Flushing gas heating systems: flushing methods and procedure
Has the heating in your house begun to work noticeably worse? Does the boiler have to be turned on more and more frequently and gas bills are growing steadily? Do not rush to repair and change the heat exchanger of the boiler or battery - flushing gas heating systems in most cases eliminates such problems.
This relatively inexpensive procedure will extend the service life and increase the efficiency of each link in the system, avoiding or significantly delaying costly repairs. In this article, you will learn about the different ways to flush the heating system, their advantages and disadvantages. We will also tell you how to understand when flushing is needed, how to do it yourself and what to do to make the system clog much less.
The content of the article:
When is it necessary to flush the heating system?
The procedure for flushing heating systems is mandatory in the maintenance of heating systems, the procedure for its implementation is clearly regulated by SNiPs and PPRF. The guidelines recommend annual cleaning; however, this only applies to central heating systems.
These systems are large-scale and multi-component, they consist mainly of steel pipelines of a respectable age, and the coolant is often replenished and is not always sufficiently cleaned. The combination of these factors makes the annual flushing justified and necessary.
However, private heating systems serving a single-family house or apartment operate in different conditions, and therefore they need to be washed out if necessary, and not annually.

It is possible to determine that the system needs to be flushed by the following signs:
- The radiator heats up unevenly: individual sections or the lower part are much colder.
- Steel feed pipes are much hotter than batteries.
- The whole system heats up more slowly than before.
- Gas consumption has increased, a boiler with mechanical control often needs to be set to high power.
- Extraneous sounds appeared in the boiler or in any part of the system.
- The filter installed in the return line is clogged regularly.
Even if you have all the symptoms described above, flushing is not always necessary - airing the system has the same symptoms, and it is much easier to fix it - through Mayevsky crane or a special valve. Therefore, first of all, they exclude the possibility of air congestion in the cold part of the radiator, and only then choose the method of cleaning.
Neglecting timely flushing of the heating system, you risk not only overpaying for gas. Accumulating in the boiler heat exchanger, solid particles overheat the metal and provoke its burning. In addition, a raid is able to disable circulation pump, expansion tank, boiler, cause leaks.

On the other hand, cleaning too often, especially with chemicals, can do more harm than good. Firstly, the inner surface of the pipeline and all connections wear out faster. Secondly, fresh coolant carries a new portion of salts and air, which provokes a new wave of corrosion.
Less often, cleaning is necessary for systems with plastic pipes and aluminum radiators, because they do not form rust. However, they do not exclude limescale, and therefore you should not completely forget about flushing.
Mechanical cleaning methods
A mechanical effect on deposits is safer for pipes than a chemical one, but it is not always possible to flush the system with these methods to a pure metal. Nevertheless, mechanical cleaning is popular because of its availability and effectiveness for a not too dense coating, in private networks it is quite enough.
With self-cleaning, the main thing is not to harm. Do not disassemble the system if you are not sure that you can assemble it without leaks, and when choosing flushing agents, strictly observe the compliance of the materials and the recommended exposure times.
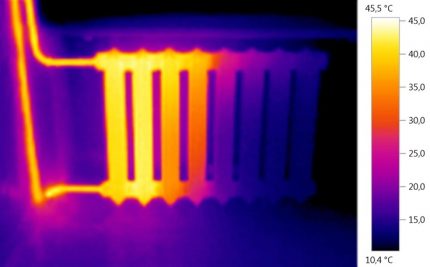
The choice of flushing method depends on many factors:
- Material of radiators and pipes. Hard rust forms on steel, dark oily coating on cast iron; only plaque or mucus can be found in plastic at low pressure and temperature, for example, a warm floor.
- Forced or gravitational circulation of the coolant. The higher the pressure in the system, the less deposits on the walls, and the denser they are.
- The type and thickness of deposits - it is easy to determine after opening the system.
- System age and last flush time. Up to 3-5 years, even rust is quite loose and can be easily removed.
- Availability and condition of filters.
- Location of the boiler and structural features of the system: availability indirect heating boiler, pipelines of complex shapes, the total length of the pipeline, etc.
Employees of specialized services can take into account all these parameters of your particular system, conduct diagnostics with a thermal imager and choose the most rational cleaning methods.
Water tap flushing
The easiest way to flush is to open the heating circuit and run tap water through it. To do this, shut off the taps for supplying and exiting water from the boiler, jamming expansion tank.
Then the coolant is drained through a special valve in the return line, preferably in a prepared container. If you plan to reuse it, the coolant will need to be carefully filtered.
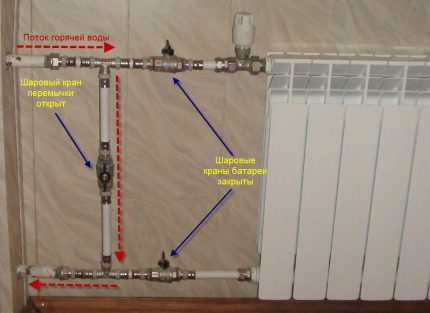
One hose connects a water tap and the beginning of the heating circuit, at the outlet of the boiler. The second hose is discharged from the discharge valve into the sewer.
Open the tap to supply water at maximum pressure and watch what flows into the sewer. When the outlet water is clean, its flow is shut off.
For greater efficiency, it is recommended to swap the hoses and flush the system in the opposite direction, and then repeat the procedure again, but only in the opposite direction.
In the last flush, the water supply is not blocked, but only reduced, and the expansion tank is opened. Then remove the discharge hose, close the valve and feed the system to the desired level. Only after that turn off the water supply and connect the boiler to the circuit.
The effectiveness of this flushing method depends on the type of contamination and pressure in the water supply. If your water flows gently and smoothly from a tap as wide as possible, such a cleaning is practically useless. Among its indisputable advantages is the possibility of independent washing, without special equipment, as well as the discharge of waste directly into the sewer.
Hydrodynamic flushing method
This method requires special equipment, but is one of the most effective and safe.

The essence of the method is to use a special head on a flexible hose that forms thin high-pressure jets inside a pipe or radiator. Water is supplied to this head through the pump, and the tip itself is introduced into the gap in the heating circuit. In general, the principle is similar to a car wash.
In this way, you can safely flush the most problematic and inaccessible areas - for example, the bottom and middle sections of a large radiator. It is suitable for any material and type of contamination, and flushing waste is absolutely safe. Point exposure allows you to wash any surface to metal without using chemicals, as well as stay more thoroughly in places of greatest pollution.
Among the disadvantages of the method is the need to open the heating circuit, organize the drainage of water into the sewer, as well as the need for special equipment and the limited range of the head.
Air brushing
Compressed air from a compressor is often used to clean anything, including a heating system. This option is safe and effective, and therefore popular.
You can purge the entire system at once, in the forward and reverse direction, as well as its individual sections, having previously dismantled them. The second option is more time-consuming, but more efficient, especially in systems of considerable length.

Cleaning is carried out not with a constant air pressure, but with short pulses with a maximum pressure, if possible with a change in the angle of supply to the pipe. Before filling the system with a constant coolant, it must be washed with clean water to remove all particles knocked down from the walls.
In addition to turbulent flows of compressed air in empty pipes, hydropneumatic flushing is also used. Its key difference is that air is fed into pipes filled with coolant. As a result, bubbles form, water boils in the system, washing away all deposits from the walls. Such washing is effective even in large apartment building systems, and due to the low cost of consumables, it has become very popular.
Hydropneumatic impulse flushing involves supplying a mixture of compressed air and water with a series of short jerks, using a pneumatic gun. After 60 m of the pipeline, or with a diameter of more than 4 inches, the tremors lose their speed, and hence the destructive force for a raid.

Nevertheless, in private heating systems, hydropneumatic impulse cleaning allows achieving the best results by uniformly cleaning the entire system in a short time. In addition, no toxic waste remains after it, and the pipes are not damaged.
Flushing each assembly with dismantling
If you decide to flush the heating system as efficiently and safely as possible without the help of professionals and special equipment, it is better to completely disassemble it. In a private house, it’s convenient to wash everything on the street, so choose a warm, clear day.
In the autumn, shortly before start-up, dismantle the radiators, pump, expansion tank, if available, turn off the indirect heating boiler and other equipment. Remember where the gasket was, or better, buy new ones in their place. Arm yourself with hoses with adapters, cable for sewer cleaning, a long brush with a metal bristle, possibly a metal brush for the grinder, if available, a pump.
First of all, try to clean as many deposits as possible with a cable and brushes. Unscrew all plugs from the radiators, clean all openings and joints, each thread. Pass the cable and twist it well to wipe all the walls. It is convenient to clean the pipes with a brush, the handle can be extended with a rigid wire.

After cleaning each element, rinse it with clean water, connecting the hose from the water supply and plugging the excess holes in the radiators. Pass the pressure of water in both forward and reverse directions. Repeat cleaning with a cable and brushes, and rinse again. Repeat the procedure until clean water starts immediately after cleaning.
Do not forget to rinse the boiler coil, just do not use brushes in it. If there was a lot of hard coating on other elements of the system, clean the coil with a cable, and then rinse by connecting two hoses.
After reassembling and filling the system with coolant, check all connections for leaks.
Chemical cleaning methods
The most impressive results are obtained from the use of chemical compounds; moreover, such a cleaning is the least time-consuming. However, most means for flushing a heating system with a gas boiler are based on acids that can destroy not only plaque, but also metal.
Therefore, this method of cleaning is used where others can not cope, and as little as possible.

When choosing a chemical flushing agent, pay attention to such points:
- Compatible materials. Owners of aluminum radiators should be especially careful - most of the compositions for them are unacceptable, but specialized solutions exist.
- Proportions and time of use. Running into the system too concentrated solution, or for too long a period, will surely damage it.
- Type of sediment. Remember, the more types of deposits that can remove funds, the greater the likelihood of damage to pipes, radiators, gaskets on the joints.
- The need for disposal. Many compounds are not allowed to be drained into the sewer, and the collection, removal and processing of such a volume of liquid can be a problem.
How to use the composition for chemical cleaning of the heating system is described in detail in its instructions. In most cases, it is necessary to drain the coolant, prepare a solution from the same volume of water and reagent, mix well, pour into the system and put into operation.
As a rule, the composition should circulate along the circuit from 2 to 24 hours, after which it must be drained, and the entire system should be washed with clean running water and filled with new coolant.
Please note that the coolant with the reagent must always circulate through the system forcibly, under pressure - that is, through the pump.

Reagent cleaning of a part of the heating circuit is also possible, including boiler heat exchanger. In this case, it is advisable to flush in the direction opposite to the normal course of the coolant.
Among the varieties of chemical treatment, it is worth highlighting microbiological and dispersed. They differ only in the formulations used: in the first case, they are of biological origin and do not require special disposal.
Dispersed washing is a new, advanced technology in which the bonds of the sediment particles are destroyed, and the metal does not enter into a reaction.
After dispersed washing, a film is formed inside the pipes and radiators, which prevents the metal from contacting with water and its oxidation, as well as reducing friction resistance. This film is preserved, according to the manufacturers, for 3 seasons, which means that during this period your heating system will not clog.
Electrohydropulse cleaning of heating systems
This is another method of professional cleaning of the heating system, in which pulse cleaning devices are placed in a pipe filled with water. In this way, even the most neglected pipes can be cleaned, regardless of the complexity of their shape and bends, at a speed of 1–8 m per minute.
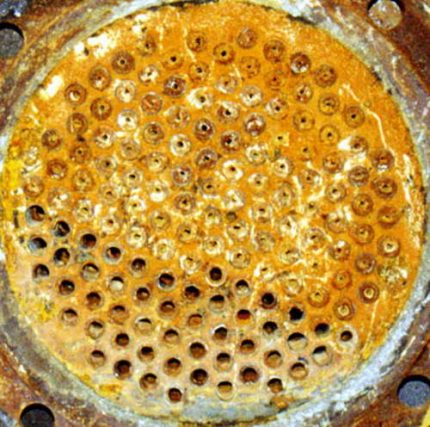

This method cleans the pipes completely, to metal or plastic, without damaging them. It is safe for equipment from any materials, consumables are inexpensive, and the waste is absolutely safe. This method perfectly removes scale, salt and lime deposits, however, is powerless against rust.
How to fill the system after flushing?
After you washed the heating system and saw how many different deposits there are, the question of choosing a new coolant becomes especially acute. It should contain a minimum of impurities of salts and calcium, microorganisms, as well as air, because all this provokes corrosion and forms a coating on the walls of pipes and radiators.
Filling the heating circuit directly from the water supply is perhaps the worst choice. It is often too hard, that is, with an abundance of salts of various metals. In addition, it carries all the dirt from the pipes of the central water supply, and is enriched with oxygen so much that sometimes it is white - with strong pressure.
To use such water for the heating circuit, at a minimum, it must be allowed to settle well so that all gases, including chlorine, are weathered, and solid particles settle to the bottom. In addition, it would be nice to pass it through the filter.

Alternatively, you can use rainwater, because it is soft and affordable. However, sedimentation or filtration is still required. In addition, microorganisms often multiply in rainwater, which may not affect radiators in the best way.
Distilled water is a good choice, because it does not contain absolutely any impurities that precipitate.In addition, such a choice is not cheap, because the volume of the heating system is not 5-10 liters, but ten times more.
Oddly enough, one of the best options is an old coolant drained from the system before flushing. All impurities that could react with pipes and settle on their walls have already done this, and the air has escaped during operation.
It is enough to filter it well to remove particles washed off the walls of the pipes, and you can add distilled water to the desired level - in this case, it will be needed very little.

It is sometimes advised to fill the heating circuit with antifreeze with special anti-rust additives. Indeed, such a heat transfer agent does not form plaque, but it is expensive, and its heat capacity and heat transfer are worse than that of water. As a result, filling such an expensive coolant, you will pay even more for gas, because the system will not work as efficiently.
With this in mind, it is possible to recommend antifreeze only if the heating in winter is not used constantly, and each time there is no possibility or desire to drain the coolant. More information about the different types of coolant for heating systems can be found in this stuff.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
You can see how to flush the heating system, which consists entirely of underfloor heating, in this video. The chemical method of washing was not chosen by chance, because other options are almost impossible to implement with so many tubes, joints and bends:
Hydropneumatic cleaning of an individual radiator is shown and described here:
When choosing a flushing method for your heating system, try to find a balance of convenience, price and safety for both pipes and the environment. Remember that only you live with this system and repair it in subsequent years.
And how often do you flush your heating system? Do you use the services of professionals or do it yourself? Which flushing method do you prefer? Join the discussion of the topic in the block under the article.

 Features of flushing the heating system: an overview of the best ways
Features of flushing the heating system: an overview of the best ways  What should be the coolant for heating systems: fluid parameters for radiators
What should be the coolant for heating systems: fluid parameters for radiators  Installation of copper heating pipes: features of the technology of work
Installation of copper heating pipes: features of the technology of work  Types of heating systems for a private house: a comparative overview + the pros and cons of each type
Types of heating systems for a private house: a comparative overview + the pros and cons of each type  Do-it-yourself greenhouse heating system: the best ways to winter heat greenhouses
Do-it-yourself greenhouse heating system: the best ways to winter heat greenhouses  Installation of heating from polypropylene pipes: how to make a heating system from polypropylene
Installation of heating from polypropylene pipes: how to make a heating system from polypropylene  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements