How to thread a pipe: a detailed overview of the main methods
Do you like to do home improvement work yourself, without involving various craftsmen for this? Self-installation or repair not only saves money on the call of specialists, but also greatly enhances self-esteem, right?
In the process of installing communications, it is often necessary to prepare threads on pipes. We have to find ways not to spoil the product.
We will tell you how to cut threads using different tools, which method is preferable to use in a given situation. The article describes the methods available for implementation by an unskilled performer. The features of threading of various types of thread and the equipment used in this process are highlighted.
The stated material is equipped with visual photographs depicting tools for performing work. A video with recommendations will help to understand in detail all the intricacies of this process.
The content of the article:
Pipe thread classification
The term "pipe" has a privileged position in the field of plumbing. This term is classified with an eye on a group of standards that define the criteria for connecting various elements of sanitary structures.

For example, the size of a pipe thread is indicated by a numerical value indicating the standard pipe bore, but not the physical diameter of the thread.
In practice, pipe threads are used:
- cylindrical (G / bspp),
- conical (R / BSPT),
- round under locking sanitary fittings (Kr),
- inch cylindrical (American standard Npsm),
- inch cone (American standard NPT).
It is recommended that the locksmith, whose main working area is household, is to take as a basis the conditional division of pipe thread into two main types:
- cylindrical (G),
- conical (R).
It is with these two types that the home locksmith serving the household plumbing equipment performing the laying most often has to face water pipes or heating.
Pipe cutting is carried out in the following cases:
Basic cutting methods
You can cut threads on pipes in one of two ways:
- automatic - on machine tools, power tools;
- manually - using a hand tool.
For living conditions, of course, manual technology is more relevant. Manual threading of water pipes or other pipes is often done using a die.
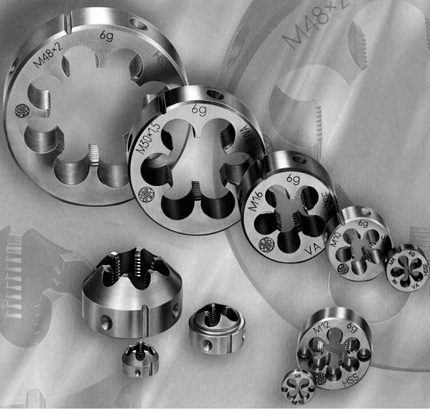

The die is a simple device for threading pipes at home. The same tool is successfully used on industrial machines.
The fixture looks like a disk, on the inner diameter of which several axial holes are drilled. The edges of these holes form several incisors (usually 8-10). The material for the dies is alloy steel or other hard alloys.
There are several types of such devices:
- whole;
- spring loaded (split);
- kluppovye (sliding).
According to the form of execution, the die is produced in the form of a circle, square, hexagon, prism. The most common disc (round) tools. They are used for threading water pipes up to a diameter of 36 mm.
For the convenience of working with dies, use:
- simple gates with fixing screws - hand tools;
- threading chucks on lathes.
Solid threads (metric, tapered) of the best quality on pipes in manual operation mode or on machines give.
However, this type of tool due to the rigidity of its own design has its negative sides. Cutters wear out quickly.

Spring-loaded (split) dies have a design less rigid, which makes it possible to cut the thread on the pipes and at the same time change the diameter of the thread in the range of 0.1-0.3 mm.
Such devices are characterized by increased wear resistance of the cutters, but do not provide high accuracy and purity of thread cutting.
Sliding dies consist of two working parts. They are intended for installation in the mounting module - screwdriver.
Mounting in the die is carried out by a mechanism consisting of a cracker and an adjusting screw. The screw adjusts the diameter size for threading. Usually, a screwdriver is equipped with a set of dies for several different diameters.
Method # 1 - making pipe threads with dies
The process of creating a thread on a pipe with a die or a screwdriver involves the execution of some preliminary actions by a mechanic:
- The pipe surface in the cutting area must be carefully cleaned.
- The end part of the pipe should be filed (make the input chamfer).
- Apply grease to the work surface to reduce resistance.
If possible, it is desirable to fix the pipe vertically, for example, in a bench vise, leaving free access to the upper part - the area of the cut. The fastener force should be correctly calculated so as not to deform the pipe body.
Then they take a pre-prepared head with a rough die (No. 1) of the desired diameter and suitable thread characteristics.

The tool is held horizontally - perpendicularly with respect to the end region of the pipe. Put the rough die on the chamfer of the edge with the inner hole. Light pressure and successive short turns of 25-30 ° make the initial incision.
This work should be done carefully, without rushing, constantly monitoring the right angle between the die horizon and the pipe vertical.
The first two or three threads are carefully cut using this technique. Usually, after cutting the first two or three threads, the tool firmly occupies the working position. Further, the right angle can no longer be controlled.
But cutting technology with short (without particularly strong traction) circular motions should be maintained until the end of the cut. It is recommended to periodically add grease at the cutting point.
After the first pass, twist the device and then repeat one or two more times with a finishing die (No. 2).
Method # 2 - chopping technique
Klupp is a variation of the same die for threading, including on pipes. A distinctive feature of the klupp is the ability to customize the incisors.

There are klupps for manual use, as well as similar devices with electric drive.
Option # 1 - manual cutter cut. Manual pipe cutting, as a rule, is carried out by a screwdriver, which is installed in the ratchet holder. Such a holder makes the work of cutting pipe threads convenient and less complicated.
Of course, depending on the conditions for performing locksmith work, other types of hand holders can be used. For example, a standard two-handle locking knob.
The principle of creating a screw thread is almost the same as the method of working with traditional dies:
- Clean the working surface of the pipe, make sure that there are no defects.
- Sand the cut to a look with a pronounced metallic sheen.
- Treat the outer working part of the end edge at an angle of 45-60º (chamfer).
- Lubricate the prepared surface with petroleum jelly.
- Secure the pipe in a mechanical vice or hold it with a gas wrench.
After these procedures, the cutting tool (screw die) is inserted with an internal hole on the chamfer of the pipe and with moderate uniform pressure they begin to rotate it with short reciprocating movements.

If a clamp-ratchet is used as a holder, only straight-forward cutting is carried out. It should be noted the ease of use of the ratchet-clamp when working in cramped conditions.
For example, when you need to process a pipe laid in close proximity to a wall.
Option # 2 - cutting with an electric die. Along with hand tools, devices with an electric drive are widely used. An obvious advantage for a locksmith is a significant reduction in labor intensity.
But on the other hand, not all electric machines are able to provide work in cramped conditions. In addition, when working with a hand tool, it is possible to get a better result.
To obtain a similar result from electric screwdrivers, a wealth of experience with this tool is required.

Work with an electric switch:
- Pipe surface preparation in the cutting area - cleaning, chamfer, lubrication.
- Fixture of the pipe with devices capable of providing rigid fixation.
- Fixing at the starting point of the die holder with the clamp included in the kit.
- Checking the stroke and direction of rotation of the die.
- Cutting the first two or three turns in the jog feed mode.
Next, the pipe thread is cut in automatic mode. The length of the cut is considered optimal when the upper edge of the cutting heads of the die reaches the leading edge of the pipe.
At this point, the action of the device is stopped, the function of reverse rotation is turned on, and the bug is twisted from the pipe by push feeding. Be sure to periodically wet the cut area with oil throughout the entire process.
Method # 3 - using lathes
Large-scale construction and repair work, as a rule, exclude the use of hand tools. Here, lathes are usually used for appropriate pipe processing.
Thread-cutting functions are supported by many universal-action lathes.

Using machines, both internal and external pipe threads are efficiently and easily made. The fastening pneumatic (or mechanical) module of the lathe provides high-quality reliable fastening of the pipe, and an accurate supply of the machined part to the cutter.
To perform thread-cutting functions, different types of cutters are used:
- pivotal
- lamellar
- insertion.
Work on lathes is carried out by specialists trained in such a case, having the appropriate qualifications. Without experience and professional skills, trying to thread with your own hands on the machine is not recommended.
The following tips will help the home craftsmen who decide to do plumbing and carving on metal workpieces:
A few words about GOST pipe thread
In working with gaseous and liquid media, according to GOST 6111, if necessary, the introduction of detachable connections in piping schemes, the manufacture of such connections on a threaded basis is allowed.
It is possible to design not only pipe but also tapered threads (GOST 3662).

Despite the rare use of tapered threads in pipe joints, it is considered more convenient in terms of screwing / screwing characteristics.
It should be recalled that the taper angle of the tapered thread is directly related to parameters such as pitch and diameter. The permissible value of this angle may not be less than 26 °. The standard value of the angle of the tip of the profile on a tapered thread is 60 °.
Pipe threads are distinguished by a characteristic feature - they have a rounded profile top. Subject to cutting standards, the value of the rounding is 10% of the size of the radius of the thread.
With this cutting technology, it is possible to achieve a significant reduction in internal stresses over a small area of metal occupied by a threaded profile.
Established tolerances GOST 6357along with cylindrical and conical threads, metric threads are provided for pipes.
Here, the standard angle of inclination is 55 °, which is due to the increase in the number of turns in the section along the length equal to the section with a different type of thread.
The result is a compound with a higher degree of tightness, but the complexity of using such compounds increases.
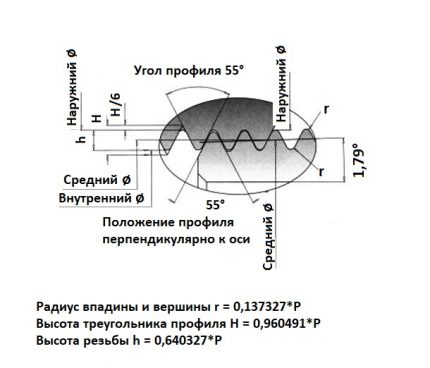
Existing GOST installations also provide for the possibility of execution of persistent and trapezoidal threads on pipes. But in practice, these types of cuts are not used because of their low operational strength.
In plumbing works, different methods of connecting pipes are used. The choice of method largely depends on the material of the pipeline and its “area of responsibility”. Threaded docking of parts is recommended for use in areas accessible for periodic inspection.
Information on alternative pipe connection methods is provided in the articles:
- Plumbing pipe connection methods: an overview of all possible options
- The connection of plastic pipes with metal: analysis of methods and examples of installation work
- Connecting copper pipes: instructions and comparison of various installation technologies
- Inserting into a pipe without welding: welding and mortise technology
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
All the nuances of pipe threading in one video:
Knowledge of the creation, operation, maintenance of threaded joints on pipes is always relevant for every person who is engaged in household, plumbing, and other utilities.
Without this information, it is impossible to make high-quality repairs, upgrade piping systems, and simply maintain the operation of household economic systems.
Have something to supplement, or have questions about threading pipes? Please leave comments on the publication, suggest your own methods and effective tools for creating threads. The contact form is located in the lower block.

 DIY welding technology for polypropylene pipes: an overview of methods and nuances
DIY welding technology for polypropylene pipes: an overview of methods and nuances  How to arrange a pipe box in the toilet: an overview of the best ways to mask the pipeline
How to arrange a pipe box in the toilet: an overview of the best ways to mask the pipeline  How to hide pipes in a bathroom: an overview of the best ways to mask a pipe
How to hide pipes in a bathroom: an overview of the best ways to mask a pipe  The connection of plastic pipes with metal: an analysis of the best methods and mounting nuances
The connection of plastic pipes with metal: an analysis of the best methods and mounting nuances  Inserting into a pipe without welding: a review of the technology for mortise work
Inserting into a pipe without welding: a review of the technology for mortise work  Pipe cutting at an angle: advantages and disadvantages of different methods + example of work
Pipe cutting at an angle: advantages and disadvantages of different methods + example of work  How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply
How much does it cost to connect gas to a private house: the price of organizing gas supply  The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips
The best washing machines with dryer: model rating and customer tips  What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs
What is the color temperature of light and the nuances of choosing the temperature of the lamps to suit your needs  Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
Replacement of a geyser in an apartment: replacement paperwork + basic norms and requirements
I make the thread on the pipes manually, using dies. I have them whole. There is nothing complicated in this. It is important to have skills. I clean the pipe, fix it in a vise and take the knob with the right die. By rotational movements, I gradually cut. It is important to cut the first 2 threads, then it will go easier. I use this infrequently, but on a large scale, of course, you need to cut it with a loop.
Everything is extremely simple for me. Pipe, vise and die. I think that paying for threading makes no sense, since everything is done in one or two minutes. If of course there are no skills, then you can buy pipes with threaded threads, however, “in place” along the length of such billets is difficult to pick up, to be honest, it is almost impossible. So I advise everyone to buy a set of dice.
Of great importance is the quality of the rifled tool. When I bought the first klupp, I got dies (as it turned out later) of disgusting quality. The thread was cut with great difficulty, lubricated with various types of lubricant (liquid, plastic) - they helped little. And, about happiness, once the die broke. Quickly bought a new one ... And it turned out - for several months I was tearing my belly button down.
A good teacher is experience, but still it’s better to first get a theory about a knowledgeable person. But I haven’t met one like that.