Do-it-yourself greenhouse heating system: the best ways to winter heat greenhouses
To maintain a certain temperature in the greenhouse, different heating systems are used. The choice of heat supply method depends on the dimensions of the building, the climatic conditions of the region, the availability of a particular type of fuel, financial capabilities and other factors.
Some home craftsmen undertake to organize the heating of the greenhouse with their own hands - such a solution will significantly reduce labor costs, agree? Of course, the independent arrangement of stable heating is a difficult task, but it is quite feasible. The first step is to choose a heat source.
We will tell you what options for greenhouse heating exist, what are their specific features, advantages and disadvantages of use. Based on the above information, you will be able to determine the type of heating, perform a preliminary calculation of the heat capacity, select the working units and elements of the system.
The content of the article:
Specifics of maintaining temperature in greenhouses
The heating of the greenhouse is necessary to compensate for heat losses that occur through the walls and ceiling of the structure, as well as due to external air. To reduce heating costs, it is necessary first of all to qualitatively insulate the greenhouse and minimize air exchange with the street.
In addition to the material from which the greenhouse is made, special attention must be paid to the tight fit of the structure to the soil. For this, it is better when building a greenhouse to make a foundation of small depth insulated from the inside.
It must reliably hold the structure in strong winds, prevent the formation of cracks and minimize heat exchange with the street through the topsoil.
To solve the latter problem, even in the conditions of the northern regions, 30 cm depth is sufficient, since the thermal conductivity of the soil is very low. The intensity of vertical heat transfer between the soil layer inside the greenhouse and the underlying soil layer is very small.
In winter, snow can be used as a natural outdoor insulation along the edges of the greenhouse.

For normal plant growth, it is necessary to maintain the temperature of the air and the soil-plant layer in a certain range. If the greenhouse functions continuously, the fertile soil will be warmed up by heat exchange with the internal air. Moreover, its temperature will be almost the same as under natural conditions in the summer.
In winter, the soil and soil strata freeze to a depth depending on the geographical latitude of the region and the rock structure. To warm the soil and the adjacent upper layer before planting, it is necessary either very long (up to a month) maintaining a positive air temperature.
An alternative solution is to carry out special actions to transfer heat directly into the soil. This can be done using a system of underground pipes into which the coolant is supplied.
The amount of energy spent on heating the greenhouse depends on the following factors:
- The surface area of the walls and roof of the greenhouse. The lower this indicator, the less heat loss. Therefore, to save energy, it is better to use a rectangular or semicircular shape of the structure.
- Thermal conductivity of the material. The lower this parameter, the better the material retains heat.
- Temperature difference between indoor and outdoor air. The greater its value, the greater the heat loss.
- Air exchange through leaks. To reduce energy costs, it is necessary to exclude uncontrolled influx of cold air.
A wide variety of private greenhouse projects and the quality of their installation seriously complicate the modeling of temperature conditions. Therefore, to accurately determine the amount of necessary energy for heating a particular object can only be experimentally.

Autonomous heating based on fuel combustion
Using the fuel combustion process as a heat source is the most commonly used method of heating small greenhouses. Such heating has some specifics, since it is necessary to take into account the increased tightness of the room, the desirability of heating the soil and the need to maintain humidity.
Furnaces and solid fuel boilers
One of the simplest devices used when heating greenhouses in the cold season is a stove. The popularity of the use of such a device is due to the cheapness of fuel. It can be uncalibrated firewood, dry grass, coal and coal dust, garbage and combustible liquids.
When heating stoves, it is necessary to ensure stable draft, since the ventilation of the greenhouse when it enters the combustion products will lead to its cooling.
When using a metal furnace, heating and energy transfer to the surrounding air quickly occurs. It is also the cheapest and easiest way to use heating. You can build such a unit yourself.
On our site there is a selection of articles on the manufacture of different types of metal furnaces that can be used to heat the greenhouse:
- How to make a Buleryan oven with your own hands: step-by-step instructions on how to make
- Do-it-yourself gas stove from a gas cylinder: diagrams, drawings + step-by-step guide
- The furnace for working out of the pipe: how to make an effective furnace for used oil from improvised materials
The stone stove heats up more slowly and keeps heat longer. This is more suitable for heating small rooms with a medium or narrow temperature range. However, such a furnace must be folded and if necessary it cannot be moved, like its metal counterpart.
There is an idea to heat the space in the greenhouse using hot combustion products. To do this, they suggest placing the furnace in a pit, and laying the chimney horizontally below ground level with its subsequent exit to the surface.
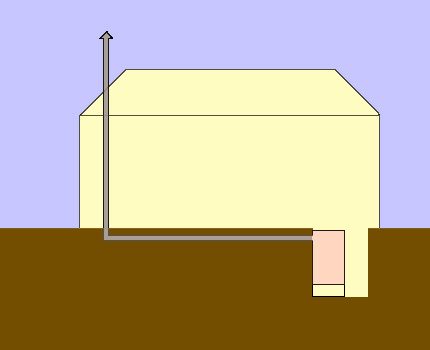
This option will really increase the heating efficiency.
However, in practical implementation the following difficulties will arise:
- Demanding for the material of the assembly of the chimney. At the outlet of the furnace, the air temperature is very high. Therefore, the chimney should not have good heat transfer; otherwise, soil will burn around it. As a material for the removal of combustion products, asbestos pipes can be used.
- Compliance with the rules for placing the chimney. In the chimney, it will be necessary to provide revision windows for cleaning it from soot. Therefore, you need to lay the pipe between the beds.
- The need for power supply. A long horizontal section does not contribute to the creation of normal traction, so it will be necessary to install a smoke exhaust. This means the need to supply electricity to the greenhouse or periodic recharging of the battery.
Therefore, the idea of underground placement of the chimney in practice has not found wide application.
Instead of a standard furnace, solid fuel can be used. long burning boilers. They burn fuel more efficiently and prevent the rapid release of heat, which eliminates the possibility of damage to plants from high temperature. These factory-made boilers are easy to use and maintain, as well as compact.
Gas boilers and convectors
For greenhouses, a good alternative to stove heating was the use of gas liquefied gas boiler or convector. For small private facilities, gas cylinder equipment is usually used.

It is better to place a gas cylinder outside the greenhouse. But in this case, it is necessary to solve the issue of preventing freezing of the gearbox for a long period with a negative temperature.
Connecting a greenhouse to a gas network is a rather complicated bureaucratic procedure. In addition, comments will be made at the annual mandatory inspection by a gas service specialist.
In any case, the presence of a combination of gas supply and the use of an open flame in an enclosed space requires increased security measures. The best solution is the presence of a gas analyzer, as well as an automatic flame extinguishing system that operates when the maximum permissible concentration of a combustible substance in air is exceeded.
From the position of comparing financial costs during the installation and use of furnaces and gas equipment, an unambiguous conclusion cannot be drawn. A simple gas convector costs about 12-14 thousand rubles.
It is more expensive than solid fuel metal devices:
- the cost of metal and consumables for the independent manufacture of a potbelly stove is about 3 thousand rubles;
- a small-scale solid-fuel plant for example, the NVU-50 “Tulinka” model costs about 6.6 thousand rubles.
- installation of long-term combustion model NV-100 “Klondike” costs about 9 thousand rubles.
A stone stove will come out more expensive than a gas convector due to the cost of installing the foundation and laying it.

The cost of liquefied or natural gas spent on heating any room will be cheaper than purchased firewood and coal. However, greenhouses are heated, as a rule, with free or cheap combustible waste, which is always sufficient in rural and suburban areas.
The problem of air leaks and humidity
The use of heating devices, in which open combustion of fuel occurs, leads to the need to remove combustion products through the chimney. In this case, compensation is required for the volume of exhaust air.
In buildings, it is possible through uncontrolled inflow (infiltration) which occurs due to the presence of gaps and holes in the walls and ceiling.
The design of modern greenhouses, such as polycarbonate, creates an airtight space. In this case, the problem of air intake is solved by the presence of air vents and the installation of a special air inlet.
It should be placed in such a way as to avoid a concentrated stream of cold air on the plants. It is also possible to use several small holes to organize a distributed inflow.
Exhaust systems for closed gas convectors are already equipped with a pipe for the influx of external air into the combustion chamber.
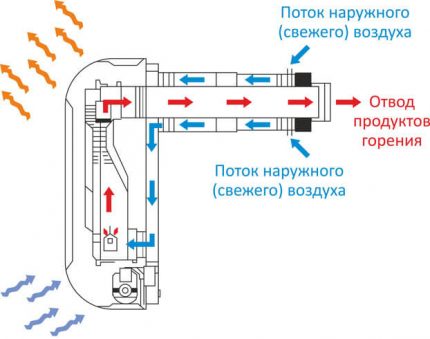
Often after the operation of furnaces and boilers, the effect of air drainage is observed. This is due to the lower absolute humidity of the supply cold stream (especially frosty) in relation to the warm air leaving the greenhouse through the chimney.
To maintain the exact parameters of air humidity, a humidifier with a hygrometer is used, which can operate from a local energy source. In the absence of such a need, an open container of water can be placed in the greenhouse. Then, in the case of strong dehumidification of the air, the evaporation process will naturally occur.
Ways to evenly distribute heat
For small greenhouses, it is sufficient to place one heating source. The air circulation in the room will be provided due to the vertical temperature difference and, thus, the distribution of warm air will occur.
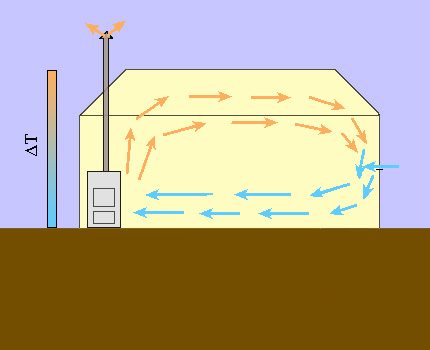
In rooms of a large area or complex geometry, the formation of zones with different microclimate parameters is possible. This is sometimes done specifically in industrial greenhouses, but in most cases this phenomenon is undesirable.
For uniform heat distribution, two methods are used:
- The creation of artificial air circulation. Usually use paddle fans. Sometimes they build a duct system with integrated pumps so that air is drawn in at one end of the room and the discharge is at the other.
- Heat transfer due to intermediate heat carrier. As a rule, an ordinary forced circulation water system is used. Pipes can be laid both around the perimeter of the greenhouse and under a layer of soil.
Forced heat distribution is also necessary to prevent the formation of a high temperature zone near the heater. Otherwise, plants located close to the furnace or boiler may receive thermal damage.
Popular heating methods without open flame
The use of open fire has some limitations, as there is a release of combustion waste, and it is also necessary to observe fire prevention measures. Therefore, other methods are often used to generate heat in the greenhouse.
The use of electrical appliances
Using electricity to heat a greenhouse in winter is the most expensive way.However, it is also the simplest, since the installation of such heating includes only wiring and installation of devices.
The use of simple automation systems frees a person from the need to participate in the constant control of the microclimate.
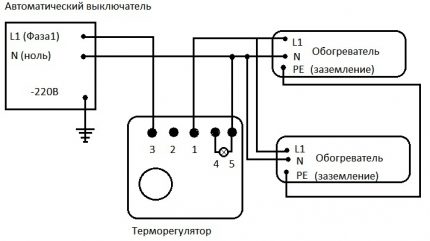
Electric heating of the greenhouse can be performed using the following devices:
- Heater. The simplest and cheapest device that you can do yourself.
- Convector. The presence of a fan allows in addition to heating the air to carry out its uniform distribution in the greenhouse.
- Heat pump. A powerful device for heating air in large-volume greenhouses, which is often used to distribute heat in conjunction with a duct system. To heat a compact room, you can make heat pump by yourself.
- Infrared lamps. The specifics of the operation of such devices is the heating of the surface on which the radiation enters. Thus, it is possible to equalize the vertical temperature gradient in the room without the use of air circulation.
- Heating cable. It is used to heat local areas in the greenhouse.
In the case of small room sizes, the use of electric heating is justified because of its simplicity and safety. In large and industrial greenhouses it is advisable to use other methods.

Biochemical heat generation
One of the interesting ways of heating is to introduce unrefined organic fertilizer into the soil - animal manure or bird droppings. As a result of the biochemical reaction, a large amount of energy is released, which increases the temperature of the fertile layer and indoor air.
When rotting manure, carbon dioxide, methane, and a small amount of hydrogen and hydrogen sulfide are released. Manure also has a specific smell. All this imposes certain restrictions on its use, associated with the need to ventilate the room.
In winter, as well as during prolonged cooling in spring and autumn, intense air exchange is undesirable. In this case, a much larger amount of energy may be required to restore the heat balance after airing than was released as a result of the rotting process of manure.
The use of such a “biological” method of heating the earth and air is justified in late spring, when airing occurs at positive daytime temperatures.
Systems with an external heat source
Heating of the greenhouse is possible due to the proximity of the house or other heated structure. This simplifies the whole procedure, since there is no need to install an autonomous heat source. Using wired or wi-fi relays, you can remotely receive information about the temperature in the greenhouse and adjust its microclimate from home.

Creating a separate heating circuit
If the house uses water or steam heating, then it is possible to create a separate circuit leading to the greenhouse. It must be equipped with a separate pump, since the total horizontal extent of the new segment will be large.
Also in the greenhouse, you need to install an open expansion tank for venting air from the system.The area of open water of the tank must be minimized to prevent the intensive evaporation of hot water inside the room.
Radiators are rarely installed in a greenhouse, as the design of its premises plays a secondary role. If there is a lack of heat, it is better to lengthen the pipe circuit, as it is cheaper and reduces the risk of leaks and breakdowns.
The street segment of the circuit must be insulated to avoid heat loss and minimize the risk of freezing. An underground pipe placement option is best suited for these purposes.
The connection of the heating segment of the greenhouse to the common circuit can be performed using a three- or four-way valve.
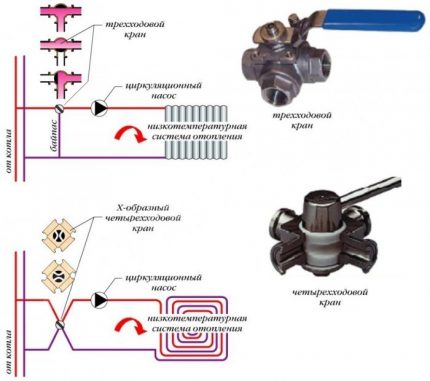
It is also possible to create an automatic temperature control system.
This can be done in the following ways:
- The change in the volume of hot water allowed, depending on the temperature sensors. In this case, it is necessary to purchase a pump with power control.
- Turning the heating circuit on and off. For this, automatic crane control systems are used.
Instead of manually changing the position of a three- or four-way valve, servo-based devices can be used. Its electronic control unit is tuned to the readings placed in the greenhouse temperature sensors.
If necessary, change the heating mode receives a control signal to the engine, which rotates the rod, setting a different position of the valve.

Extract air heating
Good heating can be obtained through the use of warm air exhaust ventilation of a residential building. By directing the insulated ventilation duct into the greenhouse, you can get a constant inlet stream with a temperature of 20-25 ° C.
The only condition is the absence in the air of excessive humidity and impurities characteristic of kitchens and bathrooms.
The outflow of air from the greenhouse can be organized in two ways:
- The local exhaust outlet to the street in the form of a tube without a fan. It should be a small cross section to create a high flow rate. In this case, at negative street temperature, the condensation zone will be located at some distance from the tube, which will prevent the formation of ice.
- Return flow using an additional duct and its mandatory connection to the common house hood. Otherwise, odors from the greenhouse will spread throughout the house.
This method is the most economical in terms of one-time installation costs and recurring fuel costs. The only question remains whether the volume of the hood is sufficient to maintain the required temperature. Check it out better experimentally.
If sometimes, during extreme cold spells, the air temperature in the greenhouse drops below the permissible value, then you can either install a small air heater in the duct or install an additional electric device on the object itself.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Homemade stove with a long chimney for heating the greenhouse:
Several options for wood stoves in a real greenhouse:
Gas burners as a source of heat. Pipe layout in the greenhouse:
There is no universal option for heating a greenhouse. The choice in favor of one of the methods or their combination must be made taking into account its reliability, low cost of installation and use of equipment, energy prices and battery life.
Most projects can be implemented on their own, which will reduce their cost and provide an opportunity for further independent modernization.
Do you have personal experience in designing and arranging heating in a greenhouse? Want to share your knowledge or ask questions about the topic? Please leave comments and participate in discussions - the feedback form is located below.

 How to pressure test a heating system with your own hands
How to pressure test a heating system with your own hands  Flushing gas heating systems: flushing methods and procedure
Flushing gas heating systems: flushing methods and procedure  Do-it-yourself economical garage heating: how to reduce heat loss and the better it is heated
Do-it-yourself economical garage heating: how to reduce heat loss and the better it is heated  How to make the right chimney for a do-it-yourself stove: a step-by-step instruction
How to make the right chimney for a do-it-yourself stove: a step-by-step instruction  Sawdust briquettes: how to make “euro-wood” for fuel assemblies with your own hands
Sawdust briquettes: how to make “euro-wood” for fuel assemblies with your own hands  How to make a gate for a chimney with your own hands: instructions for making a valve
How to make a gate for a chimney with your own hands: instructions for making a valve  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Last year, he heated the greenhouse inside with an electric air heater, but he took a lot of electricity. I decided to build a stone stove: so I will spend it once, but it will be of high quality and for a long time. I’m not going to change the location of the greenhouse yet, there are materials for the furnace, I’ll start construction, I will use the information from your article, everything is available and detailed.
Imported vegetables are inexpensive, despite the sanctions. In addition to heating in winter, you need a lot of light to extend the daylight hours. Putting heating makes sense only if you are interested. Making money on this is almost impossible. Of all the proposed, only the option with stove heating can be implemented without high costs. I myself heat the greenhouse only in spring with an old potbelly stove. It is portable and light. And to attach a pipe to it and bring it to the window is easy. Part of the smoke, however, still remains, but this is even beneficial for plants.
Heating a greenhouse is also profitable. You just need to know what to grow. On strawberries, for example, you can get a plus in just one season.