Heat recovery in ventilation systems: operating principle and options
In the process of ventilation from the room not only the exhaust air is utilized, but also part of the thermal energy. In winter, this leads to an increase in energy bills.
To reduce unnecessary costs, without prejudice to air exchange, heat recovery in centralized and local type ventilation systems will allow. For the recovery of thermal energy, different types of heat exchangers are used - recuperators.
The article describes in detail the models of units, their design features, operating principles, advantages and disadvantages. The information provided will help in choosing the best option for arranging the ventilation system.
The content of the article:
The concept of recovery: the principle of operation of the heat exchanger
Translated from Latin, recovery means a refund or a return. With regard to heat exchange reactions, recovery is characterized as a partial return of energy spent on carrying out a technological action for the purpose of application in the same process.
AT ventilation system The principle of recovery is used to save heat energy.
By analogy, cooling is recuperated in hot weather - warm supply masses heat the output “working out” and their temperature decreases.
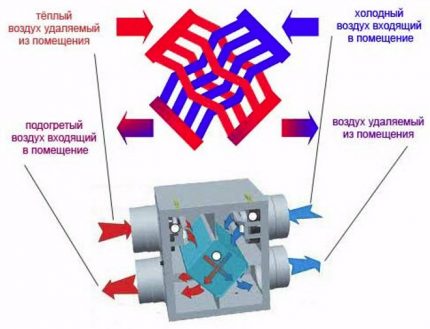
The energy recovery process is carried out in a recovery heat exchanger. The device provides for the presence of a heat exchange element and fans for pumping multidirectional air flows. An automatic system is used to control the process and control the quality of the air supply.
The design is designed so that the supply and exhaust flows are in separate compartments and do not mix - heat recovery is carried out through the walls of the heat exchanger.
Understand and understand what is recuperated ventilation a clear diagram of air circulation will help.
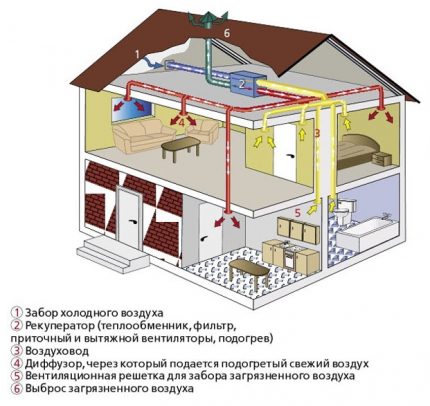
Expediency of a recuperator in ventilation
It is possible to talk about the feasibility of arranging regenerative ventilation by evaluating the effectiveness of the system and comparing its advantages with disadvantages.
The need to use heat recovery is most relevant in buildings with forced air outlet. As a rule, these are low-inertia structures constructed using innovative heat-insulating technologies (houses made of sandwich panels, gas silicate panels, foam blocks).
In such buildings, the walls do not accumulate heat well, and natural air exchange is ineffective.
However, problems with air circulation are also characteristic of “traditional” brick and concrete buildings. The presence of tight heat-insulating PVC windows blocks circulation with a natural urge - the flow of fresh air stops, and ventilation duct tilts or tends to zero.
The solution to the Euro-window problem is the organization of forced ventilation. The system restores air exchange, but at the same time, heat loss increases to 60%. And here you can not do without thermal recovery.

The efficiency factor of ventilation heat recovery:
- 0% - open window - warm air is removed into the atmosphere, and cold air gets inside, lowering the temperature into the room;
- 100% - the supply air is heated to the temperature of the "exhaust" - technically impossible to implement;
- 30-90% - an acceptable parameter, recovery is considered good with an efficiency of 60% or more, efficiency over 80% - excellent heat transfer.
The effectiveness of the system depends on the type of recuperator, the dimensions of the room and the air flow. In any case, the use of regenerative ventilation even with an efficiency of 30% is more profitable than its absence. In addition to significant savings in energy resources, “heat recovery" improves the overall indoor microclimate.
Disadvantages of using a heat exchanger:
- Volatility. The purchase of HVAC equipment is justified if the energy consumption is significantly less than its savings after installing the heat exchanger.
- Condensation Due to the temperature difference, moisture may condense on the walls of the heat exchanger. In winter, there is a chance of icing, which is fraught with a rapid decrease in efficiency or failure of the heat exchanger.
- Noisy work. Some models emit hum during operation. If during the day this drawback is not particularly noticeable, then at night the noise is uncomfortable. Recuperators with improved insulation are quiet.
High initial investments often become the main argument against energy-efficient ventilation.

Features of different types of heat exchangers
The design of the recuperator determines the flow diagram of the coolant, the efficiency of the ventilation system, the energy class and equipment cost. Five types of heat exchangers are used: plate, rotary, heat pipes, chamber devices and models with an intermediate heat carrier.
Lamellar recuperator - simplicity of a design
The basis of the heat exchanger is a sealed chamber with many parallel ducts. The channels are separated by partitions - heat-conducting plates made of steel or aluminum.
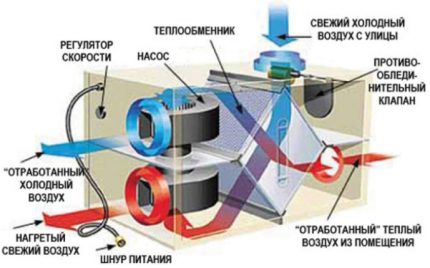
The gas flows move towards each other, intersect in the cassette of the recuperator, but do not mix. Thermal exchange is carried out due to the simultaneous cooling and heating of the plates from different sides.
Advantages of the cross heat exchanger:
- ease of installation and configuration of equipment;
- exclusion of contact of air masses;
- affordable cost and compact dimensions;
- lack of rubbing and moving parts.
The performance indicator varies in the range of 40-70%.
The main drawback of the plate model is condensation settling in the exhaust duct and ice formation in winter. To defrost the unit, the incoming stream is redirected to bypass the heat exchanger, and the warm outgoing stream melts the ice on the plates.

There are two ways to solve the problem:
- Preheating the incoming air flow to a temperature at which ice formation is excluded.
- Recuperator with hygroscopic cellulose plates. The material absorbs moisture from the exhaust air masses and transfers it to the incoming flows.
When choosing a cross-exchanger, the operational characteristics of the plates should be taken into account.
Their characteristics depend on the material of manufacture:
- Aluminium foil - affordable cost, but limited performance in winter. In addition, it is not recommended for residential premises due to air drying. Modifications with aluminum "filling" - the best option for baths and pools.
- Plastic partitions - similar in price to metal products, but differ in improved work efficiency.
- Cellulose heat exchanger - prevent freezing and maintain normal moisture content indoors.
Hygrocellulose recuperator is the most economical and optimal for ventilation of residential buildings.
Rotary recuperator - high system efficiency
The heat exchanger is presented in the form of a cylinder filled with layers of corrugated metal. As the drum kit rotates, warm or cold jets of air alternately enter each compartment.
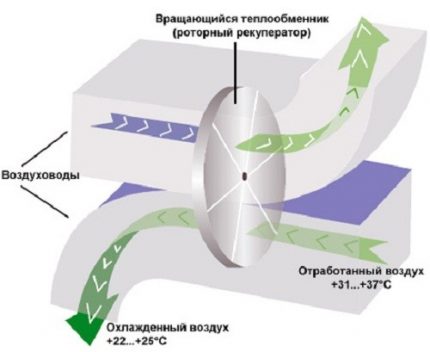
The heat transfer efficiency is determined by the rotor speed, the efficiency can be adjusted.
Arguments “for” rotary recuperator:
- heat recovery up to 65-90%;
- profitability power consumption;
- partial moisture compensation - you can do without a humidifier;
- payback period - up to 4 years.
Despite its high efficiency, the drum-type heat exchanger did not become a leader among similar installations.
Cons of the ventilation system:
- A mixture of polluted air into the influx. Through the microchannels, exhaust and supply masses circulate alternately, so about 3-8% of the “working out” is returned back. The drum often conveys the smell of outgoing air.
- The complexity of the design. Rotating parts of the rotor need regular maintenance and periodic replacement. Moving elements emit noise and vibration during operation.
- High price. The price for rotary models is higher than for plate products. This is due to the use of complex mechanics in the design of the drum heat exchanger.
- Big sizes. Installation is carried out in a spacious ventilation chamber.
Due to the bulkiness, rotor plants are mainly used in industrial enterprises.

Bound Heat Exchangers - Glycol Model
Due to its design features, a recovery unit with an intermediate coolant is often referred to as coupled heat exchangers or a glycol unit. This is one of the most flexible heat recovery systems. One heat exchanger crashes into the supply duct, and the second into the exhaust.
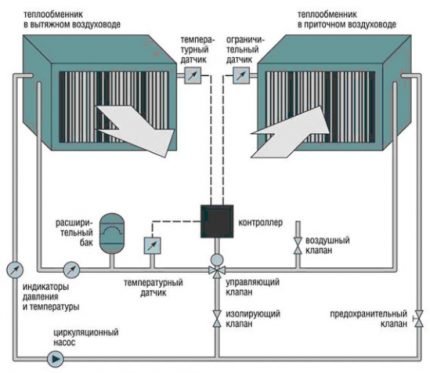
Principle of operation. Glycolic composition circulates between heat exchangers. The temperature of the coolant rises due to the heated removed stream, and then the thermal energy is transferred to fresh air. A closed system eliminates the mixing of oncoming air masses.
Features of the work of heat exchangers with a coolant:
- Efficiency - 45-55%;
- efficiency adjustment with the help of a pump - the speed of antifreeze movement is selected;
- the ability to place supply and exhaust ducts remotely from each other (up to 800 m);
- the recuperator is mounted vertically or horizontally;
- in severe frost, the surface of the exhaust heat exchanger freezes - ice appears; the use of antifreeze allows you to operate the recuperator without resorting to defrosting;
- system payback period - up to 2 years;
- a combination of 1 hood and several inflows or vice versa is acceptable.
The volume of exhaust and intake air should be approximately equal. Such recuperators are usually used if the inflow is toxic or heavily contaminated when mixing flows is unacceptable.
Chamber Assembly - Versatility
Structurally, the chamber heat exchanger is a closed box, divided inside by a moving damper. The opening partition determines the operation of the recuperator.

As a result, the inflow moves along the warm walls of the first duct, and the “mining” heats the surface of the second chamber. At a certain moment, the partition becomes back and the cycle repeats.
Advantages of the chamber heat exchange unit:
- Efficiency - 80-90%;
- in tandem with high-quality thermal insulation, heating costs are minimized;
- ease of installation - the help of specialists will be needed when choosing the parameters of the ventilation installation;
- preservation of humidity level;
- freezing of the system is excluded.
A chamber recuperator is an excellent option for regions where, over a long period of the year, there is a significant imbalance between indoor and outdoor temperatures.
The disadvantages of the heat recovery unit include:
- the need for regular maintenance of moving parts;
- oncoming air jets partially mix - odors and impurities can flow back into the building.
To reduce the mix, the system is equipped filter element. The air becomes cleaner, but the efficiency of the recuperator decreases.
Heat pipes - closed heat exchange system
The recuperator consists of many copper or aluminum tubes filled with a volatile material, such as freon. The principle of operation of a tubular heat exchanger is based on physical processes - a change in the state of a substance when heated.
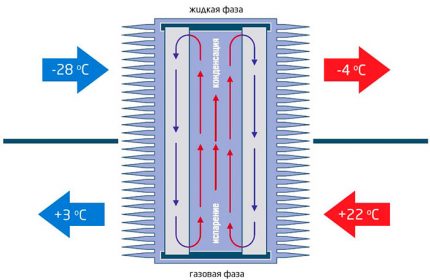
The gas rises and gives off thermal energy to the influx, after which the freon condenses and flows down the recuperator. The thermal cycle is repeated in a circle.
Technical and operational characteristics of the tubular heat exchanger:
- device efficiency - up to 65%;
- silent operation due to the absence of moving elements;
- simplicity of design and unpretentiousness in service;
- compactness - small dimensions and light weight;
- energy independence - the coolant circulates naturally;
A significant advantage is that the air flows of the inflow and return are not mixed.
Weaknesses of heat pipes:
- high level of efficiency achieved with a narrow temperature range - with sudden overheating, the entire freon evaporates, and with insufficient heating, the vaporization rate slows down;
- low tube strength - a change in shape or depressurization reduces the performance of the equipment.
Tubular recuperators are used in private construction, in administrative, office buildings and small industrial areas.
Methods of organizing regenerative ventilation
Recovery is equipped in one of the ways: centrally and decentralized. In the first case, ventilation flows from the whole room pass through the heat exchanger, in the second - from one room.
Centralized complex - air handling unit
A centralized system is equipped at the stage of construction or major modernization of the ventilation system.
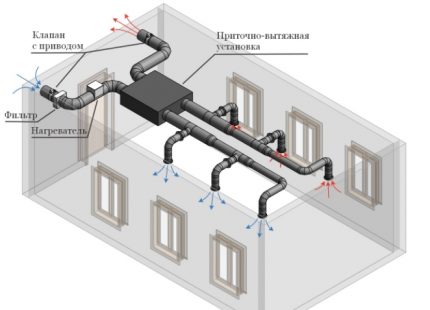
The PVU with a recuperator provides sufficient air exchange even in houses with sealed windows. At the same time, air flows are distributed evenly without creating drafts.
Integrated forced-air and exhaust installations monoblock type equipped with:
- fans - round-the-clock supply of clean air and emission of jets saturated with carbon dioxide;
- heaters - preheating of the inflow;
- filters - retain dust and microparticles;
- recuperator - Different types of installations can be used.
The functionality of some PVUs is expanded by a delay timer, a power regulator, humidity level sensors, etc.

Well-proven recuperative monoblock PVU production: Vents (Ukraine), Dantherm (Denmark), "Daikin" (Japan), "Dantex" (England).
Local units - addition to the existing ventilation system
To restore the circulation of air masses in an operating room, decentralized air inlets with heat recovery are suitable.
They cut into the facade of the building or are mounted through a window. Their main goal is to improve supply ventilation in home.

Features of decentralized ventilation systems with recovery:
- Efficiency – 60-96%;
- low productivity - devices are designed to provide air exchange in rooms up to 20-35 sq.m;
- affordable cost and a wide selection of units, ranging from conventional wall valves to automated models with a multi-stage filtration system and the ability to adjust humidity;
- ease of installation - for commissioning, no ducting is required, install wall valve You can do it yourself.
Popular manufacturers of local recuperators: Prana (Ukraine), O.erre (Italy), Blizzard (Germany), Vents (Ukraine), Aerovital (Germany).

Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Comparison of natural ventilation and forced system with recovery:
The principle of operation of a centralized heat exchanger, calculation of efficiency:
Design and operation of a decentralized heat exchanger using the Prana wall valve as an example:
About 25-35% of the heat leaves the room through the ventilation system. Recuperators are used to reduce losses and efficient heat recovery. Climatic equipment allows you to use the energy of the spent masses to heat the incoming air.
Is there anything to supplement, or have questions about the operation of various ventilation recuperators? Please leave comments on the publication, share your experience in operating such installations. The contact form is located in the lower block.

 Requirements for ventilation of public buildings: subtleties of arrangement and design of ventilation
Requirements for ventilation of public buildings: subtleties of arrangement and design of ventilation  Ventilation device in the bath: technical options and popular schemes
Ventilation device in the bath: technical options and popular schemes  Is it possible to bring ventilation to the attic in a private house? The best accommodation options
Is it possible to bring ventilation to the attic in a private house? The best accommodation options  Cottage ventilation: options for organizing an air exchange system + device rules
Cottage ventilation: options for organizing an air exchange system + device rules  Checking ventilation at school: norms and procedures for checking the effectiveness of air exchange
Checking ventilation at school: norms and procedures for checking the effectiveness of air exchange  Ventilation in the house from sip panels: the best options and layouts
Ventilation in the house from sip panels: the best options and layouts  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements