Standards for ventilation and air conditioning: air exchange in rooms for various purposes
When designing the engineering systems of any building, it is very important to provide that the norms of ventilation and air conditioning are fully respected. The health and comfort of every person in the building depends on the fulfillment of these conditions.
But how to understand a pile of documents, highlight the most important and determine whether all the necessary, regulatory requirements are being followed? The task is not an easy one, but we will help you and highlight the most important thing in the matter of ventilation and air conditioning standards for different rooms.
The content of the article:
The main criteria for good air exchange
The comfort of people living / working or indoors depends on several key factors. These are temperature, quality, speed and humidity. All of them can be regulated by ventilation and air conditioning, thereby setting comfortable parameters.
The requirements for them are fixed in a number of different documents, these are joint ventures, state standards, sanitary standards. They regulate air exchange according to optimal and acceptable criteria.
Optimum parameters are recommended norms of the most favorable quality of air exchange for a person for all factors at once.
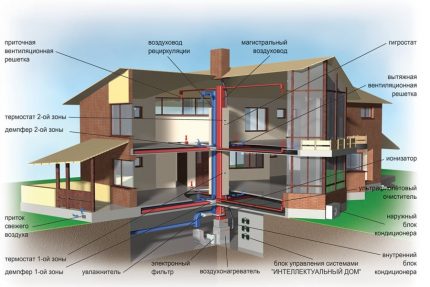
Allowed parameters are the minimum mandatory standards, they are allowed if the optimal ones for some reason cannot be organized, for example, related to technical capabilities or budget.
The sanitary norms also spell out the norms of ventilation and air conditioning - air purity, noise limit and calculations for the amount of air for each person in the room. Accordingly, the installed ventilation and air conditioning systems are required to cope with the specified standards.
For air supply to the room are used duct fans or various appliances. This is a natural or mechanical inflow. The design may include systems for filtering, heating the incoming air, for example heaters etc.
Ventilation Equipment Requirements
Suppose that all norms and parameters correspond to those required. But at the same time, a huge block of air conditioning hangs over your bed, and to clean the system you need to call a whole team with equipment that barely fits into the apartment.
You must admit that in this situation you’ll think a hundred times whether clean air is so important or whether you can get by the vents.

Some residents of apartment buildings often complain about the massive ventilation system passing through the entire room and of course, this is wrong, and needs to be corrected if technically possible.
Therefore, there are also architectural, external as well as operational requirements.
For instance:
- So, in some cases it is strictly forbidden to install air conditioning units on the facade.
- Equipment should not take up too much space, everything should be linked to a minimum.
- Low inertia of the system.
- Installation, assembly - as simplified as possible.
- Operation - devices should provide ease of control and the most rare service with repair and replacement of equipment.
- For fire safety, it is necessary to provide additional protection in the form of fireproof valves.
- To protect against vibration and noise, additional protection is installed.
- Mutual installation of 2 air conditioners, so that in case of failure 1, the second can provide a minimum of 50% air exchange.
- In addition, ventilation and air conditioning systems must meet the economic possibilities of both the equipment itself and the costs of their maintenance / operation.
The ventilation system can be natural, forced or mixed. If natural air exchange does not provide proper standards, it is developed with mechanical motivation.
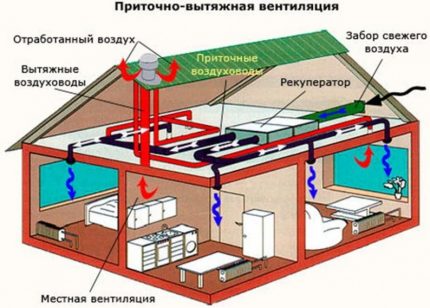
Thanks to accurate calculations, you can already find out at the design stage which circuit you need for a particular room. In addition, this is regulated by separate regulations.
The choice of ventilation and conditioning depends on:
- type and purpose of the building / premises;
- number of floors in the building;
- the possibility of releasing harmful substances;
- fire hazard.
The multiplicity of air exchange is established by SP and BCH, and it is also determined by calculations.
Most often for most types of buildings natural ventilation without the use of mechanical motivation satisfies all regulatory requirements.
However, if it does not cope, it is not possible to establish ventilation or the coldest five-day period in the region gives frosts below −40 degrees, artificial methods are provided.
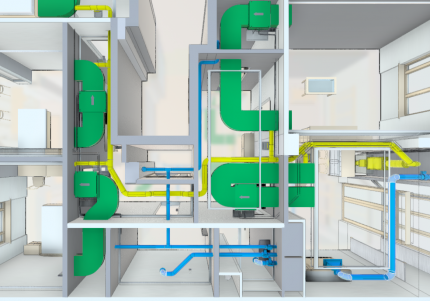
In fact, ventilation is necessary to ensure a comfortable microclimate. What can we say about the buildings where people who live and work need clean air.
The following types of buildings are documented by air exchange quality:
- residential and dormitories with premises for various purposes;
- administrative, research;
- educational, including school, pre-school, boarding schools with accommodation;
- medical direction;
- consumer services;
- retail;
- various cultural and entertainment facilities - circus, cinema, theater, club.
Each has its own normative tables with a detailed indication of which air exchange should provide good ventilation.
But first, let's deal with regulatory acts.
What documents regulate air exchange?
The main document, which describes the parameters and requirements for air exchange - SP 60.13330.2012 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning, many items of which, by the way, are included in the list of mandatory for execution, according to PP No. 1521.

It describes the basic requirements for ventilation and air conditioning of buildings, including standards, fire-fighting arrangements and mandatory schemes with calculations.
This same document refers to:
- SP 118.13330.2012 Public buildings and structures.
- SP 44.13330.2011 Administrative and domestic buildings.
- SP 56.13330.2011 Production buildings.
- SP 7.13130.2013 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning. Fire safety requirements.
- SP 158.13330.2014 Buildings and premises of medical organizations.
- GOST 12.1.005-88 General hygiene requirements for air in the work area.
- GOST R 52539-2006 Clean air in medical facilities.
- SanPiN 2.2.4.548-96 Hygienic requirements for the microclimate of industrial premises.
- SanPiN 2.1.2.2645-10 Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for living conditions in residential buildings and premises.
In all these documents, you can find answers to almost any questions related to air exchange in a particular building and premises.
There is a lot of information, and for ordinary people, most of it is superfluous, so we tried to highlight the most basic for you on some points.
Category No. 1 - residential buildings
At the design stage for residential buildings, as a rule, an exhaust ventilation system of a natural type is provided in apartments. She is installed in the form of channels in kitchens, in bathrooms (toilets, and also bathrooms).
However, if there is no through ventilation, as in some large apartments, the hood can also be equipped through living rooms.

The inflow is carried out by conventional ventilation through doorways with an external outlet and vents.
However, there are exceptions. For example, if the temperatures of a cold five-day period in a particular region can systematically reach −40 degrees, the engineer of a contractor building a 3-story building (and higher) often provides for a mechanical air supply with heating.
But for residents of climate zone IV, air conditioning or other appliances are needed to help cool the air.
With air heating, air is supplied through its channels.
It is not uncommon on the forum to ask a question regarding the integration of ventilation ducts.In residential buildings, it is allowed to combine horizontal ducts of the bathroom with a toilet or kitchen and vertical channels of the bathroom, toilet and household units.
Stairways are ventilated both naturally and with ventilation ducts, if there are no windows with windows.
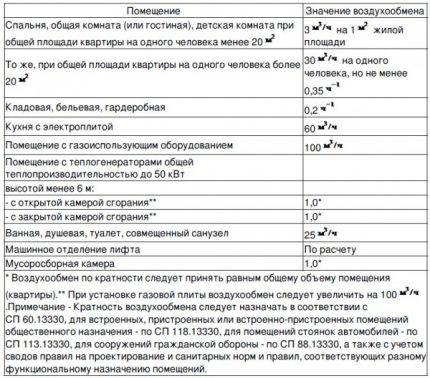
As you can see, the calculated parameters of the optimal air exchange are contained in SP 54.13330.2016. The operational responsibility for the maintenance of residential buildings lies with the homeowners and engineers of the Criminal Code in the Moscow Ring Road.
Category No. 2 - administrative buildings
In buildings of this type, not located in climate zone 4, it is used supply and exhaust ventilation. Air conditioning at the expense of the budget is allowed with economic and technical justification.

As for the inflow, the channels are individual for conference rooms and catering places. For the rest of the rooms, a single system is most often designed.
The hood is carried out naturally, except for the following rooms where mechanical induction is applied:
- Bathrooms
- smoking rooms;
- rooms over 35 square meters. m area (due to individual channel);
- film projection;
- fume hoods.
And also, a natural extractor hood is characteristic of any administrative building, with the exception of buildings over 3 floors, with the number of employees exceeding 300 people.
According to the norms of air supply, the amount of standardized air depends on the purpose of the room. All standards are contained inSP 44.13330.2011 Clause 7.2.
Category 3 - educational institutions
In institutions of this purpose, you are likely to come across a supply and exhaust system.
With the number of students up to 200 people, forced ventilation is used with natural motivation, more than 200 - always with a mechanical, but natural exhaust design with a single air exchange from the classrooms due to corridors, bathrooms and windows.

If air heating is used in conjunction with ventilation, it is necessary to arrange automatic adjustment and control, while the air supply must not exceed 40 degrees in temperature.
Separate ventilation systems should go out of classrooms, a gym, a dining room, a laboratory room with exhaust units, a first-aid post and a bathroom.
Category 4 - medical facilities
To medical institutions we include hospitals, pharmacies, clinics, medical posts. A supply and exhaust system is also designed here, however with a mechanical impulse and some features.
In particular, for example, in medical institutions there is a ban on the recirculation of air masses, which is natural, taking into account the requirements for fresh air and possible bacterial infection.

Particularly strict requirements for the quality of air exchange and the need to equip individual systems according to which rooms should have ventilation and air conditioning in the hospital.
That is, to:
- generic;
- wards for newborns and nursed newborns;
- operational, postoperative (air mobility not more than 0.15 m / s, relative humidity 55-60%);
- resuscitation;
- intensive care boxes;
- rooms for burn patients;
- X-ray departments;
- laboratories;
- Bathrooms
- pharmacy points;
- By the way, these rooms are supplied with fresh air with additional filter cleaning.
If there are no infectious patients in the wards or rooms and a single regime is in effect, then ventilation systems can be combined.
It should be noted that from an engineering point of view, in hospitals the most difficult engineering distribution of ventilation of different rooms.
The normative values of the air exchange rate in medical organizations are enshrined in SP 158.13330.2014, as well as in the “Instructions for the organization of air exchange in wards and operating units of hospitals” and “Instructions for hygiene on the design and operation of infectious hospitals and departments” .
Category 5 - Retail Buildings
You must have noticed in many stores the musty air and mixed flavors. Of course, this should not be or is allowed, but at a minimum.
Shops are equipped with air conditioning or mechanical ventilation.

For separate halls of household and food trade, ventilation and air conditioning systems are divided.
The pantries provide for a natural extract, also separate, but, in principle, it is possible to combine mechanical schemes with utility rooms, provided that fire-retardant valves are installed.
Of the features, we note that if the trading floors are part of a residential or office center and are located on the ground floor, they must have independent ventilation and air conditioning systems from the common building.
As for the air-thermal curtains, they must be installed in the vestibules of stores with an area of 150 square meters. m and markets ranging from 600 square meters. m, if the temperature during the cold period drops below 15 degrees in a particular region.
Recycle air it is possible, but not in rooms with chemical and synthetic means, as well as combustible substances. However, the supplied external air must be at least 20 cubic meters. m per hour for each visitor.
Violation of air exchange
If you see fogged up without any special windows, smell a musty smell or think that oxygen seems to be shut off, it is quite possible that the ventilation system is either improperly designed or it needs to be serviced urgently.
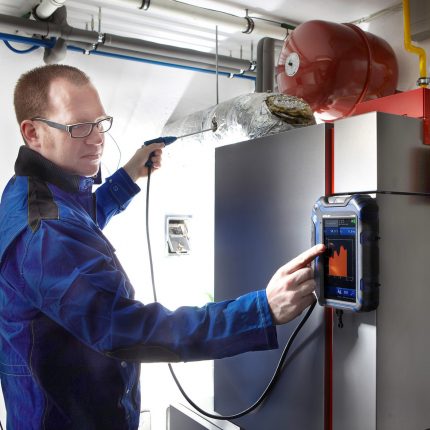

For residents of MKD, one should immediately contact the service organization, most often this is the Criminal Code, with a statement that there is a suspicion of a malfunction of ventilation equipment. Based on this application, a specialist should come to you for inspection.
If the Criminal Code has not responded to the complaint in any way, or it is a different building, it makes sense to try to complain to the Rosprotrebnadzor, Housing Inspectorate, Sanitary and Epidemiological Station for verification.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
How to deal with the difficult atmosphere in the room:
We examined the mandatory and permissible microclimate parameters in some categories of buildings, as well as in which rooms should be, and which, ventilation. As you can see, in most cases they are different. The only requirement is that no matter where they are, they must comply with current regulations. Compliance with standards is a guarantee of the safety of life and human health.
Of course, we gave you only general ideas, it is impossible to sound all the exact requirements in one article for each item. Moreover, they are often individual in terms of the dimensions of buildings, their geometry, the arrangement of halls, and so on.If you need to develop high-quality ventilation or air conditioning, you should apply to experienced firms with a license, as well as to prove that your rights to a comfortable microclimate are violated in any case.
Have you encountered microclimate problems? Or maybe they designed an air exchange system? Share your experiences and ask questions in the comments.

 Air exchange rates per person for various premises
Air exchange rates per person for various premises  Air exchange in dentistry: norms and subtleties of arranging ventilation in a dental office
Air exchange in dentistry: norms and subtleties of arranging ventilation in a dental office  Frequency rate of air exchange in office premises: norms and rules for the organization of proper air exchange
Frequency rate of air exchange in office premises: norms and rules for the organization of proper air exchange  Checking ventilation at school: norms and procedures for checking the effectiveness of air exchange
Checking ventilation at school: norms and procedures for checking the effectiveness of air exchange  Warehouse and warehouse ventilation: standards, requirements, necessary equipment
Warehouse and warehouse ventilation: standards, requirements, necessary equipment  Norms of air exchange rate in various rooms + calculation examples
Norms of air exchange rate in various rooms + calculation examples  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements