Temperature sensors for heating: purpose, types, installation instructions
When operating heating devices, it is required to control the degree of heating of the coolant, as well as the air in the room. Temperature sensors for heating help to remove and transmit information, information from which can be read visually or immediately sent to the controller.
We offer to understand how temperature sensors work, what types of control devices exist, and what parameters should be considered when choosing a device. In addition, we have prepared step-by-step instructions that will help you independently install the temperature sensor on the heating radiator.
The content of the article:
The principle of operation of the thermal sensor
You can control the heating system by a variety of methods, including:
- automatic devices for timely power supply;
- safety monitoring units;
- mixing units.
For the correct operation of all these groups, temperature sensors are needed that give signals about the functioning of the devices. Monitoring the readings of these devices allows you to identify malfunctions in the system in time and take corrective measures.

The temperature sensor can be used as a separate device, for example, to control the room temperature, or be an inextricable part of a complex device, for example, a heating boiler.
The basis of such devices used in automated control is the principle of converting temperature indicators into an electrical signal. Due to this, the measurement results can be quickly transmitted over the network in the form of a digital code, which guarantees high speed, sensitivity and accuracy of measurement.
At the same time, various devices for measuring the heating stage can have design features that affect a number of parameters: work in a certain environment, transmission method, visualization method, and others.
Types of temperature measuring devices
Thermal devices can be classified according to a number of important criteria, including the method of transmitting information, the location and installation conditions, as well as the reading algorithm.
By the method of information transfer
According to the method used to transmit information, the sensors are divided into two large categories:
- wire devices;
- wireless sensors.
Initially, all such devices were equipped with wires through which temperature sensors were connected to the control unit, transmitting information to it. Although these devices are now supplanted by wireless counterparts, they are still often used in simple circuits.
In addition, wired sensors are more accurate and reliable.

Nowadays, wireless devices, which most often transmit information using a transmitter and a receiver of radio waves, have gained distribution. Such devices can be mounted almost everywhere, including a separate room or open air.
Important characteristics of such temperature sensors are:
- the presence of a battery;
- measurement error;
- signal transmission range.
Wireless / wired devices can completely replace each other, however, there are some features in their operation.
By location and method of placement
At the place of attachment, such devices are divided into the following varieties:
- invoices attached to the heating circuit;
- submersible in contact with the coolant;
- indoor located in a residential or office space;
- external, which are located outside.
In some units, several types of sensors can be used simultaneously for temperature control.
According to the reading mechanism
By the method of demonstrating information, devices can be:
- bimetallic;
- alcohol.
In the first embodiment, it is assumed to use two plates made of different metals, as well as a dial indicator. As the temperature rises, one of the elements deforms, creating pressure on the arrow. The readings of such devices are of good accuracy, but their inertness is a big minus.

Sensors whose operation is based on the use of alcohol are almost completely devoid of this drawback. In this case, an alcohol-containing solution is expanded into a hermetically sealed flask, which expands when heated. The design is quite elementary, reliable, but not very convenient for observation.
Different types of temperature sensors
To take temperature readings, devices having a different principle of operation are used. Among the most popular are the devices listed below.
Thermocouples: accurate removal - difficulty in interpreting
Such a device consists of two wires welded together, made of various metals. The temperature difference that arises between the hot and cold ends serves as a source of electric current of 40-60 μV (the indicator depends on the material of the thermocouple).

A thermocouple is considered a high-precision temperature sensor, however, it is quite difficult to take accurate readings from it.To do this, you need to know the electromotive force (EMF) using the temperature difference of the device.
In order for the result to be correct, it is important to compensate for the temperature of the cold junction, using, for example, a hardware method in which the second thermocouple is placed in an environment of a predetermined temperature.
The software compensation method involves placing another temperature sensor in the isocamera together with cold junctions, which allows you to control the temperature with a given accuracy.
Certain difficulties are caused by the process of taking data from a thermocouple due to its nonlinearity. For the accuracy of the indications, GOST R 8.585-2001 introduced polynomial coefficients, which allow translating the EMF to temperature, as well as performing inverse operations.
Another problem is that the readings are taken in microvolts, for the conversion of which it is impossible to use widely available digital devices. To use a thermocouple in structures, it is necessary to provide accurate, multi-bit transducers having a minimum noise level.
Thermistors: easy and simple
It is much easier to measure temperature using thermistors, which are based on the principle of dependence of the resistance of materials on ambient temperature. Such devices, for example, made of platinum, have such important advantages as high accuracy and linearity.

An important characteristic of a resistor is the base resistance at a certain temperature. According to GOST 21342.7-76, this indicator is measured at 0 ° C. It is recommended that a number of resistance values (Ohms), as well as Tcop - temperature coefficient.
T indicatorcop calculated by the formula:
Tcop = (Re - R0c) / (Te - T0c) * 1 / R0c,
Where:
- Re - resistance at current temperature;
- R0c - resistance at 0 ° C;
- Te - current temperature;
- T0c - 0 ° C.
The GOST also shows the temperature coefficients provided for various measuring devices made of copper, nickel, platinum, and also indicates the polynomial coefficients used to calculate the temperature based on current resistance indicators.
Resistance can be measured by connecting the device to the current source circuit and measuring the differential voltage. Indicators can be controlled using integrated circuits, the analog output of which is equal to the supplied voltage.
Thermal sensors with similar devices can be safely connected to an analog-to-digital converter, digitizing it with an eight or ten-bit ADC.
Digital sensor for simultaneous measurements
Digital temperature sensors have also been widely used, for example, the DS18B20 model, whose operation is carried out using a chip with three outputs. Thanks to this device, it is possible to take temperature readings simultaneously from several sensors operating in parallel, while the error is only 0.5° C.
Among the other advantages of this device can also be noted a wide range of operating temperatures (-55 + 125 ° C). The main drawback is the slow operation: for the most accurate calculations, the device requires at least 750 ms.
Contactless Irometers (Thermal Imagers)
The action of these proximity sensors is based on the fixation of thermal radiation from the bodies. To characterize this phenomenon, the amount of energy released per unit time from a unit surface is used, which is per unit of the wavelength range.
A similar criterion reflecting the intensity of monochromatic radiation is called spectral luminosity.
The following types of pyrometers are available:
- radiation;
- luminance (optical);
- color.
Radiation pyrometers allow measurements within 20-25000 ° C, however, to determine the temperature, it is important to take into account the coefficient of incompleteness of radiation, the actual value of which depends on the physical condition of the body, its chemical composition and other factors.
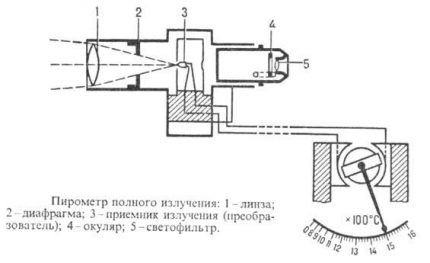
Brightness (optical) pyrometers designed to measure temperatures of 500-4000 ° C. They provide high accuracy of measurements, however, they can distort readings due to the possible absorption of radiation from bodies by an intermediate medium through which observations are made.
Color pyrometerswhose actions are based on determining the radiation intensity at two wavelengths - preferably in the red or blue section of the spectrum, are used for measurements in the range of 800 to 0 ° C.
Their main advantage is that the incompleteness of the radiation does not affect the measurement errors. In addition, the indicators are independent of the distance to the object.
Quartz temperature transducers (piezoelectric)
To take temperature readings within -80 + 250 ° C, you can use quartz transducers (piezoelectric elements), the principle of which is based on the frequency dependence of quartz on heating. In this case, the position of the cut along the crystalline axes affects the function of the converter.

Piezoelectric sensors are distinguished by fine sensitivity, high resolution, they are able to work reliably for a long time. Such devices are widely used in the manufacture of digital thermometers and are considered one of the most promising devices for future technologies.
Noise (acoustic) temperature sensors
The functioning of such devices is provided by removing the acoustic potential difference depending on the temperature of the resistor.
The method of measurement by such sensors is quite simple: it is necessary to compare the noise produced by two similar elements, one of which is at a known temperature, and the second at a determined temperature.
Acoustic temperature sensors are suitable for measuring the interval -270 - +1100°C. Moreover, the complexity of the process lies in the too low noise level: the sounds emitted by the amplifier sometimes drown it out.
NQR temperature sensors
The essence of the operation of nuclear quadrupole resonance thermometers is the action of the field gradient, which form the crystal lattice and the moment of the nucleus - an indicator caused by the deviation of the charge from the symmetry of the sphere.
As a result of this phenomenon, a procession of nuclei arises: its frequency depends on the gradient of the lattice field. The temperature also affects the magnitude of this indicator: its rise causes a drop in the NQR frequency.
The main element of such sensors is an ampoule with a substance that is placed in an inductance winding connected to the generator circuit.
The advantage of the devices is unlimited measurement duration, reliability and stable operation. The disadvantage is the non-linearity of the measurements, which makes it necessary to use the conversion function.
Semiconductor Devices
A category of devices that operates on the basis of changes in the characteristics of the pn junction caused by temperature. The voltage at the transistor is always proportional to the effect of temperature, which makes it easy to calculate this factor.
The advantages of such devices are high data accuracy, low cost, linearity of characteristics over the entire measurement range. The installation of such devices is conveniently done directly on a semiconductor substrate, making them excellent for microelectronics.
Volumetric Temperature Sensors
Such devices are based on the well-known principle of expansion and contraction of substances observed during heating or cooling. Such sensors are quite practical. They can be used to determine temperatures between -60 - + 400 ° С.

It is important to remember that measurements of liquids with such devices are limited by the boiling and freezing temperatures, and of gases by their transition to a liquid state. The measurement error caused by the influence of the environment for these devices is quite small: it varies between 1-5%.
Selection of temperature sensors
When choosing such devices, factors such as:
- temperature range in which measurements are taken;
- the need and ability to immerse the sensor in an object or environment;
- measurement conditions: for taking indicators in an aggressive environment, it is better to prefer a non-contact option or a model placed in an anti-corrosion case;
- the life of the device before calibration or replacement - some types of devices (for example, thermistors) fail quickly enough;
- technical data: resolution, voltage, signal feed rate, error;
- output signal magnitude.
In some cases, the material of the device case is also important, and when used indoors - the size and design.
DIY installation guidelines
Such appliances are widely used for various purposes: they are equipped with radiators, heating boilers and other household appliances.
Before starting installation, you should carefully read the instructions: it indicates not only the installation features (for example, dimensions for connection to the nozzle), but also the operating rules, as well as the temperature limits for which the measuring device is suitable.
It is also necessary to take into account the size of the sleeve, which can vary between 120-160 mm.
Consider the two most common cases of mounting a temperature sensor.
Connecting the device to the radiator
It is not necessary to equip all heating appliances with a thermostat. According to the regulations, sensors mounted on the batteryif its total capacity exceeds 50% of the heat production by similar systems. If there are two heaters in the room, then the thermostat is installed only on one having a higher power indicator.

The valve of the device is installed on the supply pipe in the place of connection of the radiator to the heating network. If it is impossible to insert it into an existing circuit, it is necessary to dismantle the supply lead, which can cause some difficulties.
To carry out this manipulation, it is necessary to use a tool for cutting pipes, while the installation of a thermal head is easily done without special equipment. As soon as the sensor is mounted, it is enough to combine the marks made on the case and the device, after which the head is fixed by smooth pressing of the hand.
Mounting an air temperature sensor
Such a device is installed in the coldest living room without drafts (in the hall, kitchen or boiler room, its installation is undesirable, as it can cause disturbances in the system).
When choosing a place, you need to make sure that sunlight does not fall on the device, there should not be any heating appliances (heaters, radiators, pipes) nearby.

Connecting the device is carried out according to the instructions that are in the technical passport, using the terminals or cable that are included in the kit.
Temperature monitoring required thermal sensor in the “warm floor” may be located deep in the concrete screed. In this case, a corrugated pipe having one closed end and a sloping bend can be used for protection.
The latter feature allows you to remove a broken device and replace it with a new one if necessary.
Installation of the device is as follows:
- A recess is arranged in the wall for mounting the attachment.
- The front part is removed from the temperature sensor, after which the device is installed on the prepared site.
- Next, the heating cable is connected to the contacts, while the sensors are connected to the terminals.
The final step is to connect the power cable and install the front panel in its place.
The thermostat connection diagram for the heating boiler is described in detail in this article.
If the device, for the functionality of which requires the internal connection of sensors, has a complex design, it is better to contact specialists.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
The video below details how to install thermal appliances on a boiler:
Does the installation of the sensors on the supply and return pipes differ:
Temperature sensors are widely used both in various industries and for domestic purposes. A wide range of such devices, which are based on different operating principles, allows you to choose the best option for solving a particular problem.
In homes and apartments, such devices are most often used to maintain a comfortable temperature in the premises, as well as adjust heating systems - batteries, underfloor heating.
Have something to supplement, or have questions about choosing and installing a temperature sensor? You can leave comments on the publication, participate in discussions and share your own experience using such devices. The contact form is located in the lower block.

 Distribution comb of the heating system: purpose, principle of operation, connection rules
Distribution comb of the heating system: purpose, principle of operation, connection rules  Thermostat for heating boiler: operating principle, types, connection diagrams
Thermostat for heating boiler: operating principle, types, connection diagrams  How to hide heating pipes: we disassemble the types of boxes and decorative linings
How to hide heating pipes: we disassemble the types of boxes and decorative linings  Polypropylene pipes for heating: types, selection criteria, marking
Polypropylene pipes for heating: types, selection criteria, marking  Voltage stabilizer for a gas heating boiler: types, selection criteria + overview of popular models
Voltage stabilizer for a gas heating boiler: types, selection criteria + overview of popular models  Types of heating systems for a private house: a comparative overview + the pros and cons of each type
Types of heating systems for a private house: a comparative overview + the pros and cons of each type  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
I did not spend much on sensors, with my heating system they need a few. I have a solid fuel boiler and a hot water buffer.
I bought with a dial, bimetallic, in my opinion, the German company of VATs, there is a scale up to 120C, and it can be clearly seen from anywhere. On the boiler itself it’s also worth it from the manufacturer, I just added it to the feed, to the return, and in several places to the input / output from the buffer.
I am quite happy with their accuracy and visibility, the dial is large. And about inertia: so 1-2 minutes is normal, I think, in time.