to find out the specified number by following 2 steps:
- Division 100/21. This operation allows you to find out that there is 4.76 times more air in any volume than oxygen.
- Multiplying 4.76 by 2, which equals 9.52 - exactly how many times more air will be needed to burn any amount of natural gas.
But there is one important caveat: the calculated amount of air necessary for efficient gas combustion is a theoretical flow rate. But in practice it will be needed. The reason is that the calculation was carried out for ideal conditions, but in reality there are almost always a number of factors that make significant adjustments.
These include:
- composition and quality of reagents (air, gas);
- type of equipment used to supply energy;
- equipment status;
- method of supplying gas, air, as well as a number of other points.
If you need special accuracy, then the above features can sometimes be taken into account. For example, the exact composition of the gas can be found out at the nearest gas service representative. But, when special accuracy is not needed, then the obtained value of 9.52 is simply multiplied by the so-called excess air ratio. The value of which usually lies in the range 1.1 - 1.4.
When the calculation should be as accurate as possible, then the amount of actually used air should be divided by its theoretical flow rate. But in most cases it’s easier to use the average value excess air ratio. The value of which should be multiplied by 9.52 and as a result it will turn out to find out the exact amount of air consumed, necessary to ensure the gas combustion procedure.
So if it is equal to:
- 1,1 - air mass will need 10.472 times more;
- 1,4 - air will need to be used 13,328 times more.
That is, up to 13.328 m³ of air will be needed to burn each cubic meter of energy carrier.
Formulas and calculation examples
The necessary value in each case can be obtained using a special formula or averaged indicators. We will talk about these methods in more detail.
Method # 1 - calculation using the formula
Which states that the hourly volume of air (Vh) required for combustion will be equal to:
Vh = 1.1 x Khuts x vtx vg / hx (273 + t) / 273,
Where:
- TOhuts - coefficient of excess air;
- Vt - theoretically necessary amount of air;
- Vg / h- hourly gas consumption by equipment;
- t - temperature values in the room where the gas equipment is located.
The gas flow rate required for the calculations is indicated in the passport of any gas device.
That is, if this value is 10, and:
- room temperature, for example, 18 ° C;
- the coefficient of excess air is 1.1.
Then we perform the above mathematical operations, namely:
1.1 x 1.1 x 9.52 x 10 x (273 + 18) / 273 = 122.1
As a result, it turns out that in this particular case, for burning gas, 122.1 m³ of air will be needed every hour.

Method # 2 - calculation using averaged data
If there is no desire to carry out such a calculation of the combustion air of the required amount of gas, then you can listen to the recommendations of many manufacturers, specialists.
Which say that the process will be effective if at least 1.6 m³ of air is supplied hourly for every kilowatt of power.

That is, the calculation will turn out in just one action.Why taken from the passport the value of the power of the gas device should be multiplied by the specified 1.6. As a result, you get the amount of air needed for efficient combustion.
For example, if the power of the gas boiler is 40 kW, then this value should be multiplied by 1.6:
40 x 1.6 = 64
It will turn out 64 m³ of air, which will need to be supplied to the gas device hourly.
The practical value of calculating air flow
Skills for performing such calculations may be needed to increase efficiency gas equipment, as well as eliminating the causes of its malfunction.
Prevention of breakdowns and lowering equipment efficiency
For example, knowledge of the optimal amount of oxidizing agent will be needed when the surface of the chimney (internal), structural elements of the equipment (heat exchangers, burners, etc.) quickly covered with soot depositsother combustion products.
If the elimination of pollution does not give the desired effect, like any other measures (adjustment, replacement of parts, units of units). This indicates the presence of the so-called under-energy source, which occurs due to insufficient air.

And also knowledge of the required air flow will be required in the following situations:
- Gas overrun detected, which can not be eliminated with the help of adjustments, other manipulations. Since the cause may be a mechanical underburning. That is, a process in which too much air is supplied, which also leads to incomplete combustion of gas.
- Frequent color change of "blue" fuel during burning is noticed - for example, orange, white, red, yellow. These are more complicated cases than the previous ones, since the cause can be both an excess of air and its insufficient amount.
- Unstable gas burning process. For example, if not all working openings of the burner, burners of a gas boiler, etc. are involved, and cleaning the listed structural elements does not lead to improvement, since in such situations it is necessary to supply air an order of magnitude more.
Despite the presence of various reasons, the calculation is the same, according to the method described above.
The benefits of calculations when equipping a boiler room
Calculations of the amount of air necessary for effective gas oxidation are necessary in cases of furnishing a furnace, installation, replacement of gas equipment and other similar ones.

And the calculations are performed, but the situation in each indicated case is complicated by the fact that in order to obtain all the necessary data, it is necessary to perform a series of calculations.
Which calculations include:
- total air consumption - air must be supplied to the room with gas equipment not only for the combustion process, but also for its ventilation (in SNiP II-35-76 it is clearly stated that in the rooms used as furnaces 3 volumes of air must be replaced hourly);
- sections of the exhaust duct;
- section (s) of the hole (s) of the input channels;
- natural traction in the provided exhaust duct;
- actual air velocity in sections of future ducts;
- pressure loss on all kinds of local resistance;
- the size of the window laid in a room with gas equipment.
In addition to proper arrangement boiler room ventilation, you may need to perform a number of procedures, for example, performing aerodynamic calculation.

Then all the information received should become the basis of the project replacements, installation of equipment, redevelopment, which is submitted to the local gas service for approval. Where, when errors are detected, the document can be sent back to the originator.
That is, a set of procedures for calculating all the necessary values is quite complicated. Therefore, in the case of installation, replacement, transfer of equipment, only a few will cope with the task. Most property owners will find it easier to turn to specialists for help. Which will not only perform the necessary mathematical steps, but also adapt the calculations to the requirements of the legislation on the arrangement of furnace, ventilation systems, smoke exhaust, and all others. Which are set out in SNiP II-35-76, as well as in SNiP 2.04.08-87 and a number of other less demanded specialized documents.
If in a particular case the project does not need to be drawn up, then the calculations made by the specialist will eliminate the threat to the life and health of the owner of the gas equipment, its relatives and people living nearby.
In addition, they will allow avoiding actions interpreted by law as unauthorized connection to any gas pipelines. For which Art. 7.19 Administrative Code of the Russian Federation provides for sanctions in the form of a fine, the amount of which is 10-15 thousand rubles. For example, this can happen if the owner of the premises, after making calculations, makes changes to the design of the heating system.

After calculations, it is not worth making a rash decision to replace gas equipment, especially with different power. If this happened, then it is worth notifying the gas service representatives about the actions taken. Which will help to avoid fines.
And also it is not necessary to implement the theoretical calculations made at the cost of violating the rules and norms set forth in SNiP II-35-76, which regulates the arrangement of premises intended for the use of gas equipment. Since according to Art. 9.23 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, even for the smallest violations will have to pay 1-2 thousand rubles.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video material attached below will allow you to identify a lack of air during gas combustion without any calculations, that is, visually.
You can calculate the amount of air required for efficient combustion of any volume of gas in minutes. And owners of real estate equipped with gas equipment should keep this in mind. Since at a critical moment when the boiler or any other device will not work properly, the ability to calculate the amount of air needed for efficient combustion will help to identify and fix the problem. Which, in addition, will increase security.
Would you like to supplement the above material with useful information and recommendations? Or do you still have questions about the calculation? Ask them in the comment block, write your comments, take part in the discussion.

 Technical conditions for gas connection: the procedure for obtaining the necessary documentation
Technical conditions for gas connection: the procedure for obtaining the necessary documentation  Suspension of gas supply: reasons for disconnecting from gas supply in an apartment building
Suspension of gas supply: reasons for disconnecting from gas supply in an apartment building  How to refuse gas in an apartment and a private house: legal aspects
How to refuse gas in an apartment and a private house: legal aspects  Benefits for connecting gas to large families: specifics and rules for registration of preferential conditions
Benefits for connecting gas to large families: specifics and rules for registration of preferential conditions  Gas connection in the apartment after disconnection for non-payment: procedure and legal subtleties
Gas connection in the apartment after disconnection for non-payment: procedure and legal subtleties  Re-signing of the gas contract: necessary documents and legal details
Re-signing of the gas contract: necessary documents and legal details  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements