How to warm a well for the winter: an overview of the best ways + material selection
A water well is most often used as a source of water for autonomous water supply. Its operation is carried out seasonally or year-round. If you plan to take water in the winter, you need to think about how to insulate the well for the winter and avoid problems with water interruption, equipment breakdown and pipe rupture.
We will describe how the thermal insulation of an independent water source is made, eliminating the formation of ice plugs in the system. Here you will learn how to insulate the working shaft and the water lines extending from it. Our tips will help determine the best method and material for insulation.
The article thoroughly analyzed the basic rules and subtleties of organizing a system for protecting independent water supply from freezing. For a clear perception of the topic attached diagrams, photo illustrations, video guides.
The content of the article:
Features of well protection from cold
An illiterate arrangement of water intake often creates obstacles for the normal operation of the source. Errors and shortcomings are especially acute in the winter.
The operation of the well, which is not protected from freezing by reliable thermal insulation, in frosts makes it difficult to form ice on the water mirror and the formation of ice plugs in the pipeline.
As a result, pumping equipment and the system as a whole works with increased load. A large cork can deform or even break the HDPE pipes, of which the outer water pipe branches are most often constructed.
Traffic jams and ice crust appear in the well if the water intake is not working at full capacity. Those. if there are interruptions in operation sufficient to crystallize water. Even if the owners of the autonomous water supply do not count on such pauses in the functionality, means of their prevention in the form of a warming system device must be carried out.
Activities for water system insulation conducted from the entry point into the house to a depth that is 20-30 cm below the level of seasonal freezing of the soil. This value can be found in collections on building climatology of the joint venture under the number 131.13330.2012 and in SNiP under the number 23-02-99.
The freezing depth is determined in accordance with the conditions of the region and the type of soil covered by the freezing zone. Its significance is obtained empirically based on long-term observations.
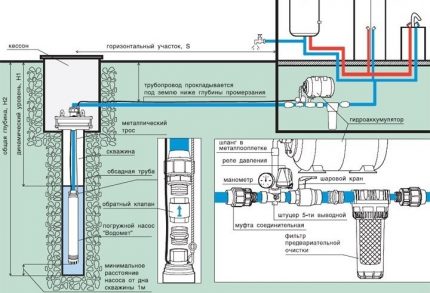
If the water supply is introduced into the house through the basement of an insulated basement, it is also necessary to insulate the branch before entering the heated room. The use of materials for warming objects located in the ground has its own specifics.
Insulators should have the following properties:
- Do not absorb water or have a protective waterproof cover. If the water is absorbed into the insulation and then freezes, then with a high probability due to an increase in the volume of water upon transition to ice, the insulation layer will be destroyed.
- Do not lose your properties under soil pressure. The pressure of the mass of the earth from above or its movement can crush the insulation and increase its thermal conductivity.
- Not be of interest or succumb to insects and rodents.
The last point is very important, because in summer mice can pull the insulation along the nests, and in winter dig holes in it to get to the warm pipes. All this will lead to direct access to the cold water supply elements.

Sometimes, to protect the well and the water supply system from the cold, it is enough to perform procedures that do not require special knowledge about the principles of warming the underground water supply system. Water that is fed into the system from a depth has a positive temperature (usually between 7 and 13 degrees Celsius).
If there is a risk of water freezing, it is necessary to adjust the mode of operation of the system so that water is supplied in small portions, but as often as possible.The constant circulation of groundwater, the temperature of which, by definition, is above 0 ° C, will prevent icing.
To insulate the head and pipes during not very cold winters in the southern regions of Russia or when the water supply is deep, it can be done without any frills with sawdust or straw. To do this, it is necessary to dig a hole near the head and a ditch along the water pipe, cover them with dry sawdust or straw and again bury the hole.
This procedure should be carried out every year in the fall, so that sawdust and straw do not have time to rot by winter. To eliminate freezing for a longer time or if the proposed methods do not guarantee a positive result, a different approach to solving the problem is needed.

Freeze tip protection
A caisson for a well is a reservoir buried in the ground located above the wellhead. It is necessary for convenient access to the main elements of the water intake system for the purpose of repair and regular maintenance.
Inside the insulated caisson mounted accumulatorpumping equipment and filters to remove them from the house and remove noise. If the equipment is placed in a heated room, the caisson is not satisfied, but an adapter is installed.
Both a well with and without a caisson must be insulated so that the direct contact of the elements of the water supply system with frozen rocks is excluded over the entire thickness of freezing soils.
The basic principles of insulation caisson
Even if the head of the well is located below the freezing depth of the soil, the bulk of the caisson is above this mark. If its walls have significant thermal conductivity, then negative temperatures can drop to the tip and the water in the system will freeze much lower, as indicated by Construction Climatology.
In geometry caissons for wells can be cylindrical or rectangular, this does not affect the method of insulation. From the point of view of insulation costs, objects of a cylindrical shape are more advantageous, and from the position of ease of installation of the material supplied in the format of rigid plates, it is more simple to insulate objects of a rectangular shape.
According to the material, the caissons can be concrete, metal and plastic, although concrete structures are rarely used now because of the complexity of their installation and the fragility of concrete when exposed to moisture.

Insulation of the caisson inside is relevant if its body is tight due to the properties of the material or the implementation of reliable waterproofing. In this case, there is no need to protect the insulation from moisture.
In addition, soil shifts or other external influences will not affect the integrity of the insulation layer. As a rule, with internal insulation, products based on polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam are used.
The caisson is insulated from the outside to preserve the internal space or if bulk materials are used. Outside, it is desirable to insulate plastic structures, protecting them from severe frosts, in which plastic becomes brittle.
External insulation is carried out by any materials, however, it is necessary to take into account the possible movement of the soil, the effects of water and the risk of damage to the insulation layer by insects and rodents.

Since heat losses during any insulation of the well will still occur, their compensation is necessary due to the influx of heat.It will happen anyway due to the positive temperature of the water in the pipes passing through the caisson and the generation of heat by the working devices.
If there is a chance that there may not be enough insulation, then you can install an elementary heating element complete with a temperature sensor.
Since the inner space of the caisson is small, with normal insulation, it is sufficient to use an ordinary incandescent lamp with a power of 40-60 watts or a heating wire 3-5 meters long as a heating element.
Installation of casing for the head
If during the design of water supply the caisson was not provided, and the head is above the level of soil freezing, then it can be insulated with the help of an additional casing pipe, the diameter of which is greater than the diameter of the stationary casing by two thicknesses of insulation.
To set an additional length casing pipe it is necessary to dig a hole around the head to the depth of freezing of the soil plus 0.3 m and insulate the head. An additional pipe must be installed on top, and the space between the casing should be filled with glass wool or mineral wool.
It is undesirable to fill the gap between the two casing pipes with sprayed thermal insulation options due to the inability to control the uniformity of the application of the insulation layer.
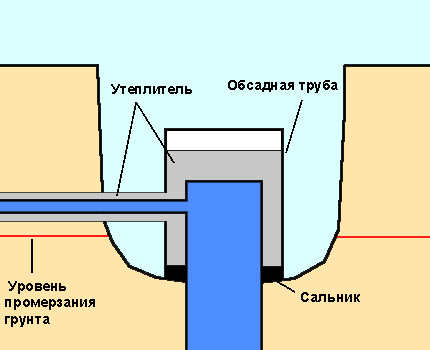
The pipe should be metal, since in the cold plastic becomes more fragile and soil movements can damage it.
It is also necessary to ensure that there is no water in the space between the casing and the tip. Mineral wool loses its insulating properties when absorbed, and the polystyrene shell can be deformed when ice forms.
To prevent getting wet before laying the insulation in the gap between the casing, it is necessary to install an oil seal. The outer size of the stuffing box should be equal to the diameter of the additional casing pipe, and the inner - the diameter of the main casing.
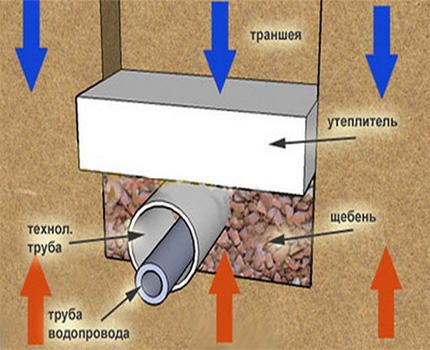
Underground pipe insulation
Warming of the water supply branch leading to the house may not be necessary if it is placed below the level of freezing of the soil. However, the deeper the water supply system is located, the more complicated is its installation and repair.
In this case, the insulation of pipes can be cheaper thermal insulation material and be easier in terms of the level of work required.
The use of modern thermal insulation materials
The oldest and most proven method of pipe insulation is filling the trench with expanded clay. Mineral wool without a waterproofing outer shell is not used for underground utilities.
Now the number of various types of thermal insulation offered for sale allows us to solve this problem for any temperature conditions. For the construction of underground lines in areas above the freezing level, a “shell” of polyurethane foam and expanded polystyrene with a foil-coated waterproofing membrane is produced.

Consider the main types of material that are most often used when warming an underground water supply:
- mineral wool or glass wool is compressed under the weight of the earth, so if it is used, additional work is necessary in the form of creating a durable casing;
- basalt fiber coated with aluminum foil for waterproofing is a rather expensive material, but it is easy to work with;
- polystyrene foam and polystyrene foam are easily cut, it retains heat well, however, protection from rodents is necessary;
- polyurethane foam holds heat well and is moisture resistant.
For knots and turns there are special shaped shells, which is convenient for installing insulation. They allow without any problems installation of thermal insulation in sections of the pipeline of any degree of complexity.
Quickly and reliably insulate the water line using sprayed polyurethane foam. In such cases, the pipe must be laid on a expanded clay pillow, because the bottom of the pipeline may turn out to be bare thermal insulation material.

For hard-to-reach places where the use of bulk materials is problematic, you can use thermal paint - a modern universal liquid heat insulator. Such paint can be applied as an ordinary brush or roller, or by spraying. In addition to its main function, it protects metal pipes well from corrosion.
Using a heating cable
The principle of operation of thermal insulation materials is reduced to the so-called "passive protection". Thanks to its proximity, the water in the pipes will not be cooled until it flows to a heated room.
It should be understood that in a closed system without an external heat source, the insulation system does not prevent freezing, but only increases the period until the water crystallizes under the influence of negative temperatures.
In the case of infrequent use of water from the well, such insulation for the winter may not be enough. In case of interruptions in operation for more than a day, it is necessary to heat the pipes, with water drained from them, using special electric cable.
There are two ways to place the heating cable: inside the heated pipe and outside.
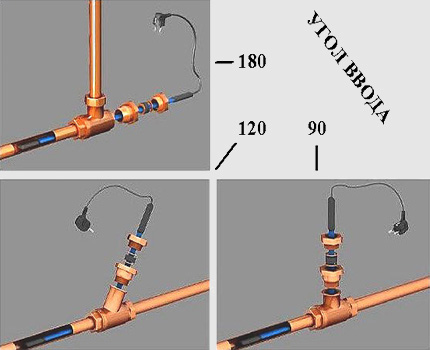
For indoor installation, special cables are used. They are non-toxic, meet the increased requirements of electrical protection (although experts recommend connection via RCD) and they are sold complete with a sealed terminal coupler. Installation of such a cable is simple and it is carried out through an ordinary tee.
The main advantage of the indoor installation option is the high efficiency of the heating system and, as a result, the reduction of energy costs. The main disadvantage is the difficulty of conducting the cable through curved sections of the water supply.
For external installation of the cable, it is necessary, first of all, to ensure its tight fit on a well-cleaned surface. The cable is attached to the pipe with aluminum tape, then the tape is held over the entire cable so that it does not come into contact with the insulation material.
Plastic pipes are pre-glued with foil to evenly distribute heat.
To increase heat transfer, several cables can be fixed linearly or in a spiral. In the case of a spiral pitch of 5 cm, the length of the conductor will increase 1.7 times with respect to the length of the covered water pipe.
Installing a thermostat can significantly save electricity, because the heating is switched on only when the set temperature is reached. The optimal values of the inclusion temperature are considered to be from 3 to 5 degrees Celsius.
A heating cable is always installed complete with thermal insulation, otherwise heating the environment will come out very expensive.
Extra protection during installation
For a well variant using submersible pump before a long downtime, the system is conserved. To do this, the pipelines are laid with a bias towards the water source, and the check valve is installed at the outlet of the supply pipe from the barrel.
After the pump is turned off, it, along with the supply pipes, is removed from the development, and the water flows by gravity into the well. When using this method, it is desirable to have no “pockets” where water could remain. The disadvantage of this method when using metal pipes is an increase in the rate of metal corrosion.
One of the rarely used methods is the creation of a “pipe in pipe” system, when a pipe of a larger diameter is put on the water supply, which is insulated from the outside. The air gap thus formed serves as additional protection against the cold.
If you introduce an external pipe into the basement of the house, providing air circulation between the layer and the basement, you can get additional heating of the underground water supply.
Another option is forced water circulation. To do this, it is necessary to install a second pipe leading from the basement to the well and a crane system to switch the water supply to the house or to this pipe.
By turning on the pump on schedule, warm ground water can be pumped into the system, and cold water can be pumped into the well from the system. This option is convenient for a long absence of home owners when there is no water consumption.
There is a widespread opinion, including on the Internet, that it is possible to prevent freezing of water by creating excessive pressure in the system. However, the temperature of the transition of water to ice decreases by only 1 degree for every 130 atmospheres of static pressure. It is unrealistic to build a water pipe that can withstand such pressure.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Video # 1. Elementary insulation of the walls and the lid of the caisson with foam from the inside:
Video # 2. Arrangement of the well using a caisson, with the disclosure of the topic of warming:
Freezing a well and a water supply system is fraught not only with the interruption of water supply, but also with damage to equipment and elements of the system, the repair of which will require money and considerable efforts. It is better to carry out thermal insulation work once and get permanent access to water for many years.
Please write comments in the block below. We are waiting for your stories about our own experience in warming an autonomous water source. Perhaps you have questions or have interesting information that you are willing to share with us and visitors to the site.

 Do-it-yourself well warming for the winter: an overview of the best materials and methods of warming
Do-it-yourself well warming for the winter: an overview of the best materials and methods of warming  How to arrange a well without a caisson: an overview of the best ways
How to arrange a well without a caisson: an overview of the best ways  Self-repair of a well: an overview of the best methods of restoration and resuscitation
Self-repair of a well: an overview of the best methods of restoration and resuscitation  Winter water supply from a well: an overview of the best options and arrangement schemes
Winter water supply from a well: an overview of the best options and arrangement schemes  Water purification from a well: an overview of the best and most effective ways
Water purification from a well: an overview of the best and most effective ways  How to find water for a well: an overview of the most effective ways to find water on a site
How to find water for a well: an overview of the most effective ways to find water on a site  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
I use a heating cable complete with suitable thermal insulation. At the same time, there is no need to hide pipes under a layer of non-freezing soil, which, in turn, significantly reduces the cost of the device and simplifies technical operation. Electricity consumption subject to proper cable installation and when using a temperature controller is small. In addition, the construction principle fully justifies itself when carrying out repair work of the pipeline, if necessary.
In our south, winters are not very frosty, and at the country house I insulated a well without a caisson. He made a wooden box in the form of a house, equipped it with mineral wool from the inside. I made an opening lid on top. Convenient in that at any time you can open and check whether everything is fine. Yes, and adds aesthetics to the site, looks very pretty. Well, in regions with a colder climate, perhaps, you can not do without a caisson.